When the Engine Remains Silent: Troubleshooting a Non-Starting Vehicle
Related Articles: When the Engine Remains Silent: Troubleshooting a Non-Starting Vehicle
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to When the Engine Remains Silent: Troubleshooting a Non-Starting Vehicle. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
When the Engine Remains Silent: Troubleshooting a Non-Starting Vehicle

The act of turning a key or pressing a start button, followed by the familiar hum of an engine coming to life, is a commonplace experience for most vehicle owners. However, the moment when the ignition is engaged and nothing happens, a sense of frustration and uncertainty can quickly set in. This article delves into the complexities of a vehicle failing to start, providing a comprehensive understanding of potential causes and effective troubleshooting techniques.
Understanding the Ignition System: A Complex Network
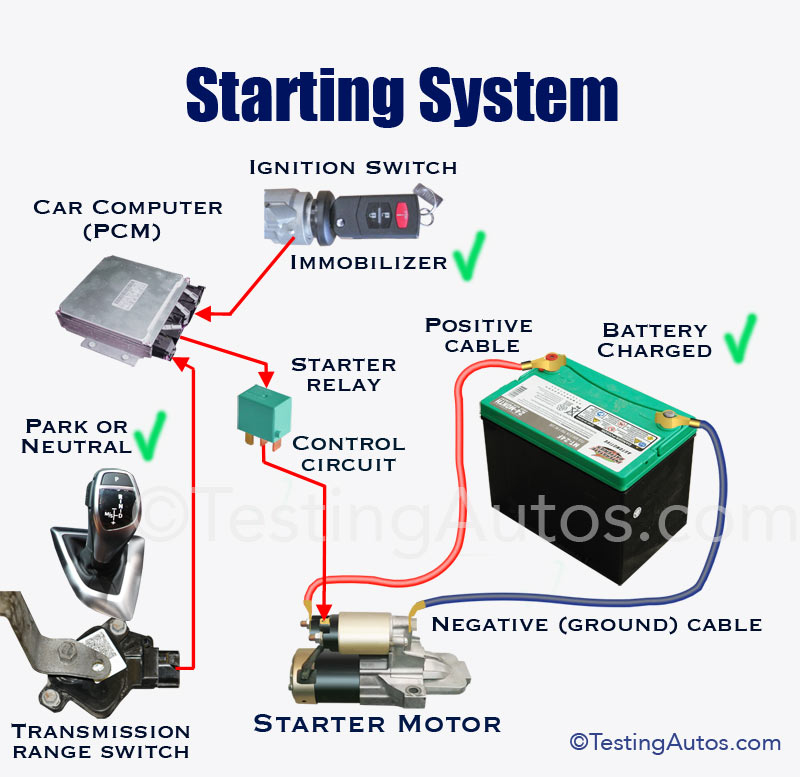
A vehicle’s ignition system is a sophisticated network of components working in harmony to initiate combustion and power the engine. The process starts with the driver engaging the ignition, triggering a chain reaction involving:
- Battery: The battery acts as the primary power source, providing the necessary electrical current to activate the starter motor.
- Starter Motor: This powerful electric motor engages the engine’s flywheel, turning the crankshaft and initiating the combustion cycle.
- Ignition Switch: The ignition switch acts as the control center, receiving the driver’s input and relaying the signal to the starter motor.
- Starter Relay: This electromagnetic switch acts as an intermediary, receiving a signal from the ignition switch and completing the circuit to the starter motor.
- Fuel System: The fuel system delivers a precise mixture of fuel and air to the engine’s cylinders, creating a combustible mixture.
- Spark Plugs: Spark plugs ignite the fuel-air mixture within the cylinders, generating the force that propels the engine.
Common Culprits: Identifying the Source of the Problem
When a vehicle fails to start, the underlying issue can stem from a malfunction within any of the aforementioned components. Here’s a breakdown of the most common culprits:
1. Battery Issues: A weak or dead battery is a frequent cause of starting problems. This can be due to:
- Low Battery Charge: A depleted battery can occur due to prolonged inactivity, excessive use of accessories, or a faulty charging system.
