The Trade-offs of Exiting S Mode in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Analysis
Related Articles: The Trade-offs of Exiting S Mode in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Analysis
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Trade-offs of Exiting S Mode in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Analysis. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Trade-offs of Exiting S Mode in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Analysis
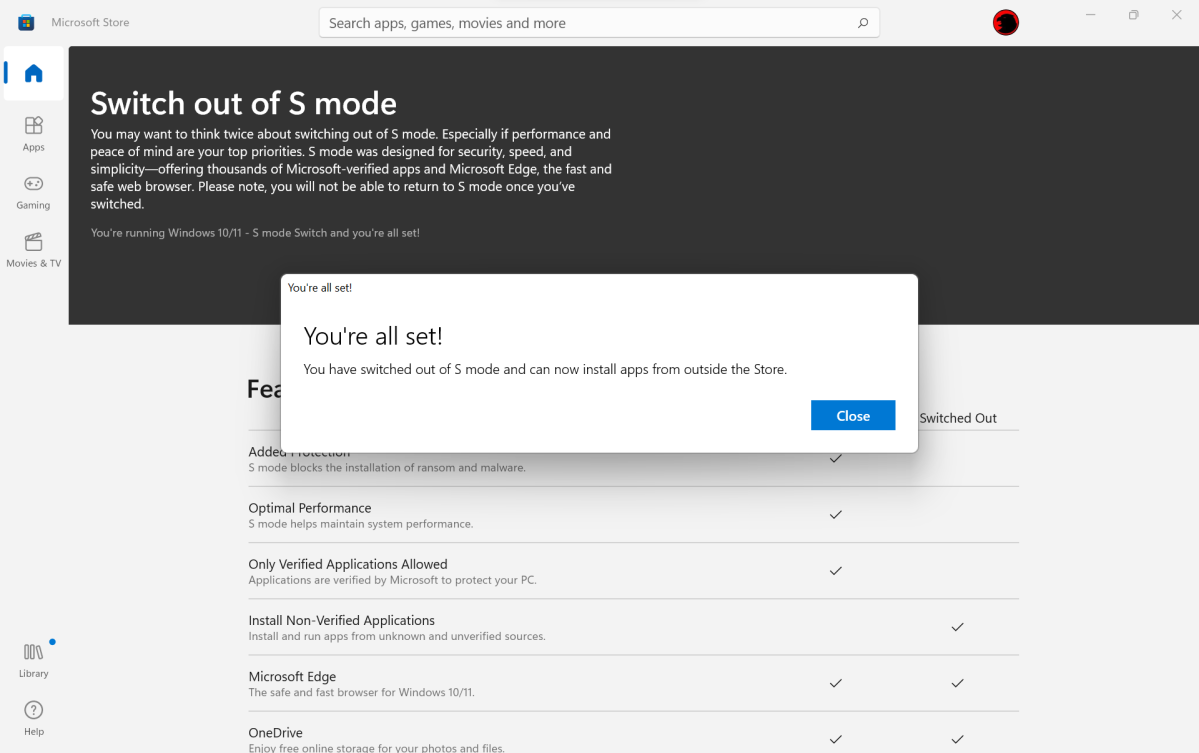
Windows 11 S Mode, a streamlined and secure operating system designed for simplicity and safety, presents users with a unique set of advantages. However, its limitations in app compatibility and customization may prompt some users to consider switching out of S Mode. This transition, while seemingly straightforward, comes with its own set of drawbacks that require careful consideration. This article will delve into the potential downsides of exiting S Mode, providing a comprehensive analysis of the trade-offs involved.
Security and Stability Considerations:
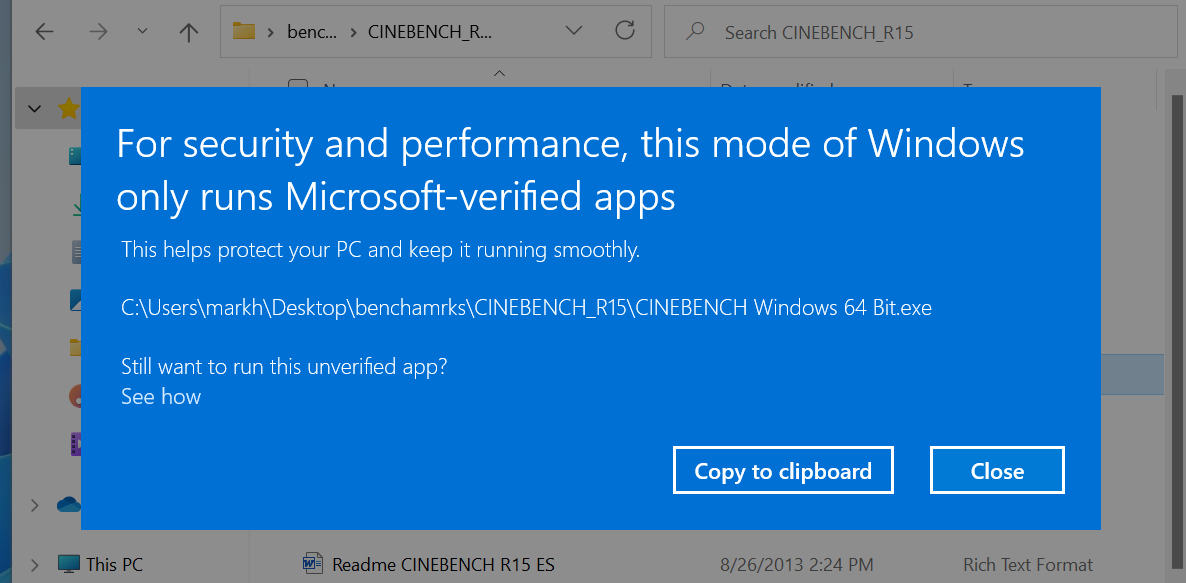
One of the primary benefits of S Mode is its inherent security. By restricting app installations to the Microsoft Store, S Mode significantly reduces the risk of malware infections and other security threats. Exiting S Mode opens the door to installing apps from external sources, potentially exposing the system to vulnerabilities. While Windows 11 incorporates robust security features, the potential for security breaches increases when users have the freedom to install apps from untrusted sources.
