The Art of Installing Windows 11 on Unsupported Devices: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: The Art of Installing Windows 11 on Unsupported Devices: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Art of Installing Windows 11 on Unsupported Devices: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Art of Installing Windows 11 on Unsupported Devices: A Comprehensive Guide
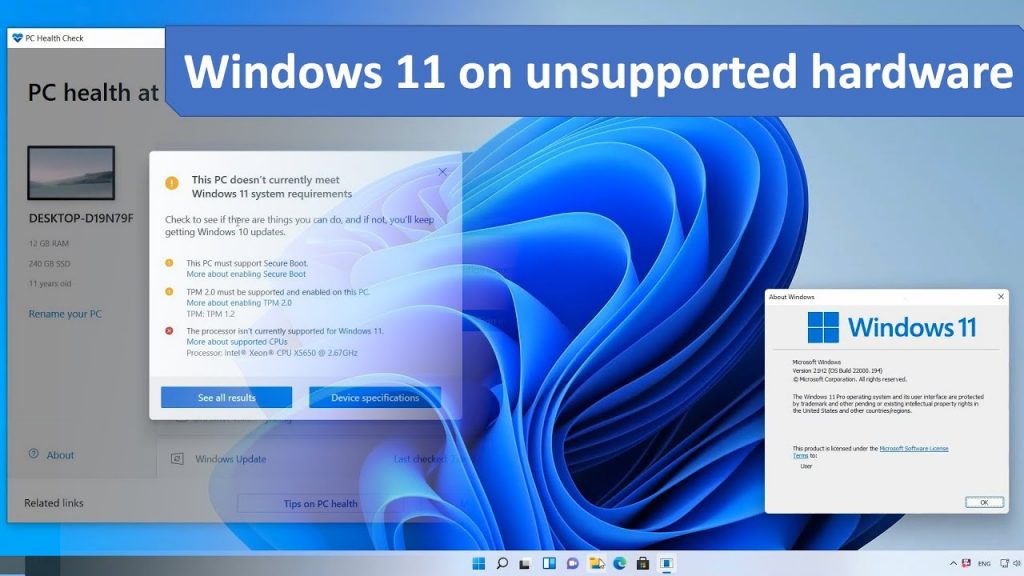
Windows 11, with its sleek interface and enhanced features, has captivated users worldwide. However, its stringent system requirements have left many with older hardware unable to upgrade. This has led to a surge in interest surrounding methods to install Windows 11 on devices that do not meet the official specifications. This guide delves into the intricacies of this process, outlining its risks, benefits, and the crucial steps involved.
Understanding the Limitations:
Microsoft has established specific minimum hardware requirements for Windows 11, aiming to ensure optimal performance and security. These requirements include:
- Processor: 1 gigahertz (GHz) or faster with two or more cores on a compatible 64-bit processor or System on a Chip (SoC).
- RAM: 4 gigabytes (GB) of RAM.
- Storage: 64 GB or larger storage device.
- System Firmware: UEFI, Secure Boot capable.
- TPM: Trusted Platform Module (TPM) version 2.0.
- Display: High Definition (720p) display, at least 9 inches diagonally, with 8 bits per color channel.
- Graphics Card: Compatible with DirectX 12 or later with WDDM 2.x driver.
- Internet Connectivity: For initial setup and some features.
Devices that fail to meet these requirements are deemed unsupported, meaning Microsoft does not guarantee their compatibility with Windows 11. This lack of official support carries significant implications for users:
- Potential for Instability: Unsupported hardware may encounter compatibility issues, leading to crashes, performance degradation, or even system instability.
- Security Vulnerabilities: Lack of official driver support could leave the system vulnerable to security threats.
- Lack of Updates: Microsoft may not release updates or security patches for unsupported devices, leaving them susceptible to vulnerabilities.
- Limited Technical Support: Users of unsupported devices may face difficulties accessing official technical support from Microsoft.
The Rationale Behind the Requirements:
Microsoft’s stringent system requirements are driven by a combination of factors:
- Performance Optimization: Windows 11 is designed to leverage the capabilities of modern hardware, ensuring a smooth and responsive user experience.
- Security Enhancements: TPM 2.0 and Secure Boot are crucial security features that protect against malware and unauthorized access.
- Feature Support: Certain features, like Windows Hello facial recognition and DirectX 12, rely on specific hardware components.
- Long-Term Support: By focusing on supported devices, Microsoft can provide consistent updates and security patches over an extended period.
The Allure of Installation Despite Restrictions:
Despite the inherent risks, many users choose to install Windows 11 on unsupported devices. This decision is often driven by:
- Desire for the Latest Features: Users may crave the new features and design enhancements offered by Windows 11, even if their hardware is older.
