Unraveling the Mystery: Why Windows 10 Can’t Save Your IP Address
Related Articles: Unraveling the Mystery: Why Windows 10 Can’t Save Your IP Address
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Mystery: Why Windows 10 Can’t Save Your IP Address. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unraveling the Mystery: Why Windows 10 Can’t Save Your IP Address
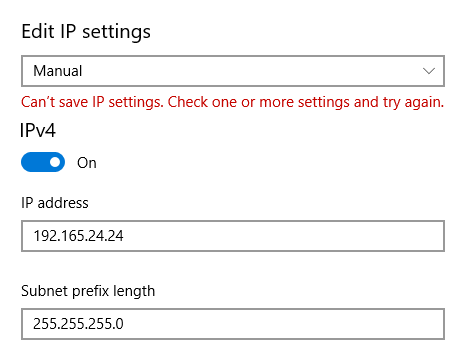
The ability to assign a static IP address is crucial for many network configurations, allowing for consistent communication and control over network traffic. However, situations arise where Windows 10 users encounter difficulties saving their chosen IP address, leading to frustration and network connectivity issues. This article explores the common culprits behind this problem, offering practical solutions to restore network stability.
Understanding the Dynamics of IP Address Assignment
Before delving into the troubleshooting process, it’s essential to grasp the fundamental principles governing IP address allocation. Windows 10, by default, relies on the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) to acquire an IP address. This process involves a request-response interaction between the computer and a DHCP server, typically located within the network router. The DHCP server automatically assigns a unique IP address to each device, ensuring smooth communication within the network.
The Challenges of Static IP Address Configuration
While DHCP offers convenience, it may not always be suitable for specific network configurations or advanced usage scenarios. In such instances, manually assigning a static IP address is necessary. This approach ensures that the computer always receives the same IP address, regardless of network changes. However, this process can sometimes be hindered by various factors, preventing the successful saving of the static IP address.
Common Culprits Behind the Inability to Save IP Address
Several factors can contribute to the inability of Windows 10 to save a static IP address. Understanding these potential culprits is the first step towards resolving the issue:
1. Network Adapter Configuration:
- Incorrect Subnet Mask: The subnet mask defines the network portion of the IP address, ensuring devices within the same network can communicate. An incorrect subnet mask can prevent the saving of the static IP address.
- Conflicting IP Addresses: If the static IP address you’re trying to assign is already in use by another device on the network, Windows 10 will not allow it to be saved.
- Disabled Network Adapter: A disabled network adapter can prevent any IP address configuration changes from taking effect.
2. Network Security and Firewall:
- Firewall Blocking: Windows Firewall or other security software might interfere with the network configuration process, preventing the saving of the static IP address.
- Antivirus Interference: Certain antivirus programs can aggressively monitor network traffic, potentially hindering the ability to save IP address settings.
3. Network Router Settings:
- DHCP Server Conflicts: If the router’s DHCP server is actively assigning IP addresses, it might prevent the saving of a static IP address on the computer.
- Router Configuration Issues: Incorrect router settings, such as a limited IP address range or a disabled DHCP server, can disrupt the network configuration process.
4. System-Level Issues:
- Registry Corruption: Corrupted registry entries can interfere with network settings, preventing the saving of the static IP address.
- Software Conflicts: Certain software programs might interfere with network settings, causing problems with saving the static IP address.
Troubleshooting Steps: Resolving the Issue
Addressing the inability to save a static IP address in Windows 10 requires a systematic approach. The following steps provide a comprehensive guide:
1. Verify Network Adapter Settings:
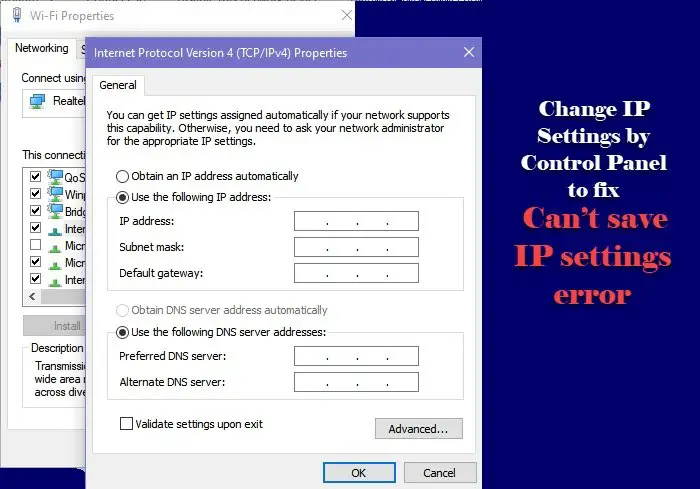
- Access Network Settings: Open the Control Panel and navigate to "Network and Sharing Center." Click on "Change adapter settings" to view the available network adapters.