Furthermore, S Mode’s restricted environment fosters a more stable system. By limiting app installation to vetted applications from the Microsoft Store, the chances of encountering compatibility issues or software conflicts are significantly reduced. Exiting S Mode exposes the system to a broader range of apps, potentially increasing the likelihood of encountering compatibility problems, performance issues, or even system crashes.
App Compatibility and Customization Limitations:
S Mode’s primary restriction lies in its app compatibility. Users are limited to apps available in the Microsoft Store, which may not include all the desired applications. While the Microsoft Store offers a wide range of software, it might lack certain specialized or niche applications that are crucial for specific tasks or workflows. Exiting S Mode allows users to install apps from external sources, expanding their app options. However, this freedom comes at the cost of potentially encountering compatibility issues or encountering apps that are not optimized for Windows 11.
Additionally, S Mode offers a simplified and streamlined user interface, prioritizing ease of use and security. This limited customization may not be ideal for users who prefer a more personalized experience or require advanced system configurations. Exiting S Mode grants users greater control over system settings and allows for customization of the user interface. However, this increased flexibility can also lead to complexity and potential configuration errors, requiring a more technical understanding of the operating system.
Performance and Resource Management:
S Mode is designed to be lightweight and efficient, optimizing system resources for a smooth user experience. By limiting app installations to the Microsoft Store, S Mode minimizes the potential for resource-intensive or poorly optimized apps to impact system performance. Exiting S Mode exposes the system to a wider range of apps, potentially including those that are resource-hungry or poorly optimized, leading to slower performance or increased resource consumption.
While Windows 11 is designed to manage resources efficiently, the potential for resource conflicts or inefficient resource utilization increases when users install apps from external sources. This can impact overall system performance and potentially lead to slower boot times, longer loading times, or reduced battery life.
Potential for User Error:
S Mode’s restricted environment simplifies the user experience, minimizing the potential for user errors or accidental system modifications. Exiting S Mode grants users greater control over system settings, increasing the potential for user errors or misconfigurations. This can lead to unexpected system behavior, performance issues, or even data loss.
While Windows 11 offers a user-friendly interface, navigating advanced system settings or installing software from external sources requires a certain level of technical knowledge. Users unfamiliar with system configurations or software installation processes may encounter difficulties or make mistakes that could compromise system stability or data integrity.
The Need for Careful Consideration:
While exiting S Mode offers increased flexibility and customization, it comes with a set of drawbacks that require careful consideration. Before making the switch, users should weigh the potential benefits against the potential downsides and ensure that they understand the implications of exiting S Mode.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Q: What are the main reasons to stay in S Mode?
A: S Mode offers a streamlined and secure environment, prioritizing simplicity, stability, and security. Its limitations in app compatibility and customization are offset by its inherent security features and a more stable user experience.
Q: What are the main reasons to exit S Mode?
A: Exiting S Mode provides users with greater flexibility and app compatibility, allowing for the installation of apps from external sources. This opens up a wider range of software options, but it also increases the risk of encountering compatibility issues, security vulnerabilities, and performance problems.
Q: Can I switch back to S Mode after exiting?
A: Yes, users can switch back to S Mode after exiting, but they will need to reset their device and lose all data and installed applications.
Q: Is it safe to exit S Mode?
A: Exiting S Mode is safe if users are cautious about the software they install and take appropriate security measures. However, it increases the potential for security vulnerabilities and performance issues.
Q: What are the best practices for managing security after exiting S Mode?
A: Users should install a robust antivirus program, keep their operating system and software updated, be cautious about opening email attachments or clicking on suspicious links, and avoid downloading software from untrusted sources.
Tips for Exiting S Mode:
- Back up your data: Before exiting S Mode, ensure that all important data is backed up to prevent data loss during the process.
- Research and choose apps carefully: Before installing apps from external sources, research the app’s reputation, security, and compatibility with Windows 11.
- Use a trusted antivirus program: Install a reputable antivirus program to protect your device from malware and other security threats.
- Keep your system updated: Regularly update your operating system and software to patch vulnerabilities and improve security.
Conclusion:
Exiting S Mode in Windows 11 offers users greater flexibility and app compatibility but comes with several trade-offs. The decision to exit S Mode should be carefully considered, weighing the potential benefits against the potential downsides. Users should be aware of the increased security risks, potential performance issues, and the need for greater vigilance in managing system settings and software installations. By carefully considering the implications of exiting S Mode and adopting best practices for security and system management, users can maximize the benefits of a more flexible operating system while mitigating the associated risks.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Trade-offs of Exiting S Mode in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Analysis. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!