The Enigma of Windows 10 Updates: Unraveling the Causes and Solutions
Related Articles: The Enigma of Windows 10 Updates: Unraveling the Causes and Solutions
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Enigma of Windows 10 Updates: Unraveling the Causes and Solutions. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Enigma of Windows 10 Updates: Unraveling the Causes and Solutions

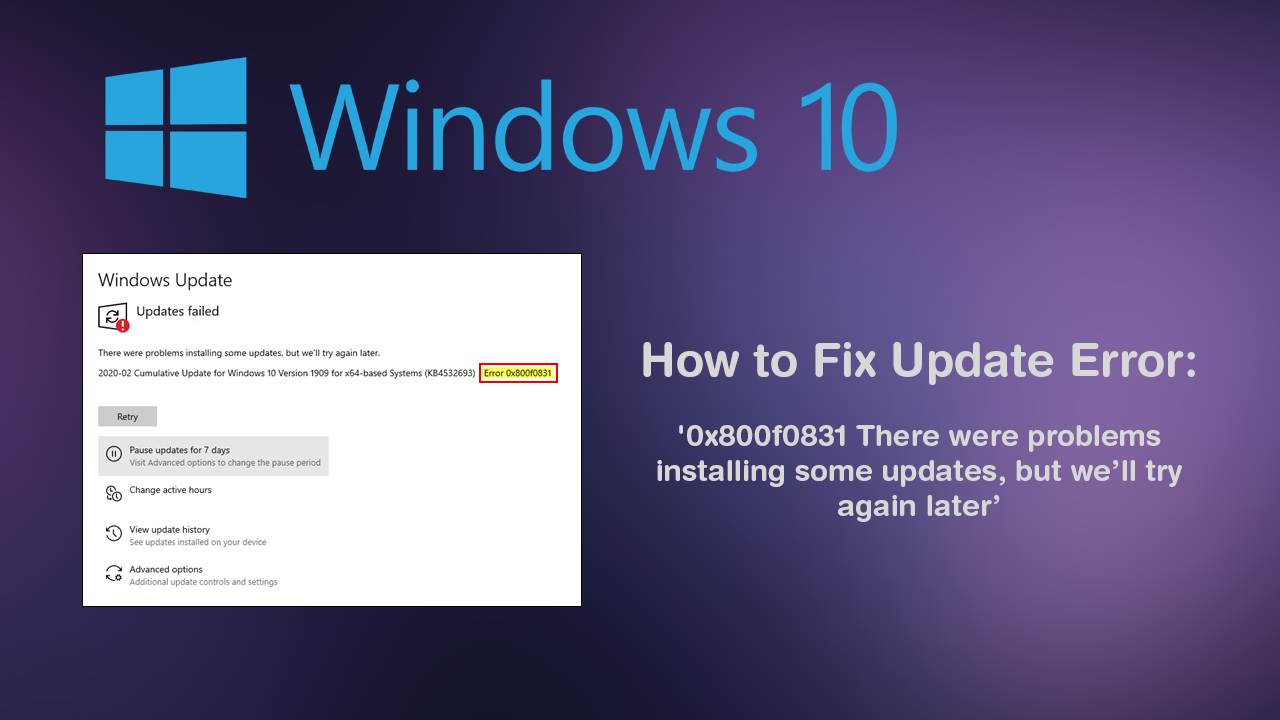
Windows 10, Microsoft’s flagship operating system, is designed to be a dynamic and evolving platform. Regular updates are crucial for enhancing security, improving performance, and introducing new features. However, users often encounter roadblocks when attempting to update their systems. These roadblocks can range from minor inconveniences to major frustrations, preventing users from accessing the latest benefits and leaving their systems vulnerable to potential threats.
This article delves into the common causes behind update failures, outlining a comprehensive guide to troubleshooting and resolving these issues.
Understanding the Update Process
Before exploring the reasons behind update failures, it’s essential to understand the process itself. Windows 10 updates are delivered in two primary ways:
- Windows Update: This is the standard method for receiving updates. It automatically downloads and installs updates in the background, ensuring your system stays up-to-date.
- Manual Updates: Users can also choose to manually initiate updates through the Windows Update settings. This allows for more control over the update process, particularly when dealing with larger updates or if specific requirements need to be addressed.
Common Causes of Update Failures
The inability to update Windows 10 can stem from various factors, each requiring a unique approach to resolution. These factors can be broadly categorized as follows:
1. Insufficient Disk Space:
Windows updates often require a significant amount of disk space for downloading and installing update files. Insufficient space can lead to update failures, prompting error messages or halting the update process altogether.
2. Network Connectivity Issues:
A stable internet connection is crucial for downloading and installing updates. Intermittent or unstable connections can lead to download failures, incomplete installations, or even corrupted update files.
3. Outdated Drivers:
Outdated or incompatible drivers can conflict with the update process, preventing successful installation. This is particularly common with graphics drivers, network adapters, and other hardware components.
4. Corrupted System Files:
Corrupted system files can interfere with the update process, leading to errors and preventing successful installation. These corruptions can arise from various factors, including malware infections, hardware failures, or software conflicts.
