Troubleshooting Network Connectivity: When Manual IP Configuration Fails in Windows 10
Related Articles: Troubleshooting Network Connectivity: When Manual IP Configuration Fails in Windows 10
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Troubleshooting Network Connectivity: When Manual IP Configuration Fails in Windows 10. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Troubleshooting Network Connectivity: When Manual IP Configuration Fails in Windows 10

Network connectivity is a fundamental aspect of modern computing, enabling users to access the internet, connect to other devices, and share resources. Windows 10, with its robust networking capabilities, typically handles IP address assignment automatically through DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol). However, situations may arise where manually configuring an IP address becomes necessary, either for specific network configurations or troubleshooting purposes. This article explores the common challenges encountered when attempting to set a manual IP address in Windows 10, along with comprehensive troubleshooting steps and explanations.
Understanding Manual IP Configuration
In a typical network, DHCP servers automatically assign IP addresses to devices, ensuring unique identification and communication within the network. This process simplifies network management and eliminates the need for manual configuration. However, there are situations where manual IP configuration becomes essential:
- Static IP Addresses: Some devices, such as servers, require a fixed IP address for consistent access and identification.
- Network Segmentation: In complex networks, manual IP assignment allows for segmenting devices into specific subnets, enhancing security and network performance.
- Troubleshooting Connectivity Issues: When network connectivity problems arise, manually setting an IP address can help isolate the issue and identify potential conflicts.
Common Challenges in Manual IP Configuration
While manual IP configuration provides flexibility, it can also lead to various challenges if not executed correctly. The most common issues encountered include:
- Incorrect IP Address Information: Providing an invalid IP address, subnet mask, or default gateway can prevent network connectivity.
- IP Address Conflicts: If the manually assigned IP address is already in use by another device on the network, it will result in a conflict, preventing communication.
- Firewall Restrictions: Network firewalls or security software might block specific network traffic, interfering with IP address assignment.
- Network Adapter Issues: A faulty network adapter or driver incompatibility can hinder manual IP configuration.
- DNS Server Problems: Incorrect DNS server settings can prevent name resolution, impacting network connectivity.
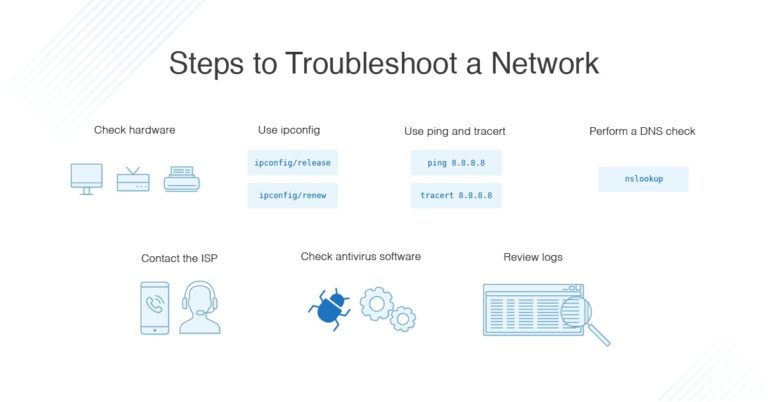
Troubleshooting Manual IP Configuration Issues
Addressing these challenges requires a systematic approach, involving a series of checks and adjustments to ensure successful manual IP configuration.
