Understanding the D Drive in Windows 10: Exploring its Purpose and Functionality
Related Articles: Understanding the D Drive in Windows 10: Exploring its Purpose and Functionality
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Understanding the D Drive in Windows 10: Exploring its Purpose and Functionality. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the D Drive in Windows 10: Exploring its Purpose and Functionality
![[Solved]: How to Fully Use D Drive in Windows 10](https://www.diskpart.com/screenshot/en/others/others/change-where-new-content-is-saved.png)
In the realm of computer operating systems, Windows 10 utilizes a hierarchical file system to organize data. This system, often referred to as the "drive letter system," assigns individual letters to different storage locations within the computer. While the "C drive" typically houses the core operating system files, the "D drive" serves a distinct purpose, acting as a secondary storage location. This article delves into the intricacies of the D drive in Windows 10, exploring its functions, benefits, and potential uses.
The D Drive: A Secondary Storage Hub
The D drive, unlike the C drive, is not a mandatory component of the Windows 10 installation process. Its presence is determined by the hardware configuration of the computer. In many cases, the D drive is a separate physical hard drive or SSD (Solid-State Drive) installed alongside the primary C drive. This configuration allows for a greater storage capacity, offering a dedicated space for files, applications, and other data.
Benefits of Utilizing a D Drive
The D drive offers several advantages for Windows 10 users:
- Enhanced Storage Capacity: By separating storage between the C and D drives, users can alleviate potential storage constraints on the primary drive. This ensures sufficient space for the operating system to function smoothly and prevents performance issues caused by a crowded C drive.
- Improved System Performance: Storing applications and large files on the D drive can reduce the workload on the C drive, resulting in faster boot times, quicker application launches, and a smoother overall user experience.
- Data Backup and Recovery: The D drive can serve as a secure location to store backups of essential data from the C drive. This allows for easy restoration in case of system crashes, hard drive failures, or accidental data loss.
- Organized Data Management: By dedicating specific folders on the D drive to different categories of data, users can create a structured and organized file system, enhancing data retrieval and management efficiency.
Common Uses of the D Drive
The D drive can be utilized for a wide range of purposes, including:
- Storing Applications: Installing applications on the D drive can free up space on the C drive, leading to improved system performance.
- Saving Large Files: Users can store large files, such as videos, images, and music, on the D drive, minimizing the impact on the C drive’s storage capacity.
- Creating Backup Copies: The D drive can be used to store backups of important data from the C drive, providing a safety net in case of data loss.
- Housing Virtual Machines: Virtual machines, which allow users to run different operating systems within their existing system, often require significant storage space. The D drive can provide a dedicated location for virtual machine files.
- Developing and Testing Projects: Programmers and developers frequently utilize the D drive to store project files, enabling them to work on multiple projects simultaneously without affecting the system’s stability.
FAQs about the D Drive in Windows 10
Q: Is it necessary to have a D drive in Windows 10?
A: No, a D drive is not mandatory for Windows 10 to function. The operating system can be installed and run entirely on the C drive. However, having a separate D drive offers significant advantages in terms of storage capacity, system performance, and data management.
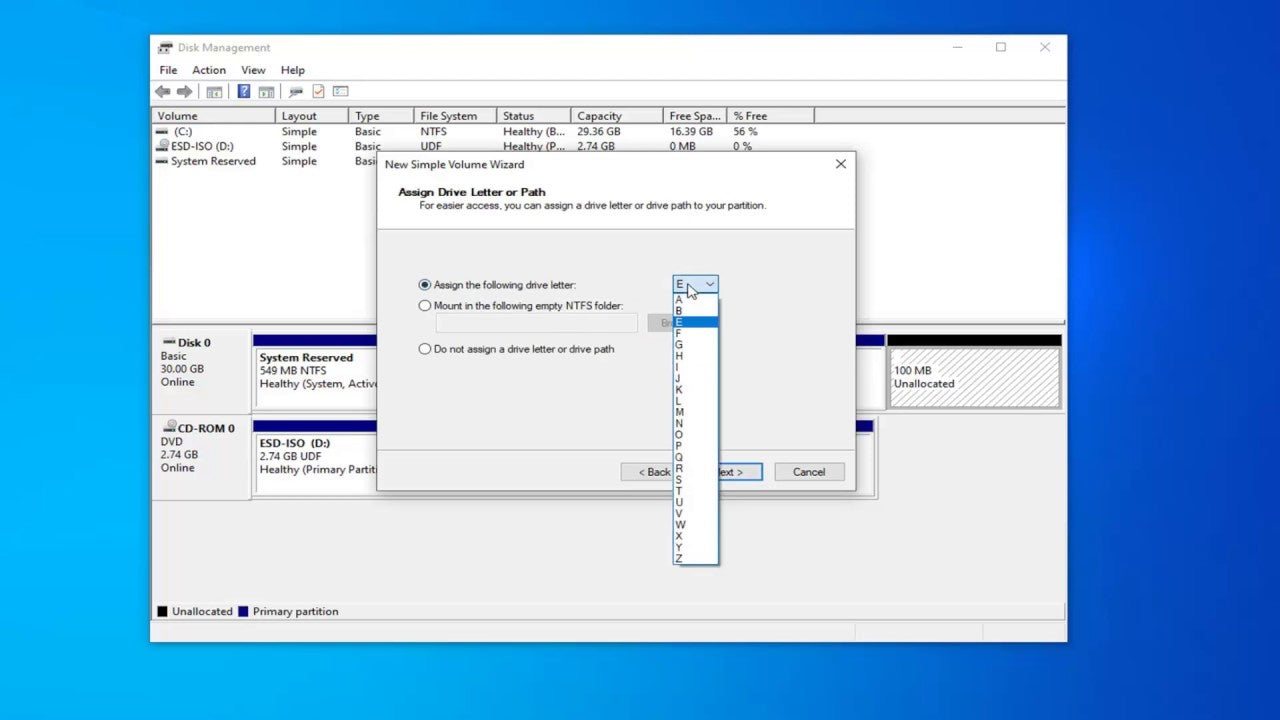
Q: How do I access the D drive in Windows 10?
