Network Connectivity Issues: When Static IP Address Configuration Fails
Related Articles: Network Connectivity Issues: When Static IP Address Configuration Fails
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Network Connectivity Issues: When Static IP Address Configuration Fails. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Network Connectivity Issues: When Static IP Address Configuration Fails

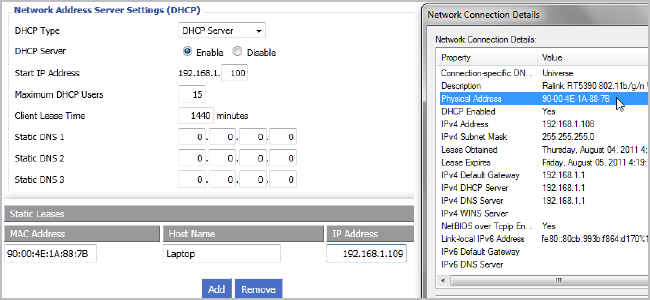
The ability to assign a static IP address to a device is a fundamental aspect of network administration. It allows for predictable and consistent communication within a network, crucial for servers, printers, and other devices requiring dedicated and persistent connections. However, situations arise where attempts to save a static IP address fail, leaving devices unable to communicate effectively. This article explores the common causes behind this issue, providing a comprehensive understanding of the underlying factors and offering practical troubleshooting steps.
Understanding Static IP Address Configuration
In a typical network, devices are assigned dynamic IP addresses, meaning they change each time they connect to the network. While convenient, this dynamic assignment can disrupt communication if a device requires a fixed address for consistent access. This is where static IP address configuration comes into play.
Static IP addresses are manually assigned to specific devices, ensuring they retain the same address regardless of network changes. This approach is particularly useful for:
- Servers: Servers often require a fixed IP address for clients to connect and access services.
- Printers: Static IP addresses ensure consistent network printing, eliminating the need to locate the printer’s changing IP address every time.
- Network Devices: Routers, switches, and other network equipment often rely on static IP addresses for efficient network management.
Common Causes for Static IP Address Configuration Failure
When a static IP address cannot be saved, it indicates a problem with the configuration process, network settings, or underlying network infrastructure. The following are common culprits:
1. IP Address Conflict:
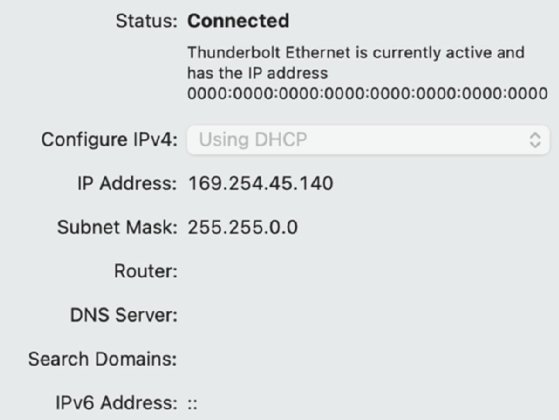
This is the most prevalent reason for static IP address configuration failure. It occurs when two or more devices on the network are assigned the same IP address. This creates a collision, preventing both devices from communicating properly.
2. Incorrect Subnet Mask:
The subnet mask defines the network portion of an IP address, determining which devices are on the same network. An incorrect subnet mask can lead to the device being assigned an IP address outside the network’s range, causing communication problems.
3. Incorrect Default Gateway:
The default gateway acts as the bridge between the local network and the external internet. An incorrect default gateway prevents the device from reaching other networks, including the internet.
4. DHCP Server Conflict:
The Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server automatically assigns IP addresses to devices on a network. If a DHCP server is configured to assign the same IP address that you’re trying to assign statically, the static configuration will be overridden.
5. Incorrect DNS Server Configuration:
Domain Name System (DNS) servers translate domain names into IP addresses. An incorrect DNS server configuration can prevent the device from resolving domain names, leading to connectivity issues.
6. Network Cable Issues:
A faulty network cable or loose connection can interrupt the communication flow, preventing the static IP address configuration from being saved.
7. Firewall Restrictions:
Firewalls can block specific network traffic, including attempts to configure static IP addresses.
8. Operating System Errors:
Network settings within the operating system can become corrupted or misconfigured, interfering with static IP address configuration.