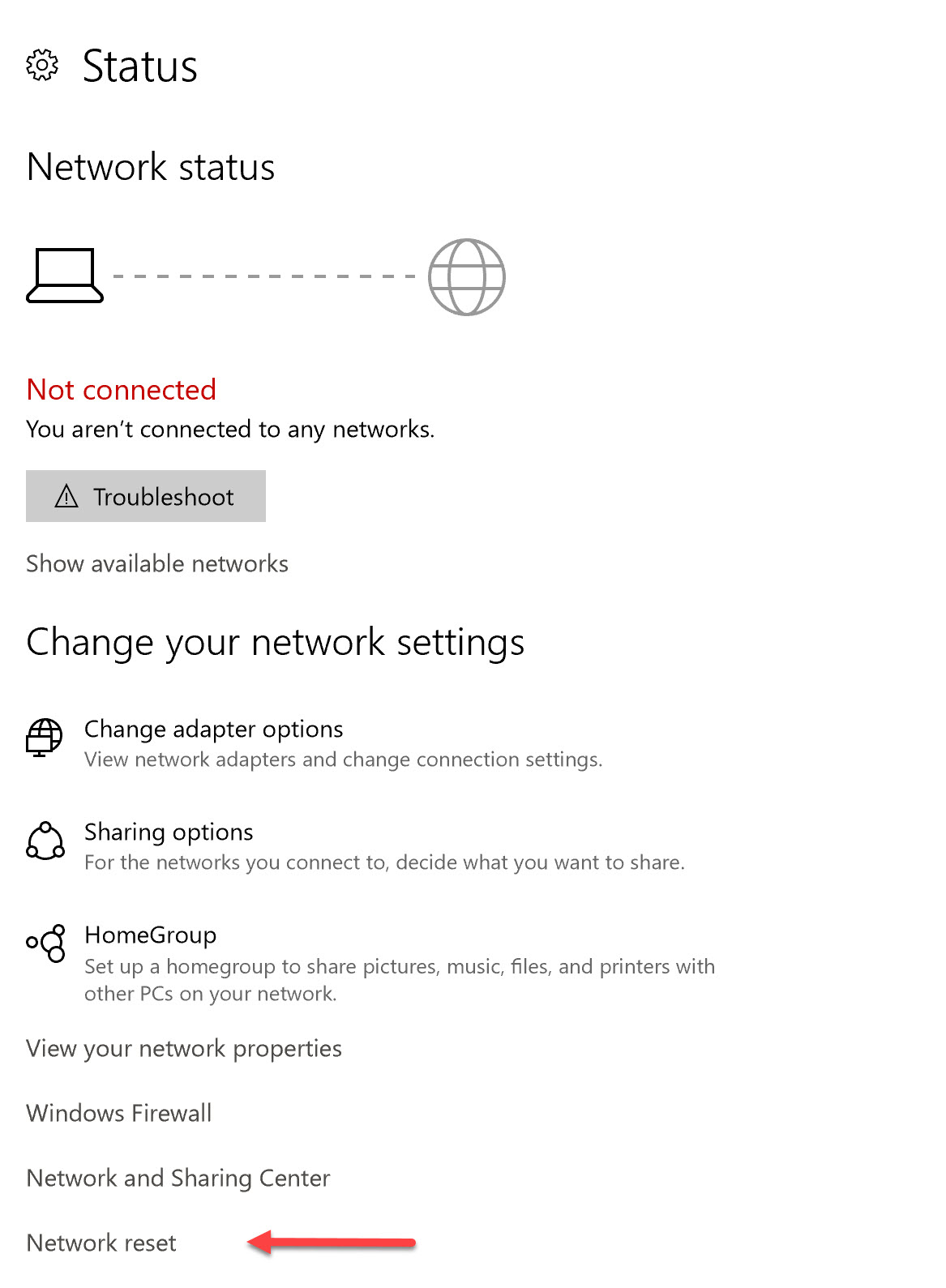
1. Verify Network Connection and Adapter Settings:
- Check Physical Connection: Ensure the network cable is securely connected to the device and the network router.
- Enable Network Adapter: Confirm that the network adapter is enabled in Device Manager. Go to Device Manager (right-click the Start Menu and select Device Manager), expand Network adapters, and ensure the relevant adapter is enabled.
- Verify Adapter Properties: Right-click the network adapter icon in the Network and Sharing Center, select Properties, and review the General tab to confirm the adapter is functioning correctly.
2. Obtain Correct IP Address Information:
- Network Information: Determine the appropriate IP address range, subnet mask, and default gateway for your network. This information can be obtained from your network administrator or router’s configuration page.
- IP Address Range: Ensure the manually assigned IP address falls within the allowed range for your network.
- Subnet Mask: The subnet mask defines the network portion of the IP address and must match the network configuration.
- Default Gateway: The default gateway acts as the gateway to the external network and is usually the IP address of the router.
- DNS Server: The DNS server translates domain names into IP addresses, enabling website access. You can obtain the preferred DNS server address from your ISP or network administrator.
