The Enigma of Manual IP Address Configuration in Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: The Enigma of Manual IP Address Configuration in Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Enigma of Manual IP Address Configuration in Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Enigma of Manual IP Address Configuration in Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide

The ability to manually configure an IP address is a fundamental aspect of network management, offering granular control over network behavior and troubleshooting capabilities. However, Windows 10 users occasionally encounter difficulties in setting a static IP address, leading to network connectivity issues. This article delves into the intricacies of this problem, providing a comprehensive guide to identify, diagnose, and resolve the inability to manually configure an IP address in Windows 10.
Understanding the Fundamentals
Before exploring the causes and solutions, it is crucial to understand the basic concepts of IP addressing. An IP address serves as a unique identifier for a device on a network, allowing communication between different computers and servers. In a typical home network, a router assigns IP addresses automatically using the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP). However, in certain scenarios, manual configuration is preferred, offering the following advantages:
- Static IP Addresses: Ensuring consistent connectivity for specific devices, particularly servers or network devices requiring fixed addresses for their operation.
- Network Segmentation: Creating isolated network segments with specific IP address ranges for enhanced security and network management.
- Troubleshooting: Identifying network conflicts and resolving connectivity issues by manually assigning IP addresses to individual devices.
The Root Causes of Manual IP Configuration Problems
When encountering difficulties in manually setting an IP address in Windows 10, the underlying cause can be multifaceted. These include:
1. Network Adapter Configuration:
- Conflicting Settings: Existing network adapter settings, such as a previously assigned static IP address or DHCP configuration, can interfere with manual configuration attempts.
- Incorrect Subnet Mask: The subnet mask defines the network portion of the IP address. An incorrect subnet mask can prevent communication within the network.
- Gateway Address: The gateway address, typically the router’s IP address, is essential for connecting to the internet. A wrong gateway address can lead to connectivity issues.
- DNS Server Address: Domain Name System (DNS) servers translate domain names into IP addresses. Incorrect DNS server addresses can hinder internet access.
2. Network Conflicts:
- Duplicate IP Addresses: If another device on the network is already using the IP address you are trying to assign, a conflict arises, preventing successful configuration.
- Address Reservation: DHCP servers can reserve specific IP addresses for particular devices, preventing manual configuration for those addresses.
3. Network Hardware Issues:
- Faulty Network Adapter: A malfunctioning network adapter can impede communication and hinder manual IP address configuration.
- Network Cable Problems: A damaged or improperly connected network cable can disrupt communication and prevent successful IP address assignment.
4. Software Issues:
- Firewall Settings: Strict firewall rules can block network traffic, interfering with IP address configuration.
- Antivirus Software: Certain antivirus software can interfere with network settings, potentially causing conflicts with manual IP address assignments.
5. Operating System Errors:
- Windows Registry Problems: Corrupted entries in the Windows Registry related to network settings can hinder manual IP address configuration.
- Driver Conflicts: Outdated or incompatible network adapter drivers can lead to network connectivity issues and prevent successful IP address configuration.
Troubleshooting Steps for Resolving Manual IP Address Configuration Issues
1. Verify Network Adapter Settings:
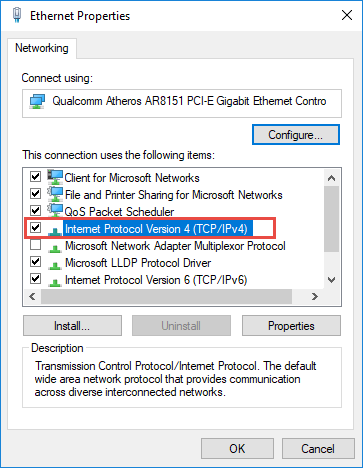
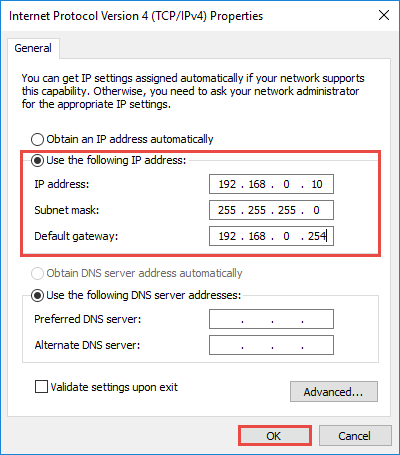
- Access Network Adapter Settings: Open the "Network and Sharing Center" by searching in the Windows search bar. Click on "Change adapter settings."
