Windows Defender: A Comprehensive Guide to Enabling and Utilizing Windows 10’s Built-in Antivirus
Related Articles: Windows Defender: A Comprehensive Guide to Enabling and Utilizing Windows 10’s Built-in Antivirus
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Windows Defender: A Comprehensive Guide to Enabling and Utilizing Windows 10’s Built-in Antivirus. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Windows Defender: A Comprehensive Guide to Enabling and Utilizing Windows 10’s Built-in Antivirus
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Windows Defender: A Comprehensive Guide to Enabling and Utilizing Windows 10’s Built-in Antivirus
- 3.1 Understanding Windows Defender: A First Line of Defense
- 3.2 Enabling Windows Defender: A Simple Process
- 3.3 Optimizing Windows Defender: Maximizing Protection
- 3.4 Exploring Windows Defender’s Advanced Features
- 3.5 FAQs: Addressing Common Concerns
- 3.6 Tips for Enhanced Protection
- 3.7 Conclusion: Empowering Security with Windows Defender
- 4 Closure
Windows Defender: A Comprehensive Guide to Enabling and Utilizing Windows 10’s Built-in Antivirus
Windows 10 comes equipped with a powerful built-in antivirus solution known as Windows Defender. While often overlooked, this security program provides essential protection against malware, viruses, and other online threats. Enabling and utilizing Windows Defender effectively is crucial for maintaining a secure computing environment. This article delves into the intricacies of Windows Defender, providing a comprehensive guide to its activation and use, emphasizing its importance in safeguarding your system.
Understanding Windows Defender: A First Line of Defense
Windows Defender is a real-time antivirus and anti-spyware program that continuously monitors your computer for malicious activity. It operates in the background, scanning files, applications, and websites for potential threats. When a suspicious file or program is detected, Windows Defender quarantines it to prevent further harm.
The effectiveness of Windows Defender lies in its robust features:
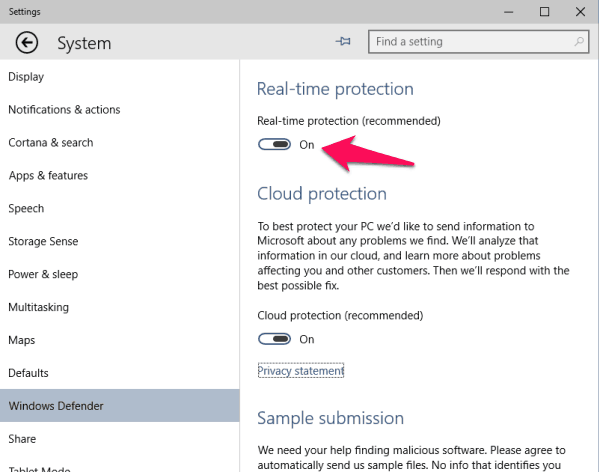
- Real-time protection: Windows Defender constantly scans your system for threats, proactively blocking malicious software before it can infect your computer.
- Automatic updates: Windows Defender automatically updates its virus definitions, ensuring that it remains current against the latest threats.
- Cloud-based protection: Windows Defender leverages Microsoft’s cloud infrastructure to enhance its detection capabilities, identifying new and emerging threats.
- Behavior monitoring: Windows Defender analyzes the behavior of programs and files, detecting suspicious activities that might indicate malware.
- Firewall: Windows Defender includes a firewall that blocks unauthorized access to your computer, preventing hackers from infiltrating your system.