Troubleshooting Static IP Address Configuration Issues
Addressing the issue of failing static IP address configuration requires a systematic approach to identify and resolve the underlying problem. Here’s a detailed troubleshooting guide:
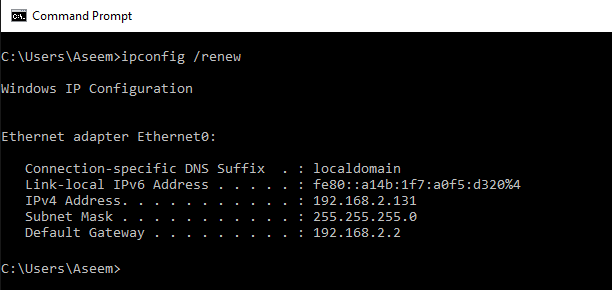
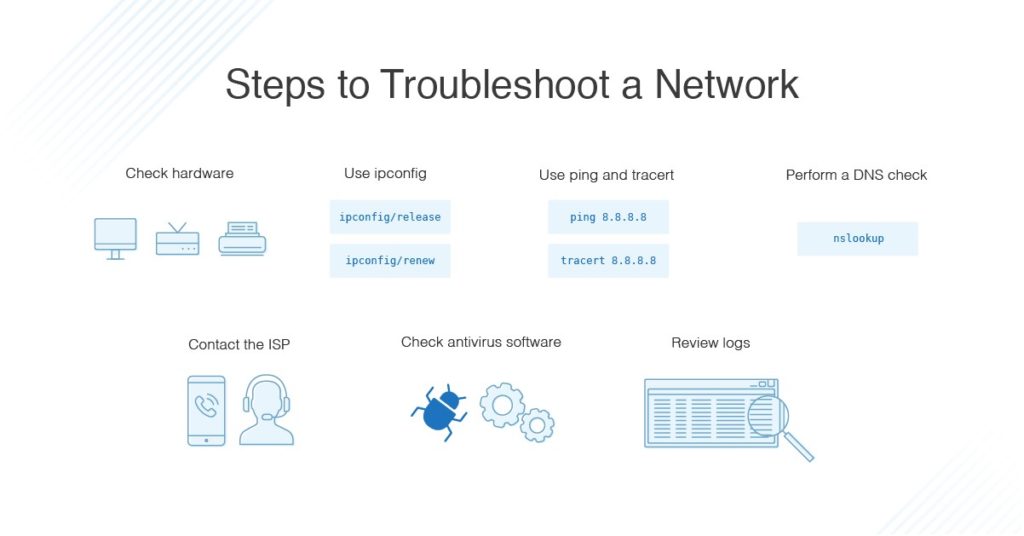
1. Verify IP Address Uniqueness:
- Use IP Address Scanning Tools: Tools like Advanced IP Scanner or SolarWinds Network Performance Monitor can scan the network for active devices and their assigned IP addresses.
- Check Network Configuration: Manually examine the IP addresses assigned to other devices on the network.
- Release and Renew IP Address: If the device is currently assigned a dynamic IP address, try releasing and renewing the IP address to obtain a new one.
2. Verify Subnet Mask and Default Gateway:
- Check Network Settings: Access the device’s network settings and verify that the subnet mask and default gateway are correctly configured.
- Consult Network Administrator: If unsure about the correct settings, consult the network administrator or refer to the network documentation.
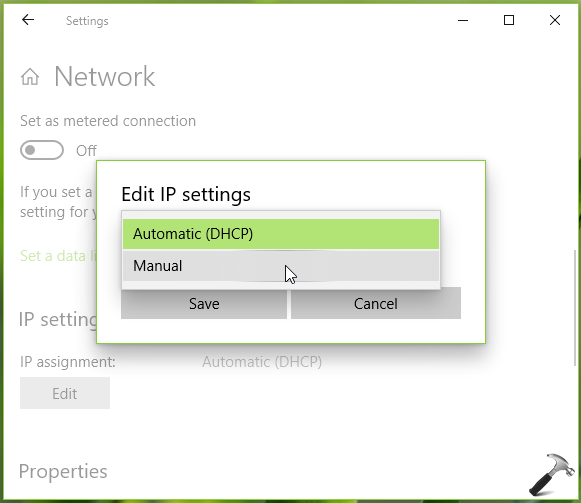
3. Disable DHCP Server Interference:
- Check DHCP Server Settings: If a DHCP server is present, ensure it’s not configured to assign the desired static IP address.
- Temporarily Disable DHCP: If necessary, temporarily disable the DHCP server to prevent it from interfering with the static IP address configuration.
4. Configure DNS Server Correctly:
- Check DNS Server Settings: Access the device’s network settings and verify the DNS server addresses are correctly configured.
- Use Public DNS Servers: If the DNS server is unavailable or unreliable, consider using public DNS servers like Google Public DNS or Cloudflare DNS.
5. Inspect Network Cables and Connections:
- Check Cable Integrity: Visually inspect the network cable for any damage or loose connections.
- Try a Different Cable: If possible, try connecting the device with a different network cable to rule out cable issues.
6. Review Firewall Rules:
- Check Firewall Settings: Access the device’s firewall settings and ensure there are no rules blocking static IP address configuration attempts.
- Temporarily Disable Firewall: If necessary, temporarily disable the firewall to see if it resolves the issue.
7. Reset Network Settings:
- Reset Network Adapter: Reset the network adapter in the device’s operating system to restore default settings.
- Reset Network Configuration: If necessary, reset the entire network configuration, including IP addresses, subnet masks, and default gateway.
8. Contact Technical Support:
If the issue persists after exhausting troubleshooting steps, contact the device manufacturer or network administrator for further assistance.
FAQs: Addressing Common Concerns
Q: Can I use any IP address for a static configuration?
A: No, IP addresses are assigned within specific network ranges defined by the subnet mask. Using an IP address outside this range will result in communication failures.
Q: What happens if I configure two devices with the same static IP address?
A: This creates an IP address conflict, preventing both devices from communicating effectively. The network will likely experience slowdowns and data loss.
Q: How do I know if my network has a DHCP server?
A: If you’re able to connect to the internet and access websites without manually configuring an IP address, a DHCP server is likely present on your network.
Q: Is there a way to prevent IP address conflicts?
A: Yes, using a network management tool or a DHCP server with proper configuration can help prevent IP address conflicts.
Q: What are some best practices for static IP address configuration?
A:
- Plan Ahead: Carefully choose IP addresses that are unique and within the network’s range.
- Document Configuration: Keep detailed records of static IP address assignments for easy reference and troubleshooting.
- Use Consistent Naming Conventions: Assign descriptive names to devices and networks to simplify identification.
- Regularly Monitor Network: Monitor network activity and address any conflicts or issues promptly.
Conclusion: Ensuring Network Stability