Understanding and Managing Windows 10 Fast Startup: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Understanding and Managing Windows 10 Fast Startup: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Understanding and Managing Windows 10 Fast Startup: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding and Managing Windows 10 Fast Startup: A Comprehensive Guide
Windows 10’s "Fast Startup" feature, introduced in Windows 8, is designed to expedite the boot process, significantly reducing the time it takes for your computer to become operational. This functionality relies on a hybrid approach, combining elements of traditional hibernation and cold boot processes. However, while Fast Startup generally offers a smoother user experience, its implementation can sometimes introduce complications or hinder troubleshooting efforts. This article delves into the intricacies of Fast Startup, exploring its advantages, potential drawbacks, and methods for managing it effectively.
The Mechanics of Fast Startup
When Fast Startup is enabled, the system does not perform a complete shutdown upon powering off. Instead, it saves a snapshot of the current system state, including open applications and user settings, to a hibernation file. This file is then used to quickly restore the system when the computer is powered on again. This approach eliminates the need for the operating system to fully load from the hard drive, resulting in a faster boot time.
Benefits of Fast Startup
- Reduced boot time: The primary advantage of Fast Startup is its ability to significantly reduce the time it takes for the computer to boot up. This is especially noticeable on systems with slower hard drives or solid-state drives (SSDs).
- Faster application loading: As the system state is partially loaded from the hibernation file, applications that were open before shutdown may launch quicker.
- Improved user experience: The faster boot process contributes to a more responsive and user-friendly experience, especially for users who frequently restart their computers.
Potential Drawbacks of Fast Startup
- Troubleshooting limitations: Fast Startup can make troubleshooting certain issues more challenging. When Fast Startup is enabled, the system may not fully shut down, which can prevent the execution of certain diagnostic tools or the identification of specific error logs.
- Increased system instability: In some cases, Fast Startup can lead to system instability or unexpected behavior. This may occur due to issues with the hibernation file or conflicts with other system settings.
- Limited compatibility: Certain hardware components or software applications may not fully support Fast Startup, potentially leading to compatibility issues or performance degradation.
Managing Fast Startup in Windows 10
Understanding the nuances of Fast Startup is crucial for optimizing system performance and troubleshooting potential issues. While the default setting is typically beneficial for most users, it may be necessary to disable or modify it based on specific needs.
Disabling Fast Startup:
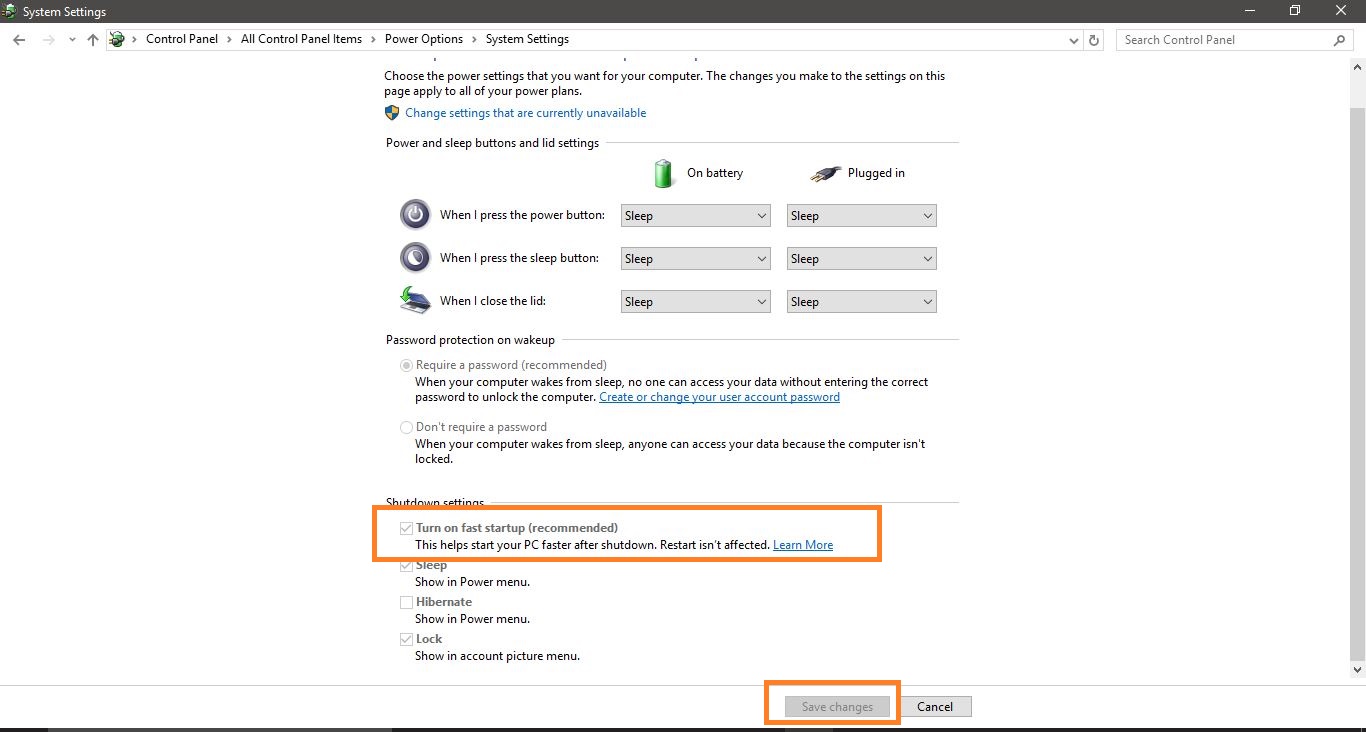
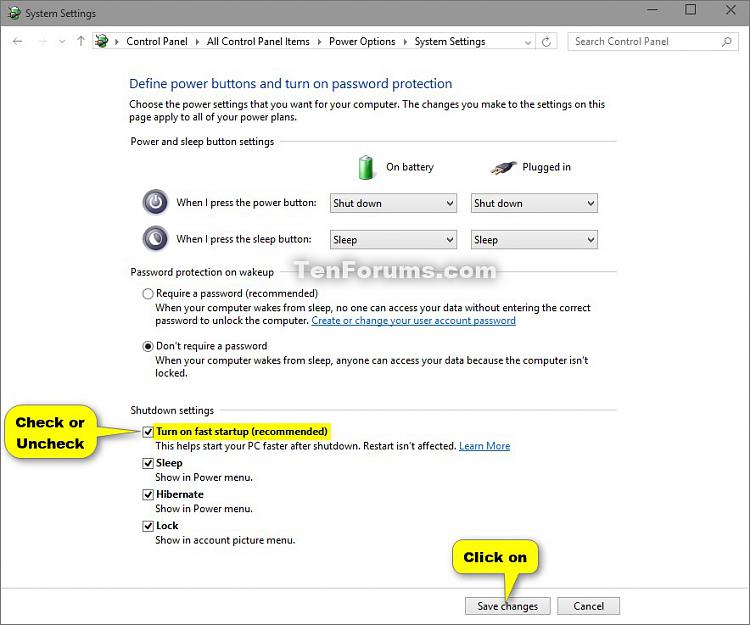
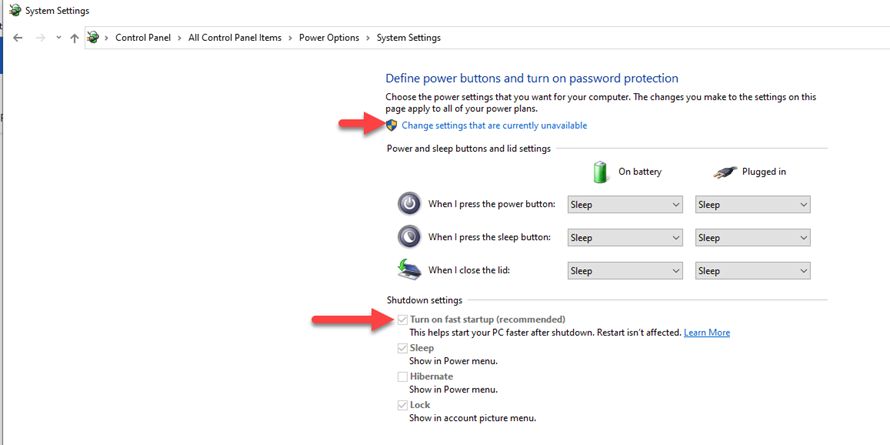
- Control Panel: Navigate to "Power Options" in the Control Panel, click "Choose what the power buttons do," and select "Change settings that are currently unavailable." Uncheck the box next to "Turn on fast startup (recommended)."
-
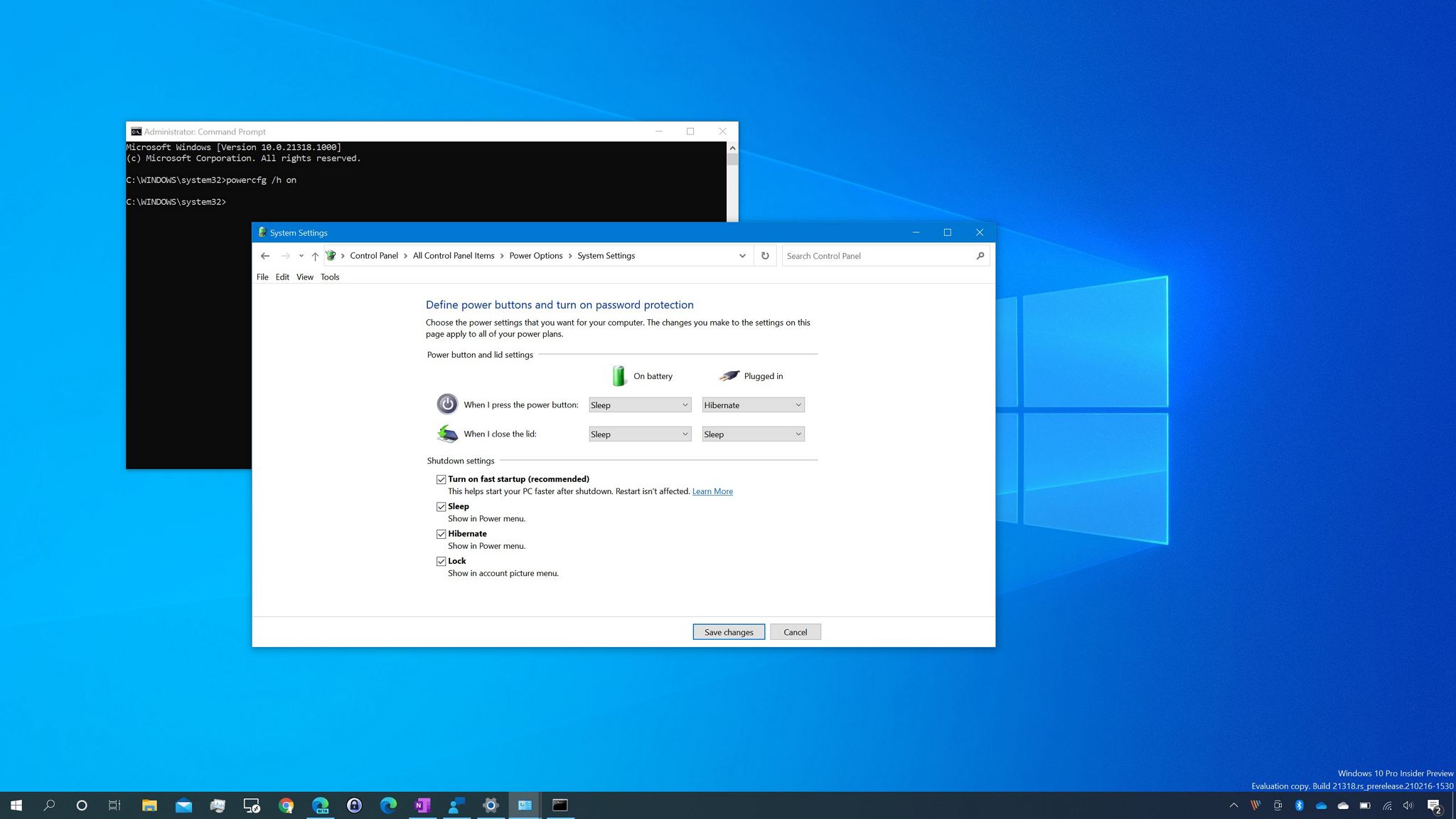
Command Prompt: Open an elevated Command Prompt window and execute the following command:
powercfg /h off
Enabling Fast Startup:
- Control Panel: Follow the same steps as disabling Fast Startup, but check the box next to "Turn on fast startup (recommended)."
-
Command Prompt: Open an elevated Command Prompt window and execute the following command:
powercfg /h on
Troubleshooting Fast Startup Issues:
If you encounter issues related to Fast Startup, the following steps may help resolve them:
- Check hibernation file integrity: Run a system scan using the "chkdsk" command in an elevated Command Prompt window.
- Disable Fast Startup temporarily: Disable Fast Startup and restart your computer to see if the issue persists.
- Update drivers: Ensure that all device drivers are up-to-date, as outdated drivers can sometimes cause compatibility issues with Fast Startup.
- Run a system restore: If the issue is recent, consider restoring your system to an earlier point in time.
- Contact support: If you are unable to resolve the issue, contact Microsoft support for assistance.
FAQs about Fast Startup:
1. Is Fast Startup suitable for all computers?
Fast Startup is generally beneficial for most computers. However, it may not be suitable for systems with specific hardware configurations or those experiencing compatibility issues.
2. Can I disable Fast Startup without losing my data?
Disabling Fast Startup does not result in data loss. The system will still save your current state in a hibernation file, which can be used to restore your system when you restart.
3. How do I know if Fast Startup is enabled?
You can check the status of Fast Startup by navigating to "Power Options" in the Control Panel and selecting "Choose what the power buttons do." The option "Turn on fast startup (recommended)" will be checked if Fast Startup is enabled.
4. Can I use Fast Startup with a mechanical hard drive?
While Fast Startup can be used with mechanical hard drives, it may not provide as significant a performance boost compared to systems with SSDs.
5. What happens to my open applications when I disable Fast Startup?
Disabling Fast Startup does not affect your open applications. The system will still save your current state in a hibernation file, which can be used to restore your system when you restart.
Tips for Managing Fast Startup:
- Consider the benefits and drawbacks: Carefully evaluate the potential advantages and disadvantages of Fast Startup before enabling or disabling it.
- Monitor system performance: Keep an eye on your system’s performance after enabling Fast Startup to ensure it does not cause any stability issues.
- Backup your data: Regularly back up your data to protect against potential data loss, especially if you are experimenting with Fast Startup settings.
- Seek professional help: If you are unsure about managing Fast Startup or encounter persistent issues, consider consulting a qualified IT professional.
Conclusion:
Windows 10’s Fast Startup feature can significantly enhance the user experience by reducing boot times and improving system responsiveness. However, it is important to understand its potential limitations and manage it effectively to avoid potential complications. By following the guidelines and tips outlined in this article, users can optimize Fast Startup for their specific needs and ensure a smooth and efficient computing experience.

![How to Enable Fast Startup on Windows 10 [Guide] Beebom](https://beebom.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/03/4-2.jpg)


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding and Managing Windows 10 Fast Startup: A Comprehensive Guide. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!