Reversing the Upgrade: Returning to Windows 10 from a Newer Operating System
Related Articles: Reversing the Upgrade: Returning to Windows 10 from a Newer Operating System
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Reversing the Upgrade: Returning to Windows 10 from a Newer Operating System. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Reversing the Upgrade: Returning to Windows 10 from a Newer Operating System
The allure of new technology often leads users to upgrade their operating systems, seeking enhanced features, improved performance, or simply a fresh start. However, the transition to a newer version can sometimes bring unexpected challenges. Compatibility issues, unfamiliar interfaces, or a lack of desired features might leave users longing for the familiarity and stability of their previous operating system. In such cases, reverting to a prior version, specifically Windows 10, might be the ideal solution.
This article explores the various methods for returning to Windows 10 from newer operating systems, delving into the prerequisites, potential challenges, and considerations involved in this process. It aims to provide a comprehensive guide for users seeking to reclaim the functionality and familiarity of Windows 10.
Methods for Reverting to Windows 10
The approach to returning to Windows 10 depends largely on the specific operating system you are currently using and the upgrade method employed. Here are the most common scenarios and their corresponding solutions:
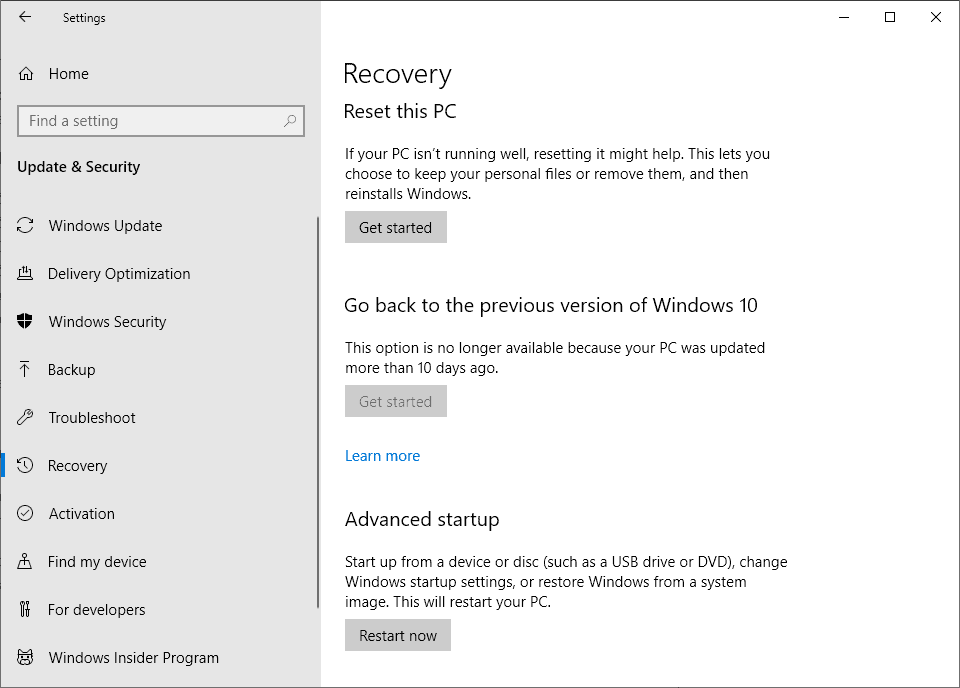
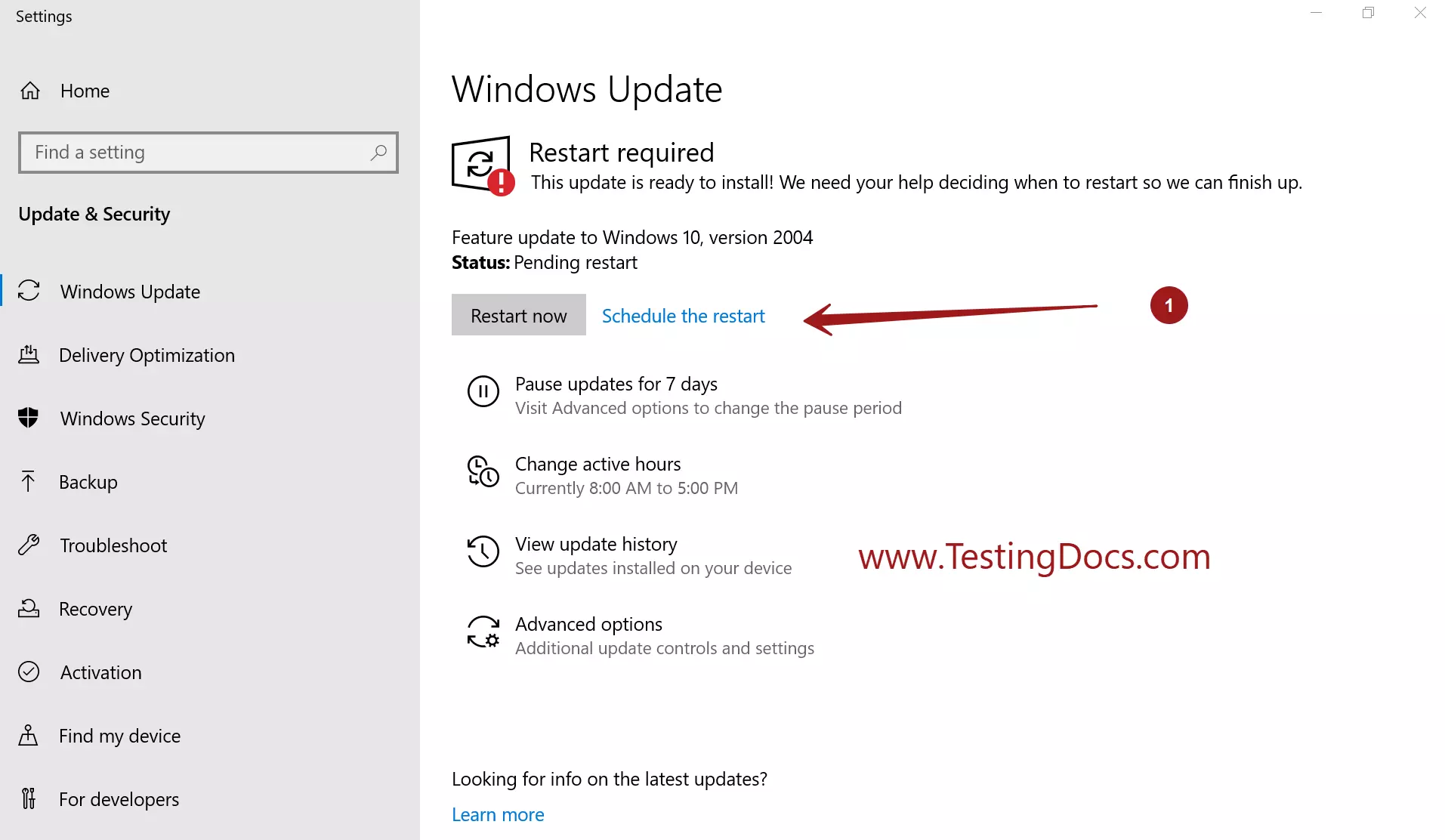
1. Utilizing the "Go Back" Feature:
This method is available for a limited period after upgrading to a newer Windows version. Typically, users have a 10-day window to revert to their previous operating system. This feature is accessible through the "Settings" app, typically found in the "Update & Security" section. This method preserves user data, ensuring a seamless transition back to Windows 10.
2. Clean Installation of Windows 10:
If the "Go Back" option is unavailable or if you prefer a fresh start, a clean installation of Windows 10 is an alternative. This method requires a bootable USB drive containing the Windows 10 installation files. During the installation process, you can choose to format the drive, effectively erasing all existing data. This approach offers a clean slate, eliminating potential conflicts or issues that might have arisen from the upgrade.