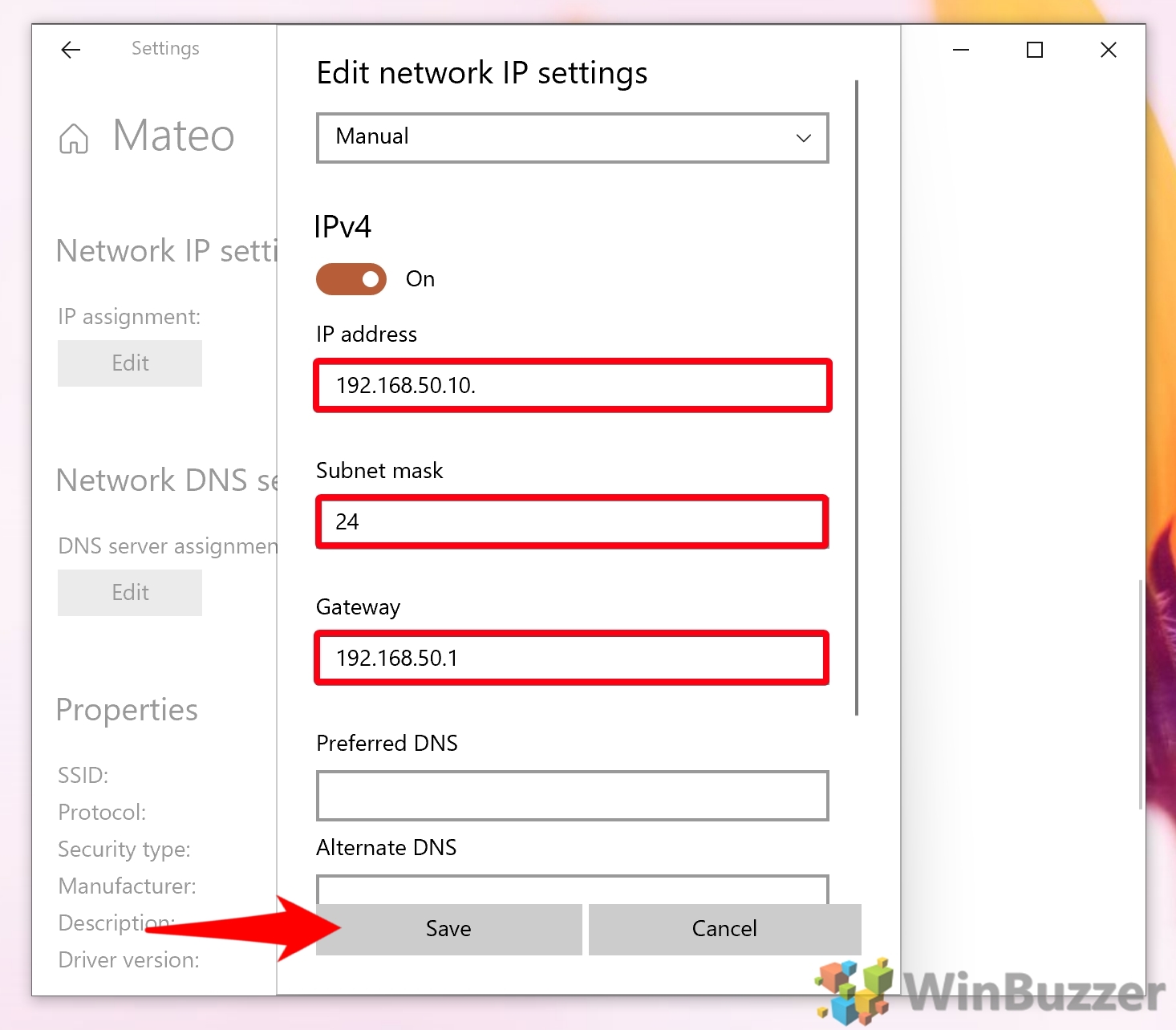
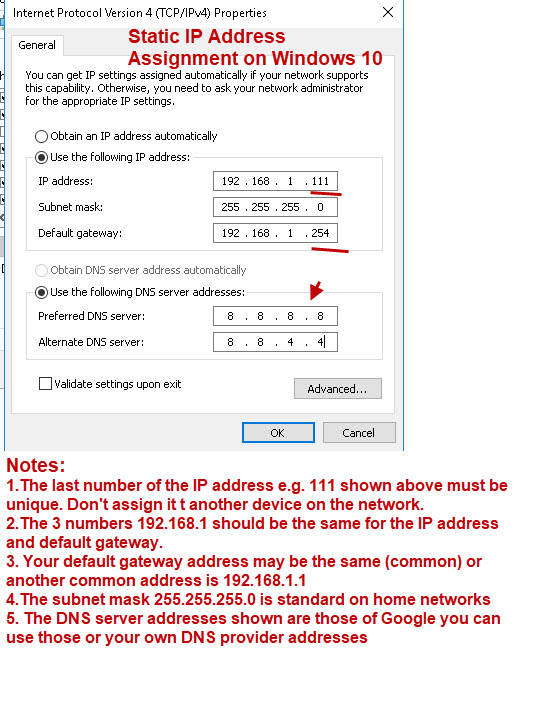
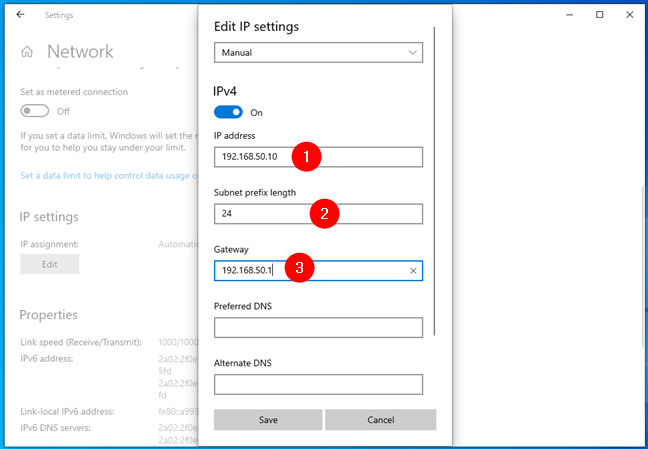
- Inspect Current Settings: Right-click on the active network adapter and select "Properties." Go to the "Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4)" and check the current IP address, subnet mask, default gateway, and DNS server addresses.
