Reverting to Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Reverting to Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Reverting to Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Reverting to Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide

The transition to a new operating system is often met with a mixture of anticipation and trepidation. While Windows 11 boasts new features and a refreshed interface, not every user finds it immediately appealing or compatible with their needs. For those experiencing compatibility issues, performance problems, or simply a preference for the familiarity of Windows 10, the option to revert back offers a welcome solution. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the process, outlining the methods available, considerations, and potential challenges.
Understanding the Reversion Process
Reverting to Windows 10 from Windows 11 is a process that involves restoring the system to its previous state. This is achieved by either using a system restore point or utilizing a clean installation of Windows 10. The method chosen depends on the individual’s circumstances and desired outcome.
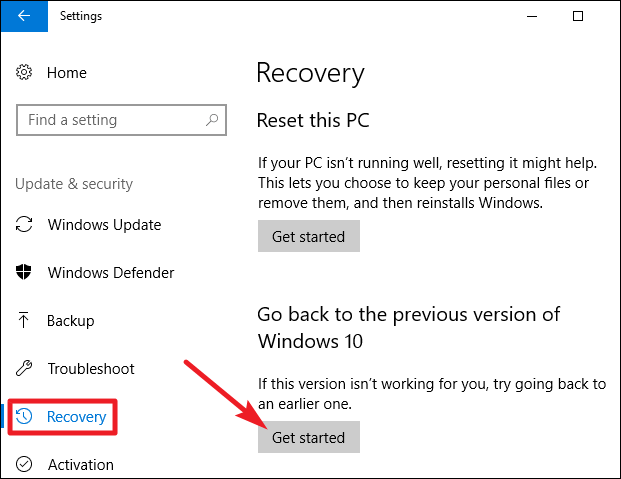
Method 1: System Restore
System Restore is a built-in Windows feature that allows users to roll back their system to a previous point in time. This option is ideal for situations where recent changes, such as software installations or driver updates, have caused instability or incompatibility. However, System Restore does not erase all data; it simply reverts the system files to an earlier state.
Steps to Perform a System Restore:
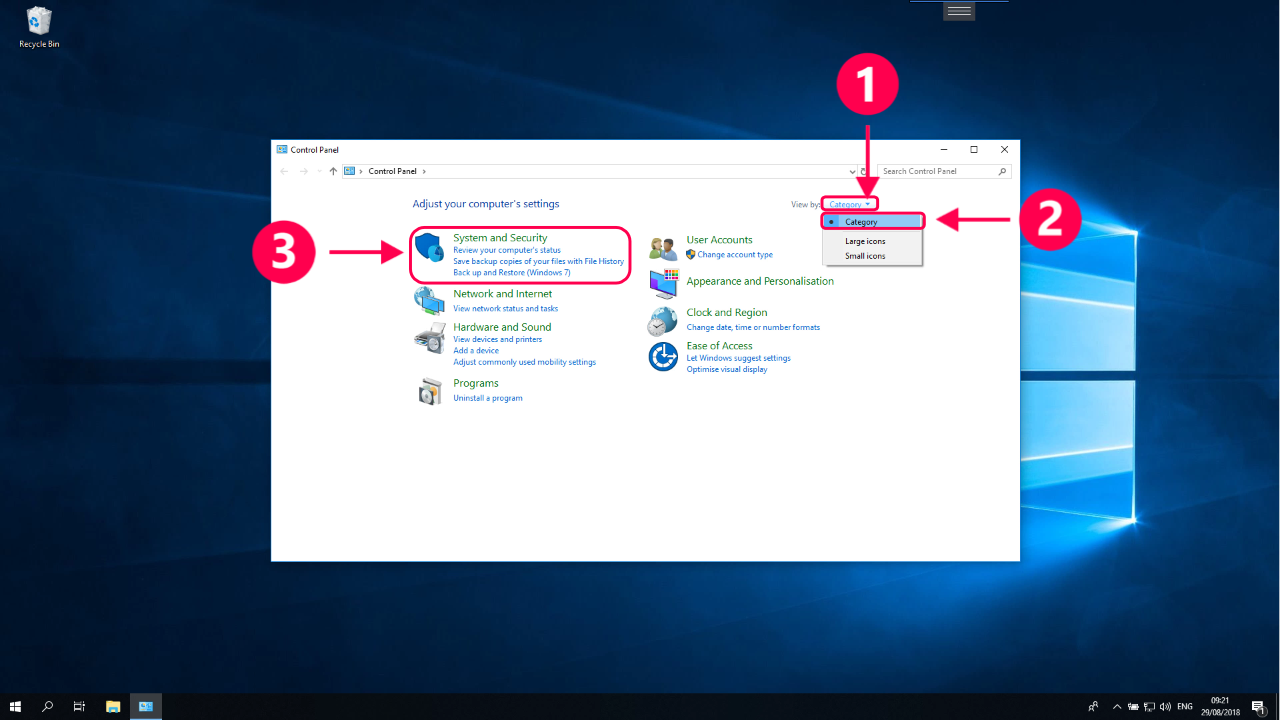
- Access the System Restore Tool: This can be accessed through the "Control Panel" or by searching for "System Restore" in the Windows search bar.