3. System Restore Point:
Prior to upgrading to a newer operating system, it is recommended to create a system restore point. This snapshot of your system’s configuration allows you to revert to a previous state, effectively undoing the upgrade. However, this method might not restore all data, as it primarily focuses on system files and settings.
4. Using a Backup Image:
A comprehensive backup image of your entire hard drive, created before the upgrade, offers the most complete method for reverting to Windows 10. This image contains all data, applications, and system settings, allowing for a complete restoration of your previous state. However, restoring from a backup image requires specialized software and might be a more technical process.
5. Factory Reset:
If the upgrade process resulted in significant system instability or data loss, a factory reset might be necessary. This option effectively returns your computer to its original state, removing all data and applications. However, it is crucial to back up important data before performing a factory reset, as this process is irreversible.
Considerations and Potential Challenges
While reverting to Windows 10 is generally feasible, certain factors can influence the process and its outcome:
- Time Limits: The "Go Back" feature has a limited time window, typically 10 days after the upgrade. This window might be shorter for certain versions or configurations.
- Data Loss: Clean installations and factory resets erase all data from the hard drive. Ensure you have a backup of important files before proceeding with these methods.
- Driver Compatibility: Older drivers might not be compatible with the newer Windows version. Ensure you have the necessary drivers for your hardware before attempting a clean installation.
- Software Compatibility: Some applications might not be compatible with Windows 10. Check software compatibility before reverting to ensure a smooth transition.
- Hardware Requirements: Windows 10 has specific hardware requirements. Ensure your computer meets these requirements before attempting to install Windows 10.
FAQs: Returning to Windows 10
Q: Can I revert to Windows 10 after upgrading to Windows 11?
A: Yes, but the method depends on the upgrade type. If you used the "Upgrade" feature, you might have a limited time window to revert using the "Go Back" option. Otherwise, a clean installation of Windows 10 is the most reliable method.
Q: Will reverting to Windows 10 delete my data?
A: Depending on the method used, data loss might occur. The "Go Back" feature preserves data, while clean installations and factory resets erase all data.
Q: Can I revert to Windows 10 without losing my files?
A: Using the "Go Back" feature is the most reliable way to revert without data loss. However, if this option is unavailable, ensure you have a backup of your files before attempting other methods.
Q: Can I revert to Windows 10 if I have a different version of Windows 10 installed?
A: Yes, but the process might involve a clean installation. You can create a bootable USB drive with the desired Windows 10 version and proceed with the installation process.
Q: What if I encounter errors during the reverting process?
A: If you encounter errors, consult Microsoft’s support documentation or seek assistance from a qualified technician.
Tips for Returning to Windows 10
- Backup your data: Ensure you have a backup of all important files and settings before attempting any reverting process.
- Check hardware compatibility: Verify that your computer meets the hardware requirements for Windows 10.
- Gather necessary drivers: Ensure you have the latest drivers for your hardware before installing Windows 10.
- Consider a clean installation: If you experience issues after reverting, a clean installation might be necessary.
- Seek professional assistance: If you are unsure about the process or encounter difficulties, consult a qualified technician.
Conclusion
Reverting to Windows 10 from a newer operating system is achievable through various methods, each with its own advantages and considerations. While the "Go Back" feature offers a seamless transition, a clean installation might be necessary in some cases. Regardless of the chosen method, it is crucial to back up data and ensure hardware compatibility to ensure a successful and smooth transition back to Windows 10. By understanding the available options and potential challenges, users can effectively reclaim the functionality and familiarity of their previous operating system.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/advanced-options-windows-10-update-3ba4a3ffc6ed499da85a450ffc61cbfd.png)



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Reversing the Upgrade: Returning to Windows 10 from a Newer Operating System. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!