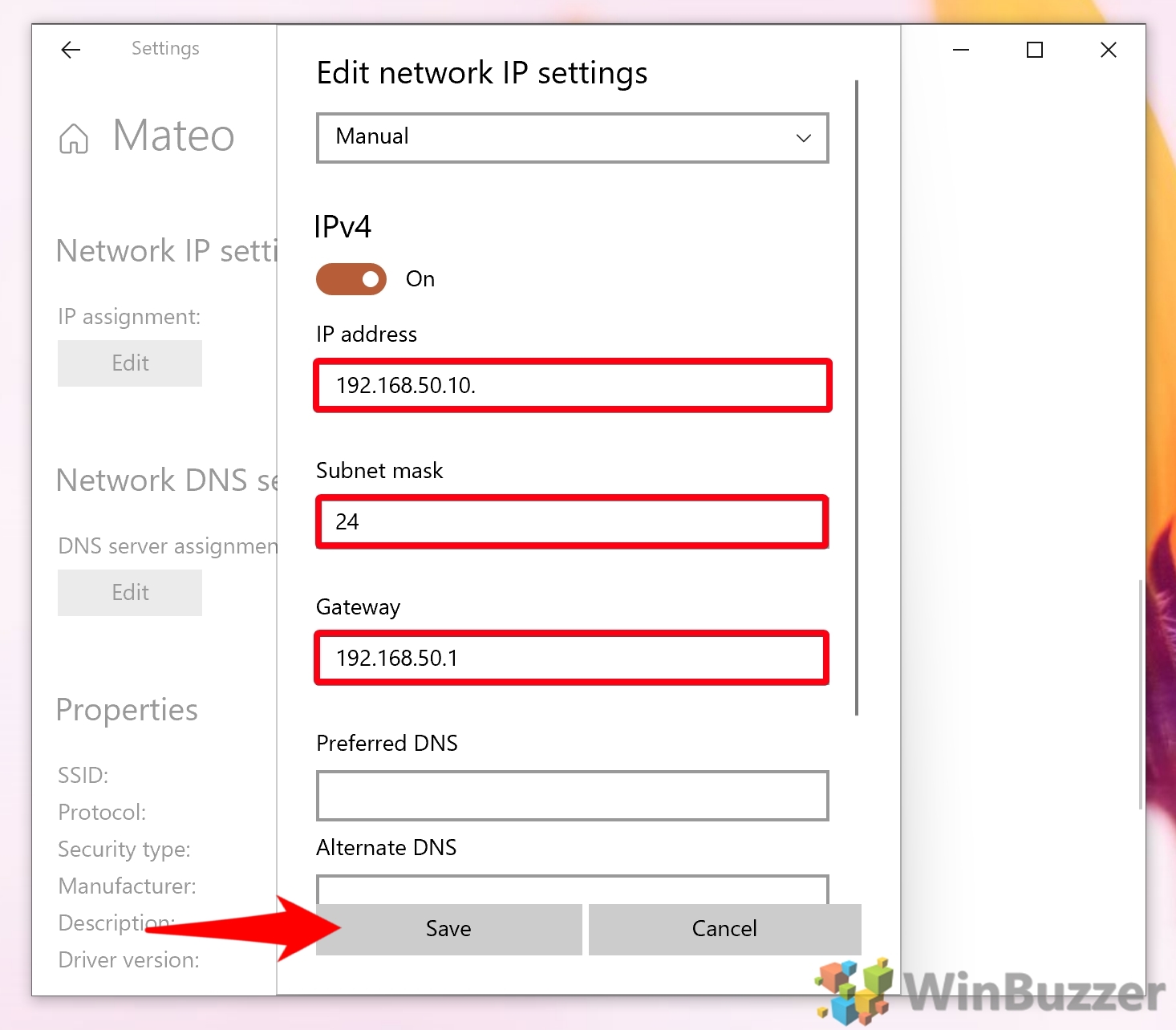
3. Configure Manual IP Address:
- Open Network and Sharing Center: Go to Control Panel, select Network and Sharing Center, and click on Change adapter settings.
- Access Network Adapter Properties: Right-click the relevant network adapter and select Properties.
- Select IPv4 Properties: In the Networking tab, select Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) and click Properties.
- Manually Configure IP Address: Select Use the following IP address and enter the obtained IP address, subnet mask, default gateway, and preferred DNS server information.