Enabling Windows Defender: A Simple Process
Enabling Windows Defender is a straightforward process, typically requiring minimal user interaction. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
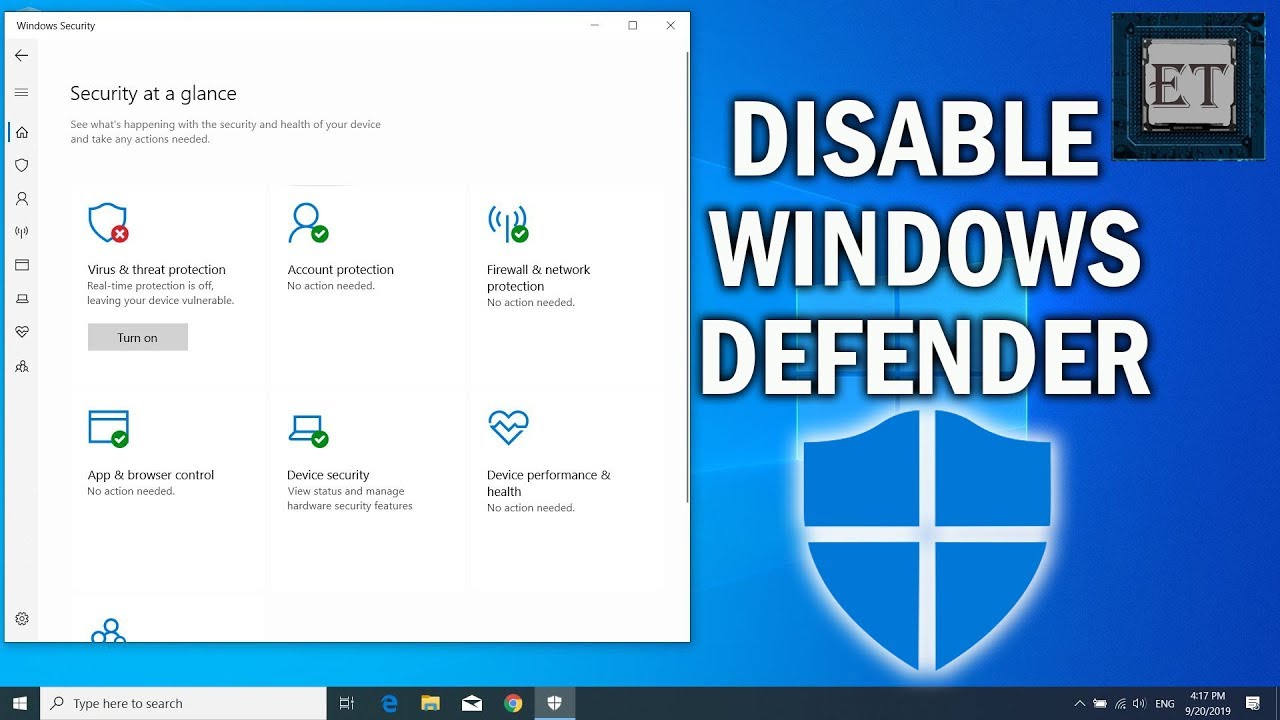
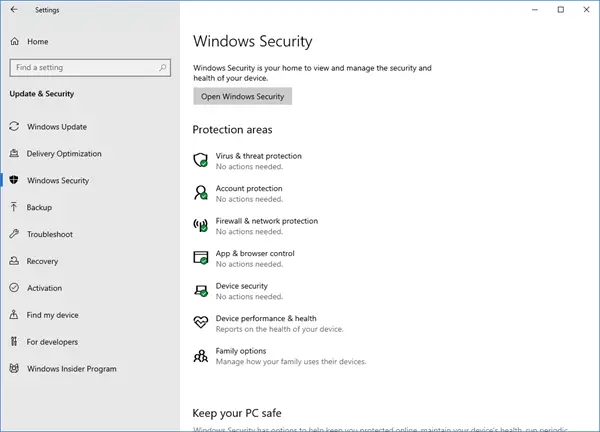
- Access Windows Security: Open the "Start" menu and search for "Windows Security." Alternatively, you can access it by navigating to "Settings > Update & Security > Windows Security."
- Navigate to Virus & threat protection: Within the Windows Security app, select "Virus & threat protection."
- Review the status: The "Virus & threat protection" section displays the current status of Windows Defender. If it’s not already enabled, you will see an option to "Turn on real-time protection." Click on it to activate Windows Defender.
Note: In some cases, Windows Defender might be disabled due to the presence of another antivirus software installed on your computer. If you have a third-party antivirus solution, it’s recommended to disable it before enabling Windows Defender to avoid conflicts.
Optimizing Windows Defender: Maximizing Protection
While Windows Defender provides robust security out of the box, optimizing its settings can enhance its effectiveness and tailor it to your specific needs.