A: You can access the D drive through the File Explorer. Simply open File Explorer, and the D drive will appear alongside other drives listed in the navigation pane.
Q: Can I move files from the C drive to the D drive?
A: Yes, you can move files from the C drive to the D drive. This can be done by dragging and dropping files or using the "Cut and Paste" functionality. However, it is important to note that moving system files from the C drive to the D drive is not recommended and may lead to system instability.
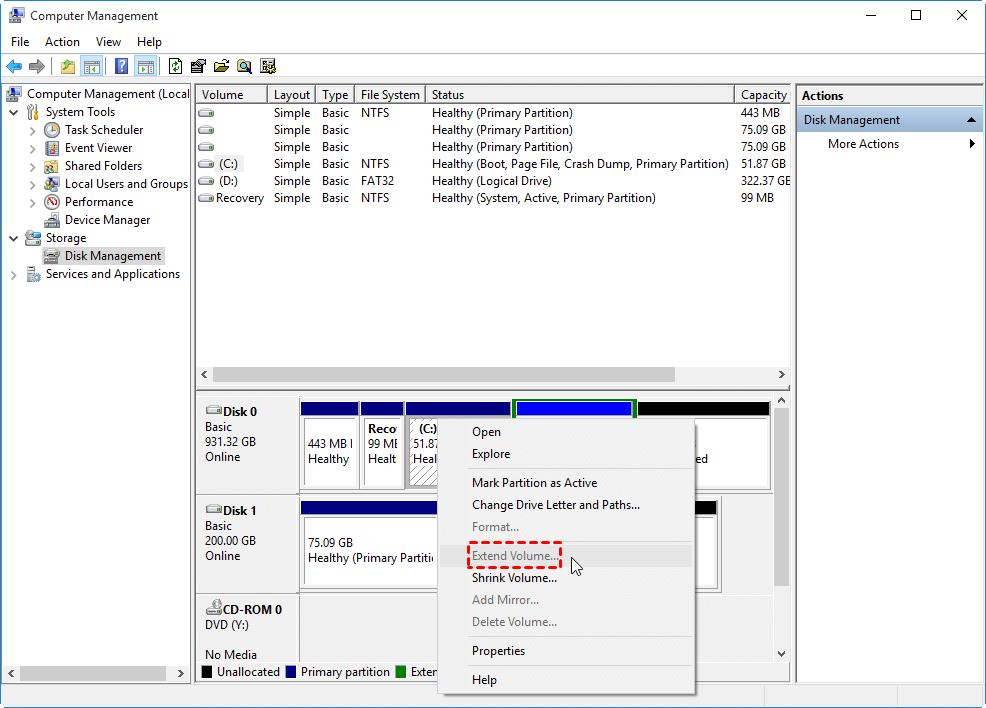
Q: Can I format the D drive without affecting the C drive?
A: Yes, you can format the D drive without affecting the C drive. Formatting the D drive will erase all data stored on it, so it is essential to back up any important files before proceeding.
Tips for Optimizing the D Drive in Windows 10
- Regularly defragment the D drive: Defragmenting the D drive can improve file access speed and overall system performance.
- Utilize file compression tools: Compressing large files stored on the D drive can reduce their size, freeing up valuable storage space.
- Optimize drive space: Regularly review the files stored on the D drive and remove any unnecessary files to maintain optimal storage capacity.
- Run disk cleanup: The Disk Cleanup tool in Windows 10 can help identify and remove temporary files, system files, and other unnecessary data from the D drive.
- Monitor drive health: Use the built-in disk management tools in Windows 10 to monitor the health of the D drive and ensure its integrity.
Conclusion
The D drive in Windows 10 serves as a valuable secondary storage location, providing users with increased storage capacity, enhanced system performance, and improved data management capabilities. By understanding the functions and benefits of the D drive, users can optimize their Windows 10 experience, ensuring a smooth and efficient workflow. Whether used for storing applications, backing up data, or managing large files, the D drive offers a versatile and essential component of the Windows 10 ecosystem.
![[Solved]: How to Fully Use D Drive in Windows 10](https://www.diskpart.com/screenshot/en/pro/app-mover/move-app-from-c-to-d/ok.png)
![How to Create D Drive in Windows 11/10/8/7 [3 Free Ways]](https://www.diskpart.com/screenshot/en/std/create-d-partition/apply.png)
![How to Create D Drive in Windows 11/10/8/7 [3 Free Ways]](https://www.diskpart.com/screenshot/en/others/windows-10/create-d-drive-disk-management/d-drive.png)


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the D Drive in Windows 10: Exploring its Purpose and Functionality. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!