- Select a Restore Point: A list of available restore points will be displayed, each representing a snapshot of the system at a specific time. Choose the point that predates the issues encountered.
- Initiate the Restore Process: Confirm the selection and allow the system to complete the restore process. This may take some time depending on the size of the restore point.
Method 2: Clean Installation
A clean installation involves erasing the existing operating system and installing Windows 10 from scratch. This method is more drastic and requires a backup of all important data before proceeding. However, it offers a fresh start, potentially resolving persistent issues and ensuring optimal performance.
Steps for a Clean Installation:
- Create a Backup: Back up all essential data, including documents, photos, and other files. This can be done using external storage devices, cloud services, or system backup tools.
- Obtain a Windows 10 Installation Media: Download the Windows 10 installation files from Microsoft’s official website and create a bootable USB drive or DVD.
- Boot from the Installation Media: Change the boot order in the BIOS settings to prioritize the installation media.
- Follow the Installation Instructions: The installation process will guide you through the steps, including formatting the hard drive and selecting installation options.
- Restore Data: After the installation is complete, restore the backed-up data to its original location.
Factors to Consider Before Reverting
Before embarking on the reversion process, it’s essential to consider several factors:
- Compatibility: Ensure that the hardware and software currently in use are compatible with Windows 10. Check for driver updates and compatibility information on the manufacturer’s website.
- Data Loss: Understand that both methods may result in data loss if proper backups are not created.
- Software Licensing: Ensure that all software licenses are valid for Windows 10. Some applications may require re-activation or re-installation.
- System Configuration: Be aware that reverting to Windows 10 will revert the system configuration to its previous state, potentially undoing any changes made in Windows 11.
Potential Challenges and Workarounds
While reverting to Windows 10 is generally straightforward, some challenges may arise:
- Driver Issues: Some drivers may not be compatible with Windows 10, requiring manual installation or updates.
- Software Incompatibility: Certain applications may not function properly or require updates to work with Windows 10.
- Data Transfer: Transferring data from a Windows 11 installation to a Windows 10 installation can be challenging. Consider using external storage devices or cloud services for data transfer.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Can I revert to Windows 10 without losing my data?
A: Using System Restore can help preserve data, but a clean installation will require a complete backup and subsequent data restoration.
Q: What happens to my Windows 11 license after reverting?
A: Your Windows 11 license remains valid. However, it may not be automatically activated on Windows 10. You may need to contact Microsoft support for activation assistance.
Q: Can I switch back to Windows 11 after reverting?
A: Yes, you can upgrade to Windows 11 again. However, ensure you have a valid Windows 11 license and the necessary system requirements.
Q: Is it possible to dual-boot Windows 10 and Windows 11?
A: Yes, dual-booting allows you to have both operating systems installed on your computer and choose which one to use at startup. This option provides flexibility but requires careful partitioning of the hard drive.
Tips for a Smooth Transition
- Back Up Your Data: Create comprehensive backups of all essential data before initiating any reversion process.
- Check for Driver Updates: Ensure that all drivers are compatible with Windows 10 and install any necessary updates.
- Verify Software Compatibility: Confirm that all required software is compatible with Windows 10 and install any necessary updates.
- Consider a Dual-Boot Setup: If you’re unsure about committing to Windows 10, a dual-boot setup allows you to try both operating systems without permanently deleting Windows 11.
Conclusion
Reverting to Windows 10 from Windows 11 offers a viable solution for users encountering compatibility issues, performance problems, or simply preferring the familiar interface of Windows 10. By carefully considering the options available, preparing for potential challenges, and following the outlined steps, users can seamlessly transition back to Windows 10 while preserving their important data. The choice ultimately rests on individual needs and preferences, but understanding the process and its implications empowers users to make informed decisions about their operating system.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Reverting to Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!