- Performance Improvements: Windows 11 can sometimes offer performance improvements even on older hardware, especially with optimized drivers.
- Extending Device Lifespan: Installing Windows 11 can provide a way to breathe new life into an aging device, extending its usability.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Upgrading to a new device can be expensive, making installing Windows 11 on existing hardware a more cost-effective option.
Navigating the Installation Process:
Installing Windows 11 on an unsupported device is not a straightforward process. It requires careful planning, a degree of technical expertise, and a willingness to take calculated risks. The following steps outline the general process:
- Research and Preparation: Thoroughly research the compatibility of your specific hardware with Windows 11. Explore forums and online resources for guidance and troubleshooting tips.
- Bypass the System Requirements: Several methods exist to bypass the system requirements check. These methods typically involve modifying system files or using specialized tools.
- Download and Create Installation Media: Download the Windows 11 ISO file from a reliable source and create a bootable USB drive or DVD.
- Boot from Installation Media: Boot your computer from the installation media and follow the on-screen instructions.
- Install Windows 11: Choose the "Custom" installation option and carefully select the drive where you want to install Windows 11.
- Post-Installation: After installation, install the latest drivers for your specific hardware. This is crucial for ensuring stability and optimal performance.
Potential Challenges and Considerations:
The process of installing Windows 11 on unsupported devices can be fraught with challenges:
- Driver Compatibility Issues: Finding compatible drivers for older hardware can be a significant challenge.
- System Stability: The absence of official support can lead to system instability and performance issues.
- Security Risks: Unsupported devices may be vulnerable to security threats due to the lack of official updates.
- Technical Expertise: The installation process requires a degree of technical expertise and familiarity with computer systems.
Weighing the Risks and Rewards:
The decision to install Windows 11 on an unsupported device is a personal one, demanding a careful assessment of the risks and potential rewards.
Risks:
- System Instability: The lack of official support can lead to system crashes, performance degradation, and other issues.
- Security Vulnerabilities: Unsupported devices may be vulnerable to malware and other security threats.
- Lack of Updates: Microsoft may not release updates or security patches for unsupported devices, leaving them vulnerable.
- Limited Technical Support: Users may face difficulties accessing official technical support from Microsoft.
Rewards:
- Access to New Features: Users can enjoy the latest features and design enhancements offered by Windows 11.
- Potential Performance Improvements: Windows 11 can sometimes offer performance improvements even on older hardware.
- Extending Device Lifespan: Installing Windows 11 can extend the usability of an aging device.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Installing Windows 11 on existing hardware can be more cost-effective than purchasing a new device.
FAQs
1. Is it safe to install Windows 11 on an unsupported device?
Installing Windows 11 on an unsupported device carries inherent risks, including potential system instability, security vulnerabilities, and lack of official support. It is crucial to weigh these risks carefully before proceeding.
2. What are the potential consequences of installing Windows 11 on an unsupported device?
Potential consequences include system crashes, performance degradation, security vulnerabilities, lack of updates, and limited technical support.
3. What are the benefits of installing Windows 11 on an unsupported device?
Benefits include access to new features, potential performance improvements, extending device lifespan, and cost-effectiveness.
4. How can I find compatible drivers for my unsupported device?
You can search for drivers on the manufacturer’s website, use driver update software, or explore online forums for community-sourced drivers.
5. Is it possible to revert back to a previous version of Windows after installing Windows 11?
Yes, you can usually revert back to a previous version of Windows using the "Reset this PC" option in the Settings app.
6. What are some alternative solutions for users with unsupported devices?
Consider upgrading to a new device that meets the system requirements for Windows 11, using a lightweight operating system like Linux, or continuing to use the existing operating system while exploring other options.
Tips
- Thorough Research: Before proceeding, thoroughly research the compatibility of your specific hardware with Windows 11.
- Backup Your Data: Create a full backup of your important data before installing Windows 11.
- Use Reliable Sources: Download the Windows 11 ISO file from a trusted source.
- Install Drivers Carefully: Install the latest drivers for your hardware after installation.
- Monitor System Performance: Keep a close eye on your system’s performance for any signs of instability.
Conclusion
Installing Windows 11 on an unsupported device is a complex decision that requires careful consideration. While it can offer access to new features and potentially enhance performance, it also carries inherent risks, including system instability, security vulnerabilities, and limited support. Users must carefully weigh these risks and rewards before making a decision. It is crucial to prioritize data security, system stability, and the overall user experience when undertaking such an endeavor.








Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Art of Installing Windows 11 on Unsupported Devices: A Comprehensive Guide. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!