- Inspect IP Address Configuration: Right-click on the relevant network adapter and select "Properties." Navigate to the "Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4)" section and click on "Properties."
- Verify Subnet Mask: Ensure the subnet mask is correct and matches the network configuration.
- Check for Conflicting Addresses: If you’re using a static IP address, ensure it’s not already assigned to another device on the network.
2. Disable Firewall and Antivirus Temporarily:
- Windows Firewall: Open the Control Panel and navigate to "Windows Firewall." Turn off both public and private network settings temporarily to see if it resolves the issue.
- Antivirus Software: Disable your antivirus temporarily, but only if you’re confident that the network is secure. Remember to re-enable it once the troubleshooting is complete.
3. Check Router Settings:
- Access Router Interface: Open a web browser and enter the router’s IP address (usually found on the router’s sticker). Log in using the router’s default username and password.
- Verify DHCP Server Settings: Ensure the DHCP server is enabled and configured correctly. Check for any conflicting IP address ranges.
- Disable DHCP Server Temporarily: If you’re confident that the router is not actively assigning IP addresses, you can temporarily disable the DHCP server to see if it resolves the issue.
4. Run Network Troubleshooter:
- Access Network Troubleshooter: Open the Control Panel and navigate to "Network and Sharing Center." Click on "Troubleshoot problems" to launch the Network troubleshooter.
- Follow Instructions: The troubleshooter will automatically scan for network problems and provide potential solutions.
5. Perform a Clean Boot:
- Access System Configuration: Press "Windows key + R" to open the Run dialog box. Type "msconfig" and press Enter.
- Disable Startup Items: Navigate to the "Startup" tab and deselect all items except essential system services.
- Disable Non-Microsoft Services: Navigate to the "Services" tab and check the box for "Hide all Microsoft services." Click on "Disable all."
- Restart Computer: Restart the computer and attempt to save the static IP address. If the issue is resolved, gradually enable services and startup items to identify the conflicting program.
6. Reset Network Settings:
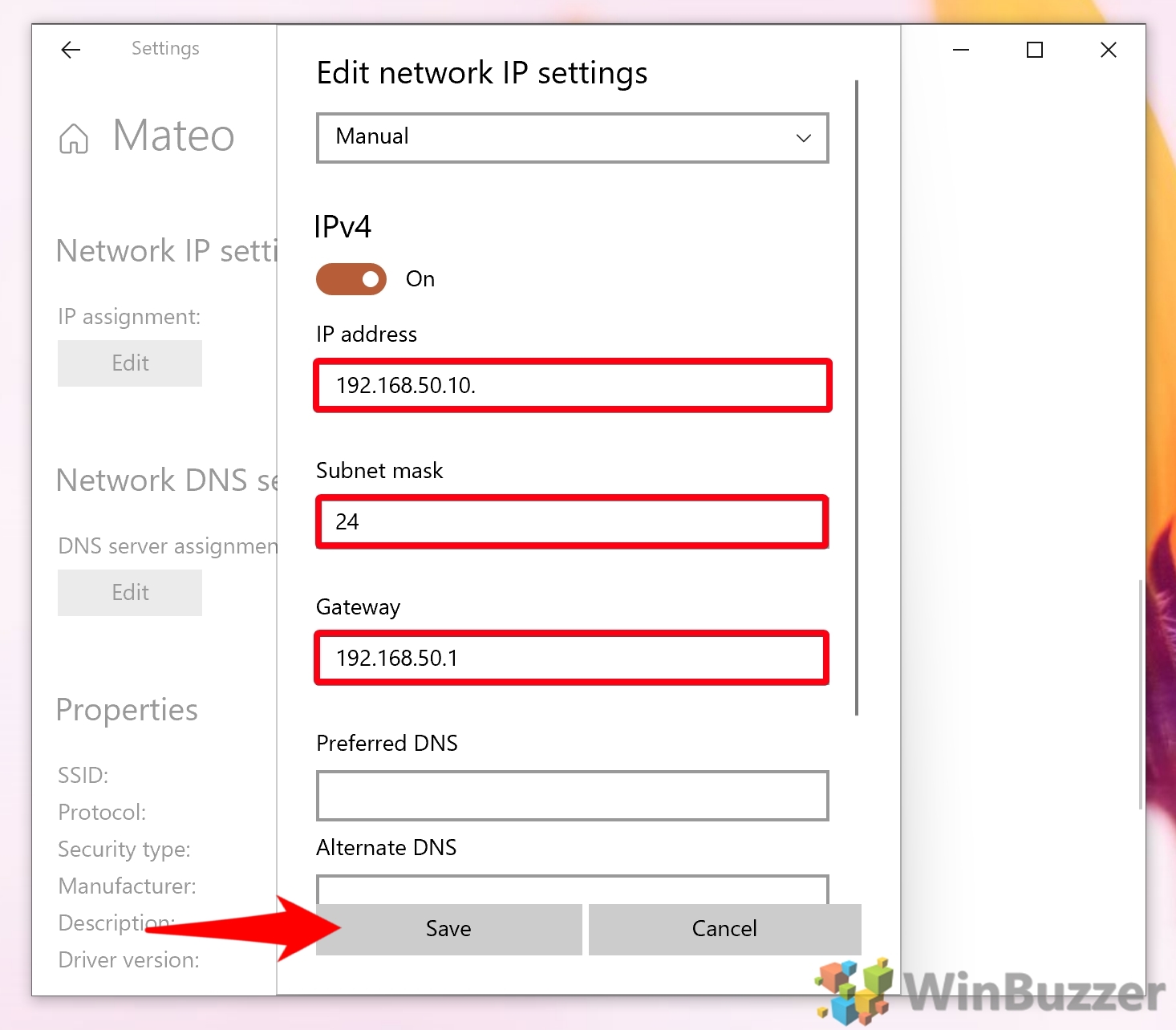
- Open Network Settings: Open the Settings app and navigate to "Network & Internet."
- Reset Network: Click on "Network Reset" and follow the instructions to reset network settings. This will remove all network configurations, including saved passwords and IP addresses.
7. Consider Registry Edits:
- Caution: Modifying the registry can be risky if not done correctly. Always create a backup before making any changes.
- Locate Registry Key: Navigate to "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetServicesTcpipParameters" in the Registry Editor.