- Confirm and Apply: Click OK to apply the changes and close all windows.
4. Troubleshoot IP Address Conflicts:
- Release and Renew IP Address: Open a Command Prompt (search for cmd in the Start Menu), type ipconfig /release and press Enter. Then, type ipconfig /renew and press Enter to attempt a new IP address assignment.
- Check for Conflicting IPs: Use the ipconfig /all command in Command Prompt to list all network adapters and their assigned IP addresses. Check for any conflicting addresses.
- Reserve IP Address: If a specific device requires a static IP address, consider reserving it on your router’s configuration page. This prevents accidental conflicts with other devices.
5. Investigate Firewall and Security Software:
- Temporarily Disable Firewall: Temporarily disable the Windows Firewall or any third-party security software to rule out interference.
- Check Firewall Rules: Review firewall rules to ensure they do not block specific network traffic related to the manual IP configuration.
6. Verify Network Adapter Driver:
- Update Network Adapter Driver: Ensure the network adapter driver is up-to-date. Go to Device Manager, right-click the network adapter, select Update driver, and follow the on-screen instructions.
- Reinstall Network Adapter Driver: If updating the driver doesn’t resolve the issue, try reinstalling the driver by right-clicking the network adapter, selecting Uninstall device, and then restarting your computer. Windows will automatically reinstall the driver.
7. Check DNS Server Settings:
- Verify DNS Server: Confirm the DNS server address is correct and accessible. You can use a DNS server test website to verify connectivity.
- Flush DNS Cache: Clear the DNS cache by typing ipconfig /flushdns in Command Prompt.
- Use Public DNS Servers: If the DNS server is not functioning correctly, consider using a public DNS server like Google Public DNS (8.8.8.8 and 8.8.4.4) or Cloudflare DNS (1.1.1.1 and 1.0.0.1).
8. Contact Network Administrator or ISP:
- Network Administrator: If you are part of a corporate network, contact your network administrator for assistance with manual IP configuration.
- Internet Service Provider (ISP): If you are experiencing network connectivity issues, contact your ISP for support.
FAQs Regarding Manual IP Configuration
Q: Why can’t I set a manual IP address in Windows 10?
A: Several factors can hinder manual IP configuration, including incorrect IP address information, conflicts with other devices, firewall restrictions, network adapter issues, and DNS server problems.
Q: What are the risks of manual IP configuration?
A: If not executed correctly, manual IP configuration can lead to network connectivity issues, including IP address conflicts, inability to access the internet, and communication problems within the network.
Q: Can I use any IP address for manual configuration?
A: No. The IP address must be within the valid range for your network and must not conflict with other devices on the network.
Q: What should I do if I accidentally set a wrong IP address?
A: If you have accidentally configured an incorrect IP address, you can revert to the automatic IP assignment by selecting Obtain an IP address automatically in the Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) properties.
Q: Why is manual IP configuration still relevant in this age of DHCP?
A: Manual IP configuration remains relevant for specific network configurations, troubleshooting purposes, and situations where static IP addresses are required.
Tips for Successful Manual IP Configuration
- Document Network Information: Carefully note down the IP address range, subnet mask, default gateway, and DNS server information before proceeding with manual configuration.
- Use Network Tools: Utilize network tools like ipconfig and ping in Command Prompt to verify IP address assignment, network connectivity, and troubleshoot potential issues.
- Consult Network Documentation: Refer to your router’s manual or network documentation for guidance on IP address ranges and network configuration.
- Test Connectivity: After configuring the manual IP address, test network connectivity by browsing the internet, accessing network resources, or pinging other devices on the network.
Conclusion
Successfully configuring a manual IP address in Windows 10 requires careful attention to detail and a systematic troubleshooting approach. By understanding the common challenges and following the outlined steps, users can overcome these obstacles and achieve reliable network connectivity. Remember to verify network connection, obtain correct IP address information, troubleshoot conflicts, investigate firewall restrictions, and check network adapter drivers and DNS server settings. With a combination of knowledge, patience, and troubleshooting techniques, users can confidently manage their network configurations and ensure seamless network access.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Troubleshooting Network Connectivity: When Manual IP Configuration Fails in Windows 10. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!