The "Command Q" Myth: Understanding Keyboard Shortcuts in Windows
Related Articles: The "Command Q" Myth: Understanding Keyboard Shortcuts in Windows
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The "Command Q" Myth: Understanding Keyboard Shortcuts in Windows. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The "Command Q" Myth: Understanding Keyboard Shortcuts in Windows

The phrase "Command Q" is deeply ingrained in the lexicon of Mac users, signifying a swift and universal method for exiting applications. While intuitive and efficient on Apple’s operating system, this keyboard shortcut does not exist in Windows. This misconception often arises from the cross-platform nature of software and the familiarity users develop with specific commands.
However, Windows utilizes its own set of keyboard shortcuts, offering a diverse range of options for navigating and interacting with the operating system. Instead of "Command Q," Windows relies on a combination of the "Alt" key and the letter "F4," which serves as a universal shortcut for closing applications, documents, and even the entire operating system.
Understanding Keyboard Shortcuts in Windows:
Keyboard shortcuts are a fundamental aspect of efficient computing in Windows. They streamline tasks, enhance productivity, and offer a more intuitive interaction with the operating system. Windows employs a comprehensive system of shortcuts, utilizing combinations of keys like "Alt," "Ctrl," and "Shift" alongside various letters and function keys.
Essential Keyboard Shortcuts for Windows:
- Closing Applications: Pressing "Alt" + "F4" closes the currently active application. This shortcut applies to most applications, providing a consistent method for exiting programs.
- Closing Documents: Within an application, "Ctrl" + "W" closes the currently open document or tab. This shortcut is particularly useful for managing multiple documents within a single application.
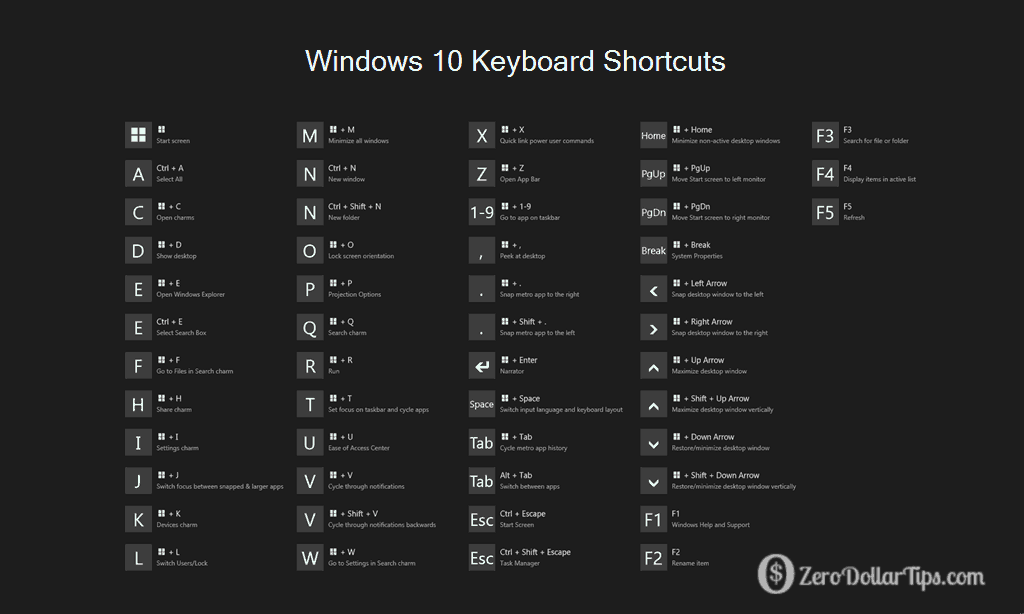
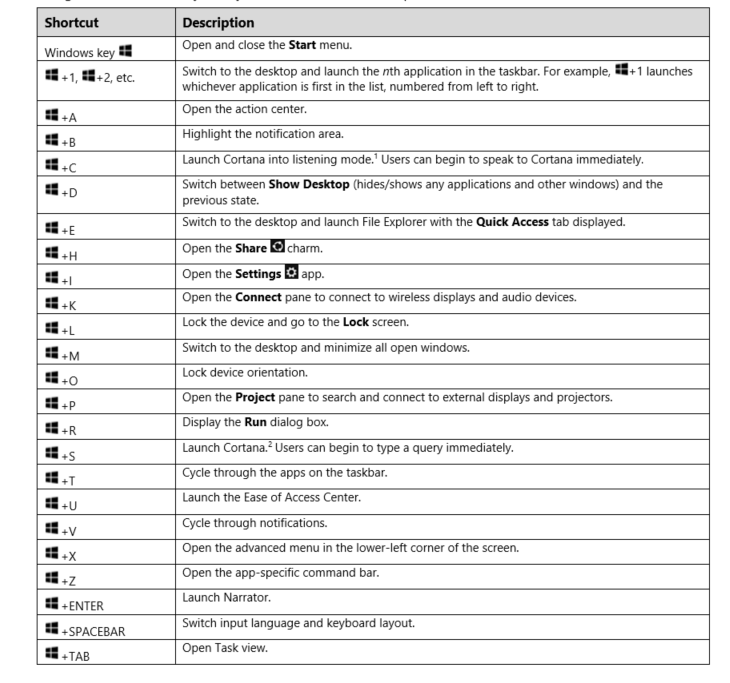
- Minimizing Windows: "Alt" + "Tab" cycles through open applications, allowing users to quickly switch between them. Pressing "Alt" + "Space" then "N" minimizes the active window.
- Shutting Down the System: "Alt" + "F4" can also be used to shut down the computer. Pressing "Alt" + "F4" and selecting "Shut Down" from the menu will initiate the shutdown process.
- Navigating Menus: The "Alt" key acts as a menu key, allowing users to navigate menus without using the mouse. Pressing "Alt" followed by the underlined letter in a menu option activates that menu.
Benefits of Using Keyboard Shortcuts:
- Increased Efficiency: Keyboard shortcuts eliminate the need for mouse movements, allowing users to perform tasks more quickly and efficiently.
- Enhanced Productivity: By streamlining workflows, keyboard shortcuts can significantly boost productivity, enabling users to complete tasks faster.
- Accessibility: Keyboard shortcuts provide a valuable alternative for users who may have difficulty using a mouse.
- Improved User Experience: Familiarizing oneself with keyboard shortcuts creates a more intuitive and seamless interaction with the operating system.
FAQs about Keyboard Shortcuts in Windows:
Q: Are there any other ways to close an application besides "Alt" + "F4"?
A: Yes, most applications also have a "Close" button in the top-right corner of the window. Additionally, right-clicking the application’s icon in the taskbar and selecting "Close window" will also close the application.
Q: Can I customize keyboard shortcuts in Windows?
A: Yes, Windows allows users to customize keyboard shortcuts for specific applications and functions. This can be done through the "Keyboard" settings in the "Control Panel."
Q: How can I find the keyboard shortcuts for a specific application?
A: Many applications provide documentation or help files that list available keyboard shortcuts. Additionally, the application’s menus often display keyboard shortcuts alongside menu items.
Tips for Using Keyboard Shortcuts Effectively:
- Start with Essential Shortcuts: Begin by learning the most common and essential shortcuts, like "Alt" + "F4" and "Ctrl" + "C" (copy) and "Ctrl" + "V" (paste).
- Practice Regularly: Consistent practice is key to mastering keyboard shortcuts. Try incorporating them into your daily workflow to make them second nature.
- Utilize Online Resources: Numerous websites and articles offer comprehensive lists of Windows keyboard shortcuts, providing a valuable resource for expanding your shortcut knowledge.
- Experiment and Discover: Don’t be afraid to experiment with different key combinations to discover new shortcuts that suit your workflow.
Conclusion:
While the "Command Q" shortcut is ingrained in the Mac experience, Windows operates with its own set of keyboard shortcuts. Understanding and utilizing these shortcuts is crucial for maximizing productivity and efficiency within the Windows environment. By mastering keyboard shortcuts, users can navigate the operating system effortlessly, streamline workflows, and enhance their overall computing experience.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The "Command Q" Myth: Understanding Keyboard Shortcuts in Windows. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!