- Modify Registry Entries: If you find any corrupted or incorrect entries related to network settings, delete or modify them as necessary.
FAQs: Addressing Common Concerns
Q: What if my network adapter is already disabled?
- A: If your network adapter is already disabled, you’ll need to enable it before proceeding with any IP address configuration changes. You can enable the adapter by right-clicking on it in the "Network Connections" window and selecting "Enable."
Q: Is it safe to disable my firewall and antivirus software?
- A: Disabling your firewall and antivirus software is not recommended unless you’re confident that your network is secure. Temporarily disabling them can expose your system to security risks.
Q: How do I find my router’s IP address?
- A: The router’s IP address is typically found on the sticker attached to the router itself. If it’s not available, you can open the Command Prompt and type "ipconfig" to view the network configuration details. The router’s IP address will be listed under the "Default Gateway" entry.
Q: What if I’m still unable to save my IP address after trying all these solutions?
- A: If you’ve exhausted all troubleshooting steps and are still unable to save the static IP address, it’s advisable to contact your internet service provider or a qualified IT professional for assistance. They can diagnose the problem further and provide specialized solutions.
Tips for Preventing Future Issues:
- Regularly Update Drivers: Ensure your network adapter drivers are up-to-date to avoid compatibility issues.
- Keep Software Updated: Regularly update your operating system and software programs to address potential bugs or security vulnerabilities.
- Monitor Network Settings: Periodically review your network settings to ensure they are accurate and consistent with your requirements.
- Backup Registry: Create regular backups of your registry to protect your system from data loss in case of errors or unexpected issues.
Conclusion:
The inability to save a static IP address in Windows 10 can be a frustrating experience, hindering network connectivity and causing disruptions in communication. By understanding the common culprits behind this issue and implementing the troubleshooting steps outlined in this article, users can effectively address the problem and restore network stability. Remember to approach registry edits with caution and seek professional help if necessary. By taking proactive measures and maintaining proper network hygiene, users can minimize the occurrence of such issues and enjoy a seamless network experience.
![Can't Save IP Settings Windows 10 [FIXED] - YouTube](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/NKvtpVbpJaQ/maxresdefault.jpg)




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Mystery: Why Windows 10 Can’t Save Your IP Address. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!