1. Schedule Scans: Windows Defender performs automatic scans on a regular basis, but you can customize the scan schedule to suit your preferences. Go to "Virus & threat protection" and click on "Scan options." Here, you can schedule full scans, quick scans, or custom scans.
2. Configure Exclusions: Windows Defender might mistakenly flag certain files or programs as threats. If you encounter such issues, you can exclude specific files or folders from scanning. In the "Virus & threat protection" section, click on "Add or remove exclusions."
3. Enable Cloud-Delivered Protection: Windows Defender utilizes Microsoft’s cloud infrastructure to enhance its detection capabilities. Ensure that "Cloud-delivered protection" is enabled in the "Virus & threat protection" settings.
4. Activate Ransomware Protection: Ransomware is a type of malware that encrypts your files and demands payment for their decryption. Windows Defender offers ransomware protection to prevent these attacks. Enable this feature by navigating to "Virus & threat protection" and selecting "Ransomware protection."
5. Update Windows Defender Regularly: Windows Defender automatically updates its virus definitions, but you can manually check for updates to ensure that you have the latest protection. In the "Virus & threat protection" section, click on "Protection history" and then "Check for updates."
Exploring Windows Defender’s Advanced Features
Windows Defender offers several advanced features that can further enhance your security posture:
1. Exploit Protection: This feature helps protect your system from known vulnerabilities by blocking malicious attacks that exploit software weaknesses. You can configure exploit protection settings by navigating to "Windows Security > App & browser control > Exploit protection."
2. Controlled Folder Access: This feature protects your most important files and folders from unauthorized access. It allows you to specify which apps can access certain folders, preventing malware from modifying or deleting your data. Enable controlled folder access by going to "Windows Security > App & browser control > Controlled folder access."
3. Tamper Protection: Windows Defender’s tamper protection prevents unauthorized changes to its settings, ensuring that the antivirus remains active and effective. You can enable tamper protection by navigating to "Windows Security > Virus & threat protection > Virus & threat protection settings."
4. Microsoft Defender Antivirus: For advanced users, Windows Defender offers a dedicated interface with more granular control over security settings. Access Microsoft Defender Antivirus by searching for it in the Start menu.
FAQs: Addressing Common Concerns
Q: Is Windows Defender enough to protect my computer?
A: Windows Defender provides a solid foundation of security, but it’s not foolproof. It’s recommended to supplement it with additional security measures such as a strong password, regular software updates, and responsible online practices.
Q: Can I use Windows Defender alongside another antivirus program?
A: It’s not recommended to run two antivirus programs simultaneously, as they might conflict and cause performance issues. If you have a third-party antivirus solution, it’s best to disable it before enabling Windows Defender.
Q: How do I know if Windows Defender is working properly?
A: You can check the status of Windows Defender in the "Windows Security" app. It should indicate that real-time protection is enabled and that virus definitions are up to date.
Q: What should I do if Windows Defender detects a threat?
A: If Windows Defender detects a threat, it will quarantine the malicious file or program. Follow the on-screen instructions to remove the threat. It’s also recommended to run a full system scan after removing the threat to ensure that your computer is completely clean.
Tips for Enhanced Protection
- Keep Windows updated: Regularly update your Windows operating system to benefit from the latest security patches and bug fixes.
- Be cautious with downloads: Only download files from trusted sources. Avoid downloading software from suspicious websites or clicking on links in unsolicited emails.
- Use strong passwords: Create strong and unique passwords for all your online accounts.
- Enable two-factor authentication: This security measure adds an extra layer of protection to your accounts.
- Be aware of phishing scams: Phishing scams attempt to trick you into revealing your personal information. Be cautious of emails or websites that request sensitive information.
Conclusion: Empowering Security with Windows Defender
Windows Defender is a powerful and reliable antivirus solution that is an integral part of Windows 10’s security arsenal. By enabling and utilizing Windows Defender effectively, you can significantly reduce the risk of malware infection and safeguard your computer from online threats. Remember, a proactive approach to security is crucial, and Windows Defender provides a solid foundation for protecting your digital life.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Windows Defender: A Comprehensive Guide to Enabling and Utilizing Windows 10’s Built-in Antivirus. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
