The Enigma of Static IP Configuration: Troubleshooting Network Connectivity Issues
Related Articles: The Enigma of Static IP Configuration: Troubleshooting Network Connectivity Issues
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Enigma of Static IP Configuration: Troubleshooting Network Connectivity Issues. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Enigma of Static IP Configuration: Troubleshooting Network Connectivity Issues

The ability to configure a device’s network settings manually, particularly assigning a static IP address, is a fundamental aspect of network administration. This manual configuration allows for greater control over network traffic, ensuring consistent and predictable communication between devices. However, situations where users are unable to save their desired static IP settings can lead to frustrating connectivity issues and hinder network operations. This article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of the common causes behind this issue, offering practical troubleshooting steps and valuable insights to resolve the problem effectively.
Understanding Static IP Configuration:
Before delving into the complexities of troubleshooting, it is crucial to understand the concept of static IP addressing. In a typical network, devices are assigned IP addresses dynamically through a DHCP server. This server automatically allocates an IP address to each device upon connection, ensuring a smooth and automated network setup. However, in certain scenarios, static IP addresses are preferred.
Benefits of Static IP Configuration:
- Consistent Device Identification: Static IP addresses provide a permanent and unchanging identifier for devices, allowing for predictable communication and easy identification within the network.
- Enhanced Security: Static IP configurations can enhance network security by restricting access to specific devices based on their known IP addresses, preventing unauthorized access.
- Dedicated Network Services: Static IP addresses are essential for hosting dedicated network services like web servers, email servers, or databases. These services require a consistent IP address for external access and seamless operation.
- Troubleshooting Network Issues: When troubleshooting network connectivity problems, static IP addresses can simplify the process by eliminating the variability introduced by dynamically assigned addresses.
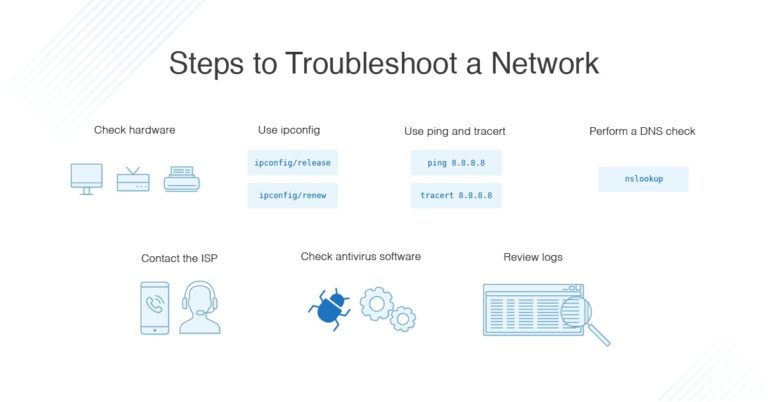
Common Causes for Static IP Configuration Issues:
When encountering difficulties saving static IP settings, the problem often lies in one of the following areas:
1. Network Configuration Conflicts:
- IP Address Duplication: A static IP address can only be assigned to one device on a network. If another device is already using the desired IP address, the configuration will fail.
- Subnet Mask Mismatch: The subnet mask defines the network range, and if it does not match the subnet mask used by the network, the device will be unable to communicate with other devices.
- Default Gateway Conflict: The default gateway is the device that acts as a bridge between the local network and the external network. If the configured default gateway does not match the actual gateway, connectivity will be impaired.
- DNS Server Misconfiguration: The DNS server translates domain names into IP addresses. If the DNS server configuration is incorrect, the device may be unable to resolve domain names and access websites.
2. Operating System or Device Limitations:
- Operating System Settings: Some operating systems may have limitations on the range of IP addresses that can be manually configured.
- Device Firmware: Older or outdated device firmware might not support certain static IP configurations.
- Network Adapter Restrictions: Certain network adapters might have specific restrictions on the IP address range they can utilize.
3. Network Security Measures:
- Firewall Restrictions: Network firewalls might block attempts to configure static IP addresses, especially if they are considered unauthorized or potentially malicious.
- Access Control Lists (ACLs): ACLs can restrict network access based on IP addresses. If the configuration conflicts with existing ACLs, the static IP settings may not be saved.