- Modify Settings: If the current settings are incorrect or conflicting, manually enter the desired IP address, subnet mask, default gateway, and DNS server addresses. Ensure the values are accurate and compatible with your network environment.
2. Check for Network Conflicts:
- Use Command Prompt: Open the command prompt as administrator. Type "ipconfig /all" to display all network adapter information.
- Identify Conflicting Addresses: Examine the output for any duplicate IP addresses or address reservations. If found, consult your network administrator or adjust settings accordingly.
3. Troubleshoot Network Hardware:
- Verify Cable Connections: Ensure the network cable is securely connected to both the computer and the router or modem.
- Test Network Adapter: Try connecting to a different network or using a different network cable to isolate the issue.
- Check Device Manager: Open the Device Manager by searching in the Windows search bar. Look for any error messages or yellow exclamation marks associated with the network adapter.
4. Review Software Settings:
- Firewall Settings: Temporarily disable the firewall to check if it is interfering with network traffic.
- Antivirus Software: Temporarily disable antivirus software to rule out any potential conflicts.
5. Address Operating System Errors:
- Run Network Troubleshooter: Open the "Network and Sharing Center" and select "Troubleshoot problems."
- Check for Driver Updates: Go to the Device Manager, right-click on the network adapter, and select "Update driver."
- System Restore: If the issue persists, consider performing a system restore to a previous point in time before the problem arose.
FAQs: A Comprehensive Guide to Addressing Common Concerns
1. Why can’t I set a static IP address in Windows 10?
The inability to set a static IP address in Windows 10 can be attributed to various factors, including conflicting network settings, network conflicts, hardware issues, software interference, and operating system errors.
2. What is the best way to manually configure an IP address in Windows 10?
To manually configure an IP address in Windows 10, access the network adapter settings, select "Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4)," and enter the desired IP address, subnet mask, default gateway, and DNS server addresses. Ensure the values are accurate and compatible with your network environment.
3. How do I know if my IP address is static or dynamic?
You can determine whether your IP address is static or dynamic by checking the network adapter settings. If the IP address field is empty or displays "Obtain an IP address automatically," your address is dynamic. If the field displays a specific IP address, your address is static.
4. Can I manually set an IP address without a router?
No, you cannot manually set an IP address without a router. A router acts as a central point for assigning IP addresses and managing network traffic.
5. What happens if I set a static IP address that is already in use?
Setting a static IP address that is already in use will result in a network conflict. This can lead to connectivity issues for both devices using the same IP address.
Tips for Preventing Manual IP Configuration Problems
- Consult Network Administrator: If you are unsure about the correct IP address configuration, consult your network administrator for assistance.
- Avoid Using Reserved IP Addresses: Do not manually assign IP addresses that are already reserved by DHCP servers.
- Use a Network Scanner: Employ network scanning tools to identify any potential IP address conflicts before manually configuring an IP address.
- Keep Drivers Updated: Regularly update your network adapter drivers to ensure compatibility and stability.
- Backup Network Settings: Before making any significant changes to network settings, create a backup of your current configuration to revert to it if necessary.
Conclusion: Navigating the Path to Network Connectivity
The inability to manually configure an IP address in Windows 10 can be a frustrating experience, disrupting network connectivity and hindering productivity. By understanding the underlying causes, following the troubleshooting steps, and applying the provided tips, users can effectively diagnose and resolve this issue, restoring their network to optimal performance. Remember, meticulous attention to detail, thorough analysis of network settings, and a systematic approach to troubleshooting are key to ensuring successful manual IP address configuration in Windows 10.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Enigma of Manual IP Address Configuration in Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!