5. Antivirus Software Interference:
Antivirus software, while crucial for system security, can sometimes interfere with the update process, leading to errors or blocking updates entirely. This interference can occur due to aggressive scanning settings or conflicts with specific update files.
6. Incompatible Hardware:
Outdated or incompatible hardware can pose challenges for update installations. This can include older processors, RAM, or storage devices that may not meet the minimum requirements for the latest Windows updates.
7. Pending Updates or Restarts:
If there are pending updates or restarts required for previous updates, the system might not be ready for a new update. This can lead to update failures or delays.
8. Group Policy Restrictions:
In corporate or managed environments, group policies may restrict update installations. These restrictions are often implemented to control update schedules or prevent unauthorized software installations.
9. Software Conflicts:
Certain software applications, particularly those that directly interact with the operating system, can conflict with updates, causing installation failures or unexpected behavior.
10. Insufficient Permissions:
Users might lack the necessary permissions to install updates, particularly in corporate or shared environments where administrative privileges are required for certain actions.
Troubleshooting and Resolving Update Failures
Addressing update failures requires a systematic approach, carefully analyzing the potential causes and implementing appropriate solutions. The following steps provide a comprehensive guide to troubleshooting and resolving common update issues:
1. Check Disk Space:
Ensure sufficient disk space is available for the update by freeing up space through file cleanup, removing unnecessary programs, or temporarily moving files to external storage.
2. Verify Network Connectivity:
Confirm a stable and reliable internet connection by running network diagnostics or testing the connection speed. Consider restarting your router or modem if connectivity issues persist.
3. Update Drivers:
Update all drivers, particularly for graphics, network adapters, and other hardware components, using the manufacturer’s website or Windows Update.
4. Run System File Checker:
Use the System File Checker (SFC) tool to scan and repair any corrupted system files. This can be accessed through the Command Prompt by running the command "sfc /scannow."
5. Temporarily Disable Antivirus Software:
Temporarily disable antivirus software to see if it’s interfering with the update process. If disabling the antivirus resolves the issue, consider adjusting the antivirus settings or using a different antivirus solution.
6. Check Hardware Compatibility:
Ensure that your hardware meets the minimum requirements for the latest Windows updates. Check the system specifications on the Microsoft website or consult your computer manufacturer.
7. Complete Pending Updates:
Install any pending updates or complete any necessary restarts for previous updates before attempting to install the latest update.
8. Review Group Policies:
If you are in a corporate or managed environment, contact your IT administrator to check for any group policies restricting update installations.
9. Troubleshoot Software Conflicts:
Identify and temporarily disable any software applications that might be conflicting with the update process. This can involve checking application logs or using a process monitor to identify potential conflicts.
10. Verify User Permissions:
Ensure you have the necessary administrative permissions to install updates. If you are in a corporate or shared environment, consult your IT administrator for assistance.
FAQs on Windows 10 Updates
Q: What are the benefits of updating Windows 10?
A: Updates provide numerous benefits, including enhanced security features to protect against malware and cyber threats, improved performance and stability, new features and functionalities, bug fixes and system optimizations, and compatibility with the latest hardware and software.
Q: How often should I update Windows 10?
A: Windows 10 updates are released regularly, with major feature updates typically released twice a year. It’s recommended to install updates as soon as they become available to ensure your system remains secure and up-to-date.
Q: Can I choose to delay updates?
A: Yes, you can choose to defer updates for a specific period. However, it’s important to note that delaying updates can leave your system vulnerable to security risks.
Q: What if I encounter an error during the update process?
A: If you encounter an error, review the error message and try the troubleshooting steps outlined earlier. You can also consult Microsoft’s support website for specific error codes and solutions.
Q: Can I roll back to a previous version of Windows 10?
A: Yes, you can roll back to a previous version of Windows 10 within a limited timeframe after an update. However, this option is only available for a certain period and might not be possible for all updates.
Q: What are the risks of not updating Windows 10?
A: Not updating Windows 10 can expose your system to security vulnerabilities, making it susceptible to malware infections and cyberattacks. It can also lead to performance issues, compatibility problems with newer software, and missing out on essential bug fixes and security patches.
Tips for Successful Windows 10 Updates
1. Schedule Updates:
Use the Windows Update settings to schedule updates during off-peak hours or when you are not actively using your computer.
2. Backup Your Data:
Before installing any major update, create a backup of your important data to avoid data loss in case of unexpected issues.
3. Check System Requirements:
Ensure your hardware meets the minimum requirements for the latest Windows updates before attempting installation.
4. Monitor Update Progress:
Keep an eye on the update progress to identify any potential issues or errors that might occur during the process.
5. Restart Your Computer:
After installing updates, restart your computer to ensure the changes are applied correctly and the system is functioning properly.
Conclusion
Windows 10 updates are crucial for maintaining a secure, stable, and up-to-date computing environment. While update failures can be frustrating, understanding the potential causes and implementing effective troubleshooting steps can help resolve these issues and ensure a seamless update experience. By following the guidelines outlined in this article, users can proactively address update challenges, keep their systems protected, and enjoy the latest features and benefits offered by Windows 10.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Enigma of Windows 10 Updates: Unraveling the Causes and Solutions. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!