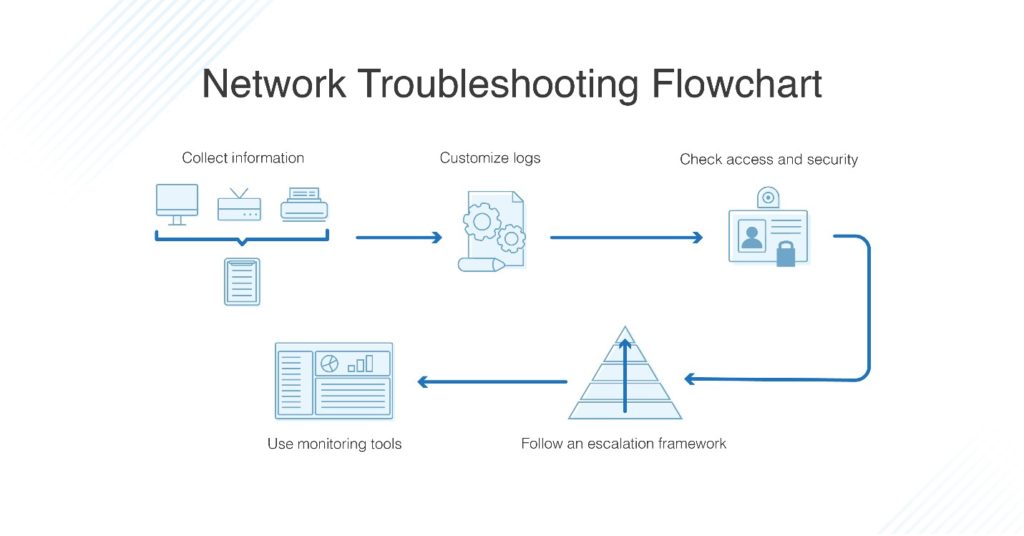
Troubleshooting Static IP Configuration Issues:
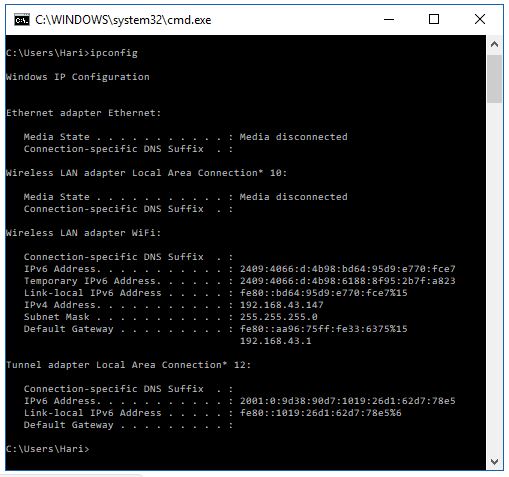
1. Verify Network Connectivity:
- Ensure the device is physically connected to the network and the network cable is functioning properly.
- Verify that the network connection is active by checking the network connection icon or running a simple ping test to a known IP address.
2. Check for IP Address Conflicts:
- Use a network scanning tool to identify devices on the network and their assigned IP addresses.
- Verify that the desired static IP address is not already in use by another device.
- If necessary, release the IP address assigned to the other device or choose a different static IP address.
3. Confirm Network Settings:
- Access the device’s network settings and verify the following:
- The subnet mask matches the network’s subnet mask.
- The default gateway is correctly configured.
- The DNS server addresses are accurate.
- If necessary, adjust these settings to match the network configuration.
4. Troubleshoot Operating System or Device Limitations:
- Consult the device’s documentation or manufacturer’s website for information on supported IP address ranges and configuration options.
- Consider updating the device’s firmware to the latest version, which may address compatibility issues.
5. Review Network Security Settings:
- Check the firewall settings to ensure that they do not block static IP configuration attempts.
- Review any access control lists (ACLs) that might be affecting network access.
- If necessary, adjust these security settings to allow for the desired static IP configuration.
6. Seek Technical Support:
- If the problem persists, contact the device manufacturer’s technical support team or a network administrator for assistance.
- Provide detailed information about the device, operating system, network configuration, and any error messages encountered.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
Q: Why can’t I save my static IP settings on my Windows computer?
A: This issue can arise due to various factors, including IP address conflicts, subnet mask mismatches, default gateway errors, or firewall restrictions. Verify the network settings, check for IP address conflicts, and ensure that the firewall is not blocking the configuration attempt.
Q: How do I know if my static IP address is causing connectivity issues?
A: If you are experiencing problems connecting to the internet or accessing network resources after configuring a static IP address, the static IP configuration might be the culprit. Try temporarily reverting to a dynamic IP address to see if the problem resolves.
Q: Can I use a static IP address on a wireless network?
A: Yes, you can configure static IP addresses on a wireless network, but it requires additional configuration steps. You need to ensure that the wireless router supports static IP allocation and configure the device accordingly.
Q: What are the security implications of using a static IP address?
A: While static IP addresses can enhance security by restricting access based on known IP addresses, they can also make devices more vulnerable to attacks if not properly secured. Ensure that the device has strong security measures in place, such as a firewall and updated security software.
Tips for Successful Static IP Configuration:
- Plan Ahead: Before configuring a static IP address, carefully research the network configuration and ensure that the chosen IP address is available and does not conflict with other devices.
- Document Configuration: Record the static IP address, subnet mask, default gateway, and DNS server addresses for future reference.
- Test Thoroughly: After configuring a static IP address, test network connectivity to ensure that the device can communicate with other devices and access online resources.
- Seek Professional Assistance: If you are unsure about configuring static IP addresses or encounter persistent issues, consult a network administrator or technical support professional.
Conclusion:
Configuring a static IP address is a powerful tool for managing network traffic and ensuring consistent device identification. However, it is crucial to understand the underlying concepts and potential challenges associated with this process. By following the troubleshooting steps outlined in this article, users can effectively diagnose and resolve issues related to static IP configuration, ultimately ensuring a stable and efficient network environment.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Enigma of Static IP Configuration: Troubleshooting Network Connectivity Issues. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!