- Corroded Battery Terminals: Corrosion on the battery terminals can hinder the flow of electrical current, preventing the starter motor from receiving sufficient power.
2. Starter Motor Problems: A malfunctioning starter motor can prevent the engine from turning over. This could be caused by:
- Faulty Starter Motor: The motor itself might be worn out, damaged, or have internal electrical issues.
- Stuck Starter Bendix: The bendix, a component within the starter motor, engages the flywheel. If it becomes stuck, the starter motor won’t be able to turn the engine.
3. Ignition Switch Malfunction: A faulty ignition switch can interrupt the electrical signal to the starter motor. This can manifest as:
- Worn-Out Switch: The switch may wear down over time, becoming less responsive to the driver’s input.
- Loose Connections: Loose or corroded connections within the ignition switch can disrupt the electrical flow.
4. Starter Relay Failure: The starter relay plays a crucial role in activating the starter motor. If it fails, the signal from the ignition switch won’t reach the motor.
5. Fuel System Issues: A problem with the fuel system can prevent fuel from reaching the engine, leading to a no-start condition. This could be due to:
- Empty Fuel Tank: The simplest reason for a no-start situation is simply running out of fuel.
- Fuel Pump Failure: A faulty fuel pump might be unable to deliver fuel to the engine.
- Clogged Fuel Lines: Blockages within the fuel lines can restrict fuel flow.
- Fuel Filter Clogging: A clogged fuel filter can prevent the flow of fuel to the engine.
6. Ignition System Problems: Issues within the ignition system can prevent the spark plugs from igniting the fuel-air mixture. This could be caused by:
- Faulty Spark Plugs: Worn-out or fouled spark plugs can hinder the ignition process.
- Broken Ignition Wires: Damaged ignition wires can disrupt the electrical signal to the spark plugs.
- Failing Ignition Coil: A malfunctioning ignition coil might not be generating the necessary high voltage to fire the spark plugs.
7. Engine Mechanical Issues: In rare cases, a mechanical issue within the engine itself can prevent it from starting. This could involve:
- Broken Timing Belt: A broken timing belt can cause the engine’s valves to collide with the pistons, resulting in significant damage.
- Seized Engine: An engine can seize due to a lack of lubrication, causing the pistons to lock up.
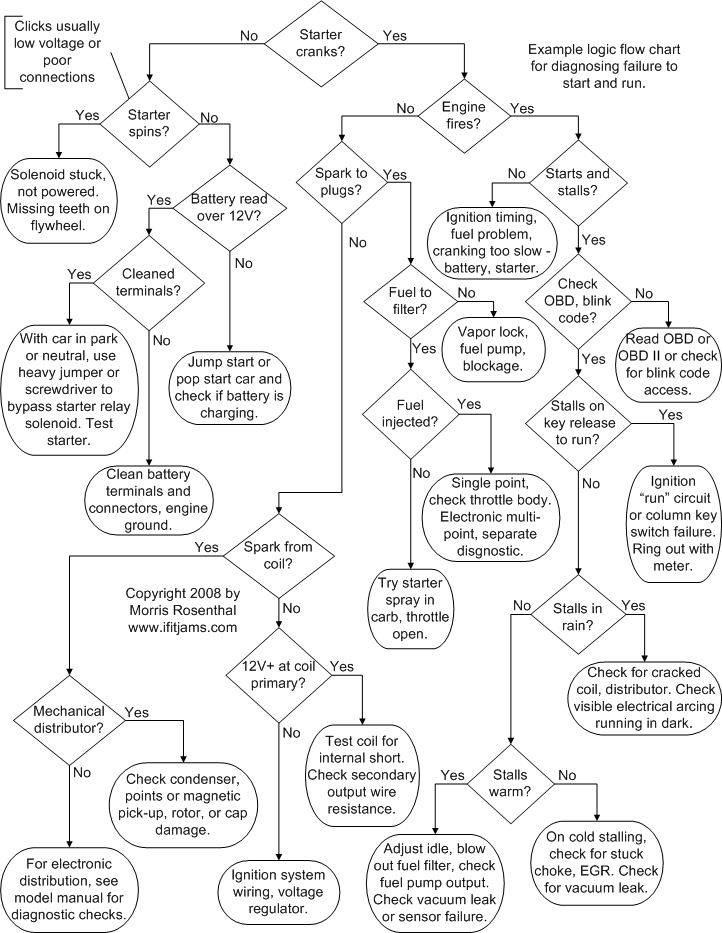
Troubleshooting Strategies: A Step-by-Step Guide
Addressing a no-start situation requires a systematic approach. Here’s a step-by-step guide to troubleshooting the problem:
1. Check the Battery: Start by examining the battery for signs of low charge or corrosion.
- Battery Charge: Use a voltmeter to check the battery’s voltage. A reading below 12.6 volts indicates a low charge.
- Battery Terminals: Clean any corrosion on the battery terminals with a wire brush and a baking soda solution.
2. Verify Starter Motor Function: Listen for a clicking sound when the ignition is turned.
- Clicking Sound: A clicking sound usually indicates a weak battery or a faulty starter motor.
- No Clicking Sound: If there’s no clicking sound, the issue might lie with the ignition switch, starter relay, or a broken wire.
3. Inspect the Ignition System: Check the ignition switch, starter relay, and ignition wires for any loose connections or signs of damage.
4. Assess the Fuel System: Ensure the fuel tank is not empty and that the fuel pump is functioning correctly.
- Fuel Tank: Check the fuel gauge to ensure there’s sufficient fuel.
- Fuel Pump: Listen for the fuel pump humming when the ignition is turned on. If you don’t hear it, the pump might be faulty.
5. Examine the Spark Plugs: Inspect the spark plugs for signs of wear or fouling.
- Spark Plug Condition: Replace worn-out or fouled spark plugs.
6. Consider Engine Mechanical Issues: If the problem persists, it’s advisable to seek professional assistance to diagnose and address any potential engine mechanical issues.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Q: What if the battery is new and fully charged, but the car still won’t start?
A: If the battery is new and charged but the car won’t start, the problem might lie with the starter motor, ignition switch, starter relay, or a broken wire. A mechanic can diagnose and repair these issues.
Q: What should I do if the car clicks but won’t turn over?
A: A clicking sound often indicates a weak battery or a faulty starter motor. Check the battery’s voltage and inspect the starter motor for any signs of damage.
Q: How can I test the fuel pump?
A: Listen for the fuel pump humming when you turn the ignition on. If you don’t hear it, the pump might be faulty. You can also test the fuel pressure using a gauge.
Q: What if the car starts but dies immediately?
A: This could be due to a fuel system issue, such as a clogged fuel filter or a faulty fuel pump. It could also indicate a problem with the ignition system or a mechanical issue within the engine.
Tips for Preventing No-Start Situations:
- Regular Battery Maintenance: Check the battery’s charge level regularly and ensure the terminals are clean and corrosion-free.
- Fuel System Maintenance: Replace the fuel filter according to the manufacturer’s recommendations.
- Preventative Maintenance: Follow the recommended maintenance schedule for your vehicle, including oil changes, spark plug replacements, and other routine inspections.
Conclusion:
A no-start situation can be a frustrating experience, but by understanding the underlying causes and employing a systematic troubleshooting approach, you can often identify and address the problem effectively. However, if you’re unable to pinpoint the issue or if you suspect a complex mechanical problem, it’s best to seek professional assistance from a qualified mechanic to ensure a safe and proper diagnosis and repair.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into When the Engine Remains Silent: Troubleshooting a Non-Starting Vehicle. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!