Unlocking the Bottlenecks: A Comprehensive Guide to Addressing Slow Performance in Windows 10
Related Articles: Unlocking the Bottlenecks: A Comprehensive Guide to Addressing Slow Performance in Windows 10
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unlocking the Bottlenecks: A Comprehensive Guide to Addressing Slow Performance in Windows 10. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unlocking the Bottlenecks: A Comprehensive Guide to Addressing Slow Performance in Windows 10
Windows 10, despite its numerous advancements, can sometimes succumb to performance issues, leading to sluggish responsiveness, prolonged loading times, and an overall frustrating user experience. This article delves into the common culprits behind slow performance in Windows 10, providing a detailed roadmap for identifying and resolving these bottlenecks.
Understanding the Causes of Slow Performance:
Slow performance in Windows 10 can stem from various factors, each demanding a tailored approach for remediation. Here are some of the most frequent culprits:
1. Insufficient Hardware:
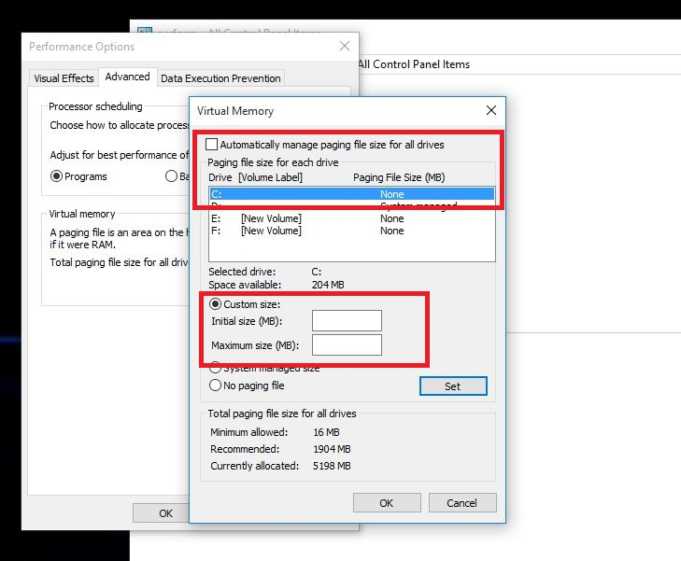
- Insufficient RAM: Windows 10 requires a minimum of 2 GB RAM for smooth operation, but a more comfortable experience necessitates at least 4 GB. When RAM is insufficient, the system resorts to utilizing the hard drive as virtual memory, significantly slowing down operations.
- Overburdened CPU: A CPU (Central Processing Unit) acts as the brain of your computer, processing data and instructions. If the CPU is constantly strained by demanding tasks or background processes, it can lead to sluggishness.
- Saturated Storage: Hard drives, especially older HDDs, can become slow when they are nearing full capacity. This is due to the increased time required to locate and access data.
2. System Resource Hogs:
- Background Programs: Numerous applications and services run in the background, consuming valuable resources without your explicit knowledge. These programs can significantly impact performance, especially if they are resource-intensive or poorly optimized.
- Malware and Viruses: Malicious software can silently infiltrate your system, consuming resources and hindering performance.
- Outdated Drivers: Out-of-date device drivers can lead to compatibility issues and slowdowns.
3. Operating System Factors:
- Cluttered System: Over time, your system accumulates temporary files, unnecessary programs, and outdated data, leading to a cluttered environment that slows down operations.
- Windows Updates: While essential for security and stability, Windows updates can sometimes cause temporary performance hiccups, especially during the installation process.
- Defragmentation: Hard disk drives (HDDs) can become fragmented over time, resulting in slower access times. Defragmentation rearranges data on the drive, improving performance.
4. External Influences:
- Network Connectivity: A slow internet connection can impact the performance of online applications and services.
- Hardware Malfunctions: Failing hardware components, such as a malfunctioning hard drive or RAM, can cause significant performance degradation.
Identifying the Source of Slowness:
Pinpointing the root cause of slow performance is crucial for effective troubleshooting. Here are some tools and methods to aid in this process:
- Task Manager: This built-in tool provides a snapshot of system resource usage, revealing processes that are consuming excessive resources.
- Resource Monitor: A more detailed tool offering real-time system performance data, including CPU, memory, and disk usage.
- System Information: Provides information about your system’s hardware and software configuration, helping to identify potential bottlenecks.
- Performance Monitor: A powerful tool for advanced monitoring and analysis of system performance metrics.
- Event Viewer: Logs system events, including errors and warnings, which can provide clues about performance issues.
Resolving Performance Issues:
Once you have identified the source of slow performance, you can implement targeted solutions to address the problem:
1. Optimizing Hardware:
- Upgrade RAM: If your system is running low on RAM, consider upgrading to a higher capacity.
- Upgrade Storage: Consider upgrading to a faster SSD (Solid State Drive) for a significant performance boost.
- Monitor CPU Usage: If your CPU is consistently running at high capacity, consider reducing resource-intensive tasks or upgrading to a more powerful CPU.
2. Managing System Resources:
- Disable Unnecessary Programs: Review your startup programs and disable those that are not essential for your daily use.
- Run Disk Cleanup: Regularly remove temporary files, system files, and other unnecessary data to free up disk space.
- Scan for Malware: Use a reputable antivirus program to scan for and remove malware that might be consuming resources.
- Update Drivers: Ensure your device drivers are up to date to improve compatibility and performance.
3. Optimizing Windows 10:
- Defragment Your Hard Drive: If you have an HDD, regularly defragment it to improve access times.
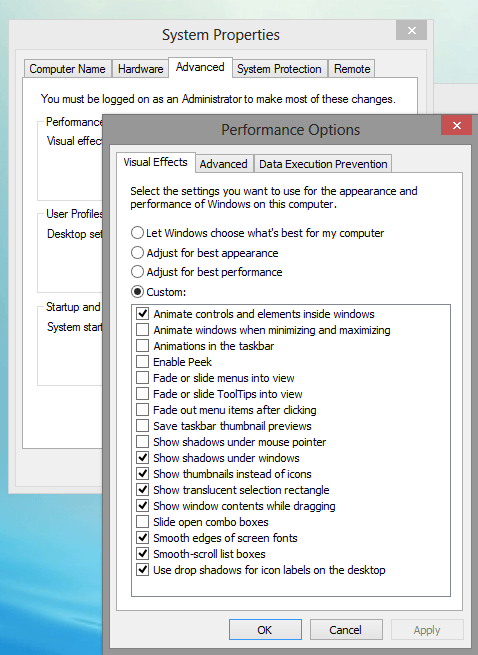
- Disable Visual Effects: Reduce visual effects in Windows to free up system resources.
- Adjust Power Settings: Optimize power settings to prioritize performance over battery life.
- Optimize Windows Updates: Schedule updates for off-peak hours to minimize performance impact.
4. Addressing External Influences:
- Improve Network Connectivity: Ensure you have a stable and fast internet connection.
- Diagnose Hardware Issues: If you suspect a hardware malfunction, consult a qualified technician for diagnosis and repair.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Q: Why is my computer suddenly running slow after a Windows update?
A: Windows updates can sometimes cause temporary performance issues due to the installation process or changes to system settings. Restarting your computer after an update can often resolve these issues. If the slowness persists, check for updated drivers or consider rolling back the update.
Q: Is it normal for my computer to slow down over time?
A: Yes, it’s normal for computers to slow down over time as they accumulate data, programs, and temporary files. Regular system maintenance, such as disk cleanup, defragmentation, and removing unnecessary programs, can help mitigate this slowdown.
Q: Can I fix a slow computer without reinstalling Windows?
A: In most cases, yes. By identifying and addressing the root cause of slow performance, you can often restore your computer to its optimal speed without resorting to a fresh installation.
Q: How can I prevent my computer from slowing down in the future?
A: Implementing preventative measures can help maintain optimal performance over time. These include:
- Regularly cleaning up temporary files and unnecessary programs.
- Running regular antivirus scans.
- Keeping your drivers up to date.
- Monitoring system resource usage and addressing potential bottlenecks.
Conclusion:
Slow performance in Windows 10 is a common issue with a multitude of potential causes. By understanding the underlying factors, utilizing available tools for diagnosis, and implementing effective solutions, you can unlock the full potential of your system, restoring it to its optimal speed and responsiveness. Remember, proactive maintenance and optimization are key to maintaining a smoothly functioning and efficient Windows 10 experience.





![Windows 10: How to Fix Slow Performance Issue After Update [2021]](https://benisnous.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/Windows-10-How-to-Fix-Slow-Performance-Issue-After-Update-800x445.jpg)
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unlocking the Bottlenecks: A Comprehensive Guide to Addressing Slow Performance in Windows 10. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!