Understanding and Enforcing Local Security Authority (LSA) Protection
Related Articles: Understanding and Enforcing Local Security Authority (LSA) Protection
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Understanding and Enforcing Local Security Authority (LSA) Protection. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding and Enforcing Local Security Authority (LSA) Protection
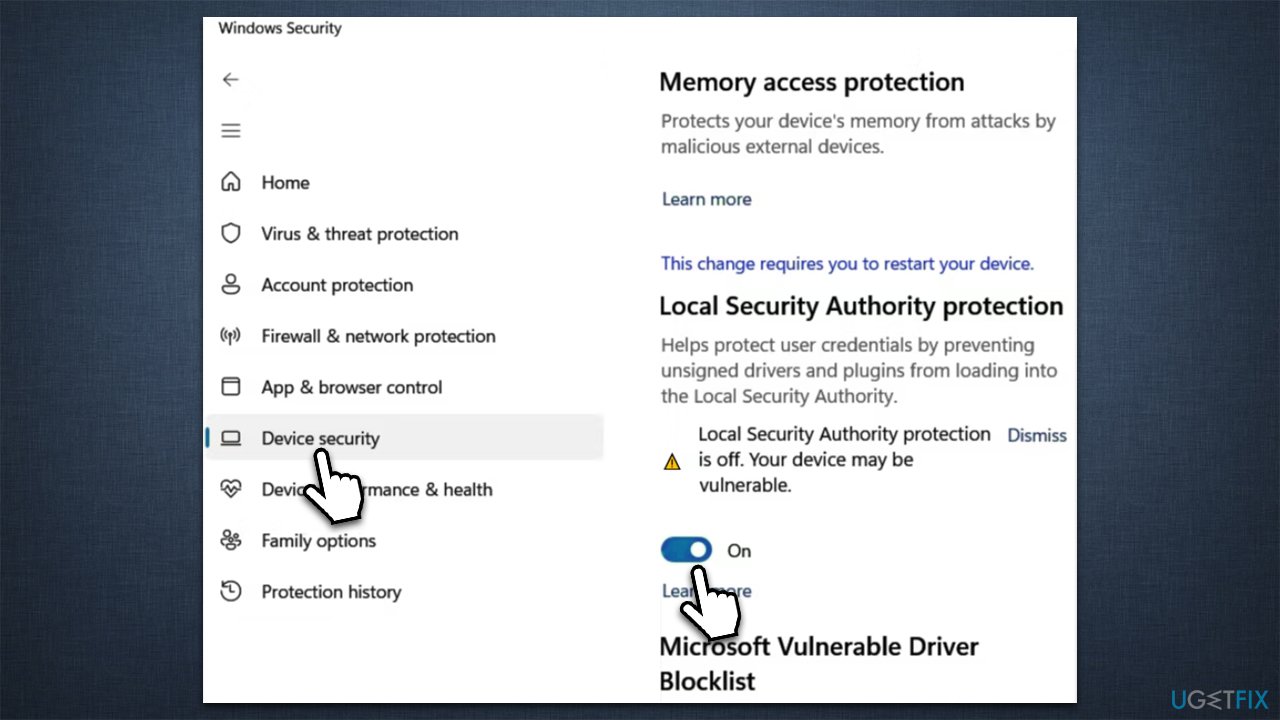
The Local Security Authority (LSA) is a critical component of Windows operating systems, responsible for managing security policies, user authentication, and access control. Its robust protection is paramount for safeguarding sensitive data and maintaining system integrity. This article delves into the importance of LSA protection, explores methods to determine its status, and provides insights into enhancing security through appropriate configuration.
The Significance of LSA Protection
The LSA serves as the central authority for security-related operations within a Windows environment. It governs:
- Authentication: Validating user identities and granting access to resources based on defined policies.
- Authorization: Enforcing access rights and privileges for users and applications.
- Policy Management: Defining and managing security settings, including password complexity, account lockout policies, and audit configurations.
Compromising the LSA can lead to catastrophic consequences, including:
- Privilege Escalation: Attackers gaining unauthorized administrative access, potentially taking complete control of the system.
- Data Theft: Accessing and exfiltrating sensitive information stored on the system.
- Malware Deployment: Installing malicious software to disrupt operations, steal data, or launch further attacks.
Therefore, ensuring the LSA is adequately protected is a crucial aspect of overall system security.
Methods to Verify LSA Protection
Determining whether LSA protection is enabled and configured appropriately requires a multifaceted approach, involving both administrative tools and security analysis.
1. Using the Local Security Policy Console:
- Access: Navigate to the "Local Security Policy" console (secpol.msc) by searching for it in the Windows Start menu.
- Policy Settings: Within the console, explore the "Local Policies" section and examine the "Security Options" category.
-
Relevant Settings: Pay particular attention to the following settings:
- "Network access: Sharing and security model for local accounts": This setting dictates how the LSA handles authentication requests from remote machines. Ensure it is configured appropriately for your security needs.
- "Account lockout threshold": This setting determines how many failed login attempts trigger an account lockout. A high threshold increases security but might inconvenience legitimate users.
- "Account lockout duration": This setting defines the period for which an account remains locked after exceeding the lockout threshold.
- "Password complexity requirements": This setting enforces the use of strong passwords, including minimum length, character types, and complexity rules.
- "Minimum password age": This setting prevents users from changing their passwords too frequently, potentially weakening security.
2. Reviewing Event Logs:
- Windows Security Log: This log records security-related events, including failed login attempts, account lockouts, and privilege changes.
- Analyzing Events: Scrutinize the security log for suspicious events that might indicate LSA compromise, such as multiple failed login attempts from unusual IP addresses or attempts to modify security settings.
3. Employing Security Scanning Tools:
- Vulnerability Scanners: These tools automatically assess systems for known vulnerabilities, including potential weaknesses in LSA protection.
- Penetration Testing: This method simulates real-world attacks to identify security gaps and assess the effectiveness of existing defenses.
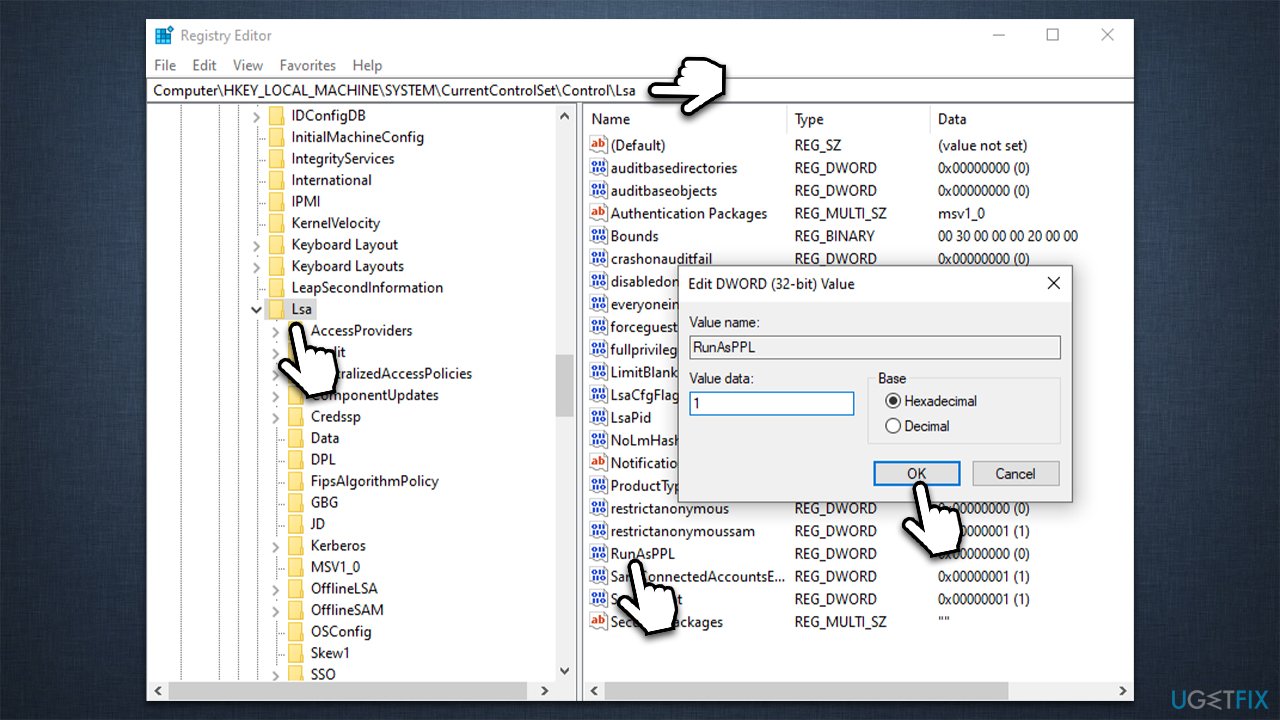
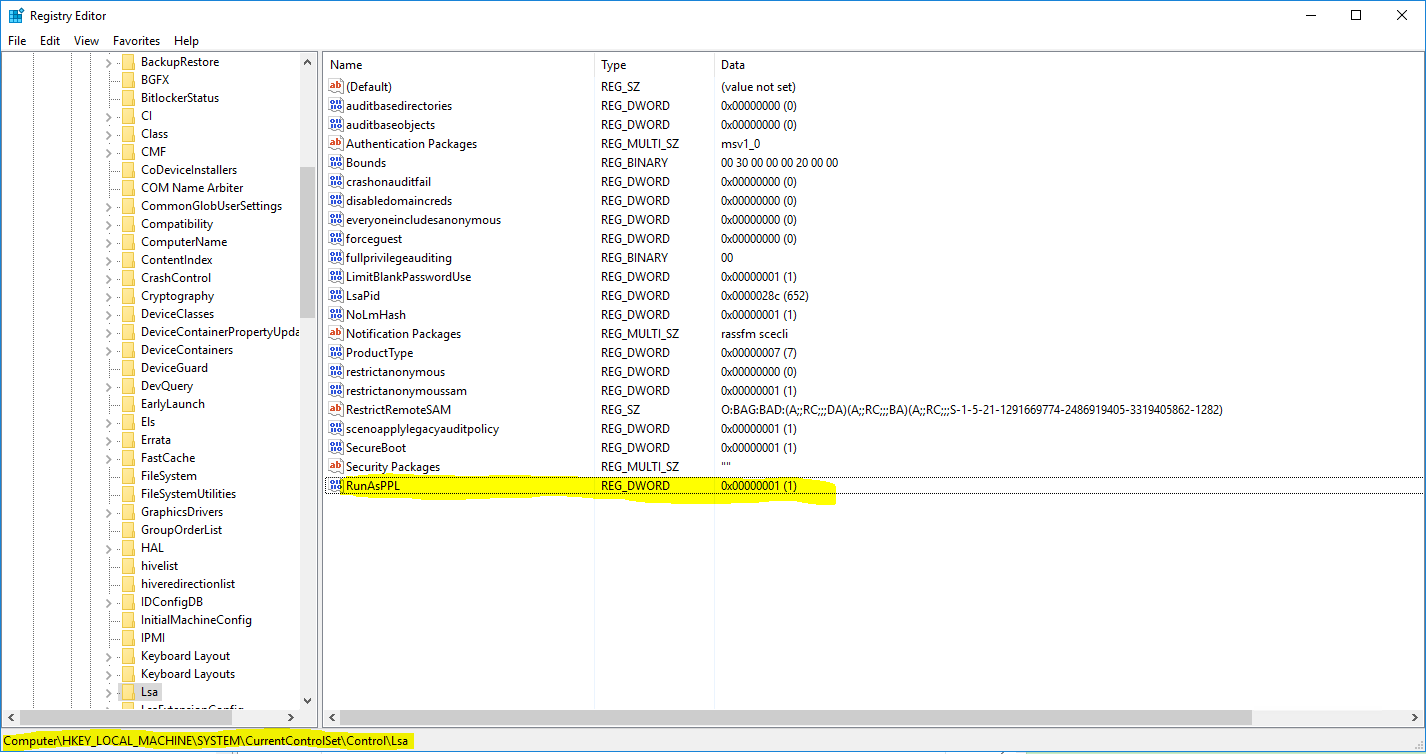
4. Analyzing Registry Settings:
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetControlLsa: This registry key contains numerous settings related to LSA configuration.
- Careful Review: Analyze these settings for any discrepancies or misconfigurations that could potentially weaken LSA protection.
Enhancing LSA Protection
Beyond verifying the current state of LSA protection, implementing additional security measures can significantly strengthen defenses:
1. Enabling Local Security Authority (LSA) Protection:
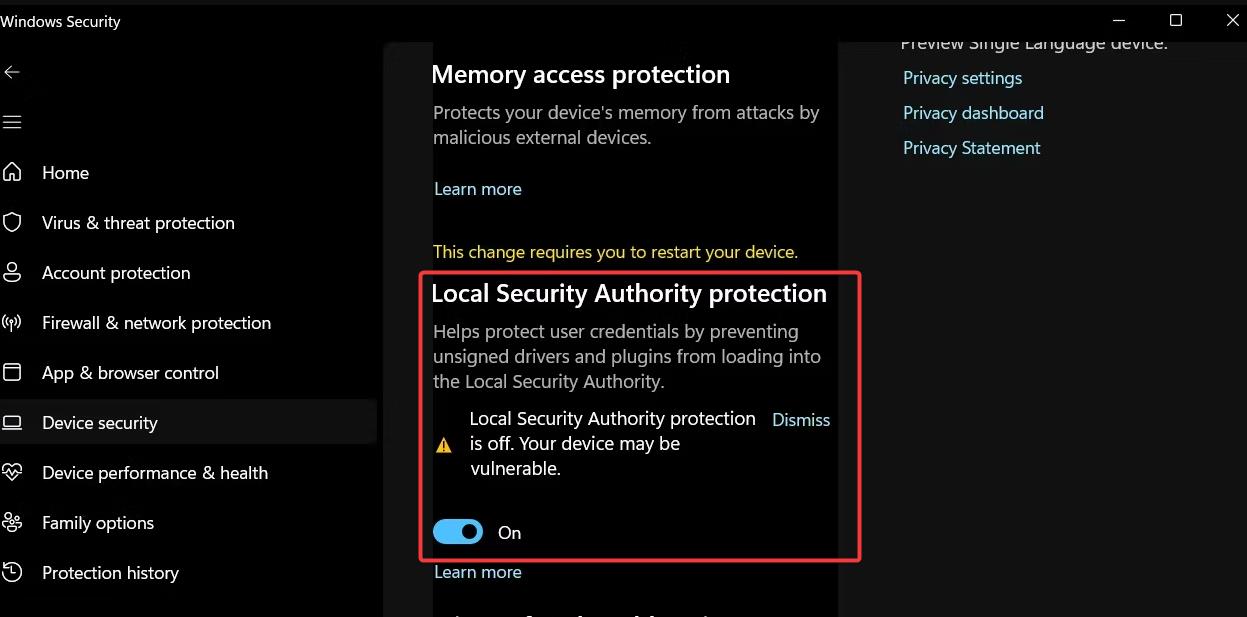
- LSA Protection: This feature, when enabled, restricts access to the LSA process, making it more difficult for attackers to tamper with security settings or gain unauthorized access.
- Configuration: This setting is typically enabled by default in modern Windows versions, but verifying its status is crucial. Use the Local Security Policy console to confirm its activation.
2. Implementing Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA):
- MFA: This security measure requires users to provide multiple forms of authentication, such as a password and a one-time code generated by a mobile app, before granting access.
- LSA Impact: MFA significantly strengthens LSA protection by making it much harder for attackers to bypass authentication mechanisms.
3. Employing Strong Passwords and Password Policies:
- Strong Passwords: Encourage users to create complex passwords that are difficult to guess.
- Password Policies: Implement strict password policies that enforce minimum length, character types, and regular password changes.
4. Regularly Patching the System:
- Security Updates: Microsoft regularly releases security patches to address vulnerabilities in Windows, including those affecting the LSA.
- Prompt Patching: Install security patches promptly to mitigate potential risks and keep the system secure.
5. Using Anti-Malware Software:
- Real-time Protection: Anti-malware software provides real-time protection against known and emerging threats, including attacks targeting the LSA.
- Regular Updates: Ensure that anti-malware software is kept up-to-date with the latest threat signatures.
6. Limiting Administrative Privileges:
- Principle of Least Privilege: Grant users only the minimum privileges necessary to perform their tasks.
- LSA Impact: Reducing administrative privileges minimizes the impact of a potential LSA compromise, as attackers will have fewer permissions to exploit.
FAQs Regarding LSA Protection
Q1: What are the potential consequences of a compromised LSA?
A: A compromised LSA can lead to severe consequences, including:
- Privilege Escalation: Attackers gaining unauthorized administrative access, potentially taking complete control of the system.
- Data Theft: Accessing and exfiltrating sensitive information stored on the system.
- Malware Deployment: Installing malicious software to disrupt operations, steal data, or launch further attacks.
Q2: How can I determine if LSA protection is enabled?
A: You can verify LSA protection status by using the Local Security Policy console, reviewing event logs, and employing security scanning tools.
Q3: What are some best practices for enhancing LSA protection?
A: To enhance LSA protection, consider implementing measures such as:
- Enabling Local Security Authority (LSA) Protection.
- Implementing Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA).
- Employing strong passwords and password policies.
- Regularly patching the system.
- Using anti-malware software.
- Limiting administrative privileges.
Q4: How often should I review LSA protection settings?
A: It is recommended to review LSA protection settings regularly, at least every three months, or more frequently if significant changes are made to the system or network.
Q5: Is there a specific tool to check LSA protection status?
A: There isn’t a dedicated tool solely for checking LSA protection status. However, you can use the Local Security Policy console, security scanning tools, and event log analysis for this purpose.
Tips for LSA Protection
- Regularly Review Security Settings: Periodically review and update LSA protection settings to ensure they remain effective against evolving threats.
- Implement Security Awareness Training: Educate users about the importance of LSA protection and proper security practices, including strong password creation and recognizing phishing attempts.
- Monitor System Activity: Closely monitor system activity for any signs of suspicious behavior or unauthorized access attempts.
Conclusion
The Local Security Authority (LSA) plays a crucial role in safeguarding the integrity and security of Windows systems. Ensuring its protection is paramount, as a compromised LSA can lead to significant security breaches and data loss. By understanding the importance of LSA protection, verifying its status, and implementing appropriate security measures, organizations can significantly mitigate risks and strengthen their overall security posture.
By adhering to best practices, employing robust security tools, and maintaining vigilance, organizations can effectively protect their LSA and ensure the integrity and confidentiality of their valuable data and systems.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding and Enforcing Local Security Authority (LSA) Protection. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!