Unrelenting Whirr: Understanding and Resolving Persistent Computer Fan Operation
Related Articles: Unrelenting Whirr: Understanding and Resolving Persistent Computer Fan Operation
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unrelenting Whirr: Understanding and Resolving Persistent Computer Fan Operation. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unrelenting Whirr: Understanding and Resolving Persistent Computer Fan Operation
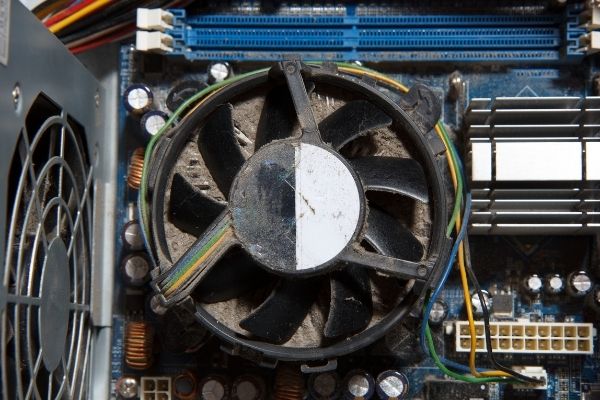
The steady hum of a computer fan is a familiar sound to many. It’s the quiet soundtrack of technological activity, a reassuring reminder that the intricate machinery within is diligently working. However, when this hum transforms into a persistent, unrelenting whir, it can be a source of concern and frustration. A computer fan that refuses to stop running, even after the system has seemingly finished its tasks, can indicate various underlying issues, ranging from simple dust accumulation to more serious hardware malfunctions. This article delves into the intricacies of this phenomenon, providing a comprehensive understanding of the reasons behind persistent fan operation, the potential risks it poses, and effective troubleshooting strategies.
The Vital Role of Computer Fans:
Computer fans serve a crucial role in maintaining optimal operating temperatures for the delicate components within a system. These components, such as the CPU, GPU, and motherboard, generate significant heat during operation. Excessive heat can lead to performance degradation, instability, and even permanent damage. Fans act as cooling agents, drawing in cool air and expelling the hot air generated by these components, ensuring they operate within their safe temperature ranges.
Understanding the Fan Control Mechanism:
Modern computers employ sophisticated fan control mechanisms, typically managed by the motherboard’s BIOS or dedicated software utilities. These mechanisms monitor the temperature of critical components and adjust the fan speed accordingly. When temperatures rise, fans spin faster to increase airflow and cool the system down. Conversely, when temperatures drop, fans slow down or even stop entirely to minimize noise and power consumption.
The Causes of Persistent Fan Operation:
A computer fan that refuses to stop running, despite seemingly low system activity, can be attributed to several factors:
-
Dust Accumulation: Dust is a common culprit in persistent fan operation. Over time, dust can accumulate on fan blades, obstructing airflow and reducing cooling efficiency. This forces the fan to run at higher speeds to compensate for the reduced airflow, leading to continuous operation.
-
Faulty Fan Controller: The motherboard’s fan controller, responsible for regulating fan speeds, can malfunction, leading to erratic behavior. This could result in fans running at full speed even when temperatures are within acceptable ranges.
-
Overheating Components: If a component, such as the CPU or GPU, is consistently running at high temperatures, the fan control mechanism will keep the fans running at higher speeds to maintain safe operating temperatures. This could indicate a thermal paste issue, inadequate cooling solution, or an overloaded component.
-
Software Issues: Certain software applications or processes can generate excessive heat, forcing the fans to run continuously. This could be due to resource-intensive programs, malware infections, or even faulty driver installations.
-
Hardware Malfunctions: In rare cases, a malfunctioning fan itself can cause it to run continuously. This could be due to a faulty motor, a broken blade, or a damaged connection.
Potential Risks of Persistent Fan Operation:
While persistent fan operation may seem like a minor annoyance, it can have significant consequences:
-
Increased Noise: Continuous fan operation can generate considerable noise, creating an unpleasant and distracting environment.
-
Increased Power Consumption: Fans running at higher speeds consume more power, potentially increasing energy bills.
-
Component Damage: In extreme cases, prolonged high-speed fan operation can lead to excessive wear and tear on the fans themselves, potentially causing them to fail prematurely.
-
System Instability: Persistent fan operation can be a symptom of underlying hardware issues, potentially leading to system instability, crashes, and data loss.
Troubleshooting Strategies for Persistent Fan Operation:
Addressing persistent fan operation requires a systematic approach, starting with simple checks and progressing to more complex troubleshooting steps:
-
Clean the System: Begin by thoroughly cleaning the system, focusing on removing dust from fans, heatsinks, and other components. This can significantly improve airflow and reduce fan speeds.
-
Check Fan Connections: Ensure that all fan connections are secure and properly seated. A loose connection can cause erratic fan behavior.
-
Monitor System Temperatures: Use monitoring software to check the temperatures of key components, such as the CPU and GPU. If temperatures are consistently high, investigate potential causes like thermal paste issues or inadequate cooling solutions.
-
Update Drivers: Ensure that all drivers, particularly those related to the motherboard and cooling system, are up to date. Outdated drivers can cause conflicts and lead to fan control issues.
-
Run Diagnostic Tests: Utilize diagnostic tools to check for hardware malfunctions, such as faulty fans or motherboard problems.
-
Reset BIOS Settings: Resetting the BIOS to default settings can sometimes resolve fan control issues caused by incorrect configuration.
-
Reinstall Operating System: In extreme cases, reinstalling the operating system can eliminate software-related issues that might be causing persistent fan operation.
FAQs about Persistent Fan Operation:
-
Q: My computer fan is running constantly even when idle. Is this normal?
-
A: No, it is not normal. A computer fan should only run at high speeds when the system is under load. If it runs constantly, it indicates a potential problem.
-
Q: How do I know if my fan is faulty?
-
A: If the fan makes unusual noises, such as rattling or grinding, or if it spins erratically, it might be faulty. You can also try disconnecting the fan and checking if it spins freely by hand.
-
Q: What should I do if my fan is not spinning at all?
-
A: If the fan is not spinning, it might be disconnected, faulty, or blocked by dust. Check the fan connections, clean it, and if necessary, replace it.
-
Q: Can I manually adjust my fan speeds?
-
A: Yes, many motherboards and cooling solutions allow manual fan speed adjustments through BIOS settings or dedicated software. However, be cautious when adjusting fan speeds, as setting them too low can lead to overheating.
Tips for Preventing Persistent Fan Operation:
-
Regular Cleaning: Regularly clean your computer system to prevent dust accumulation.
-
Proper Ventilation: Ensure adequate airflow around your computer to prevent overheating.
-
Quality Cooling Solutions: Invest in high-quality cooling solutions, such as CPU coolers and case fans, to improve thermal performance.
-
Monitor System Temperatures: Regularly monitor system temperatures to identify potential overheating issues.
-
Avoid Overclocking: Overclocking components can increase heat generation, leading to higher fan speeds.
Conclusion:
A computer fan that refuses to stop running can be a symptom of various underlying issues, ranging from simple dust accumulation to more serious hardware malfunctions. Addressing this issue requires a systematic troubleshooting approach, starting with basic cleaning and progressing to more complex diagnostics. By understanding the causes, potential risks, and effective troubleshooting strategies, you can restore your computer to its quiet and efficient operation, ensuring optimal performance and longevity of your hardware.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unrelenting Whirr: Understanding and Resolving Persistent Computer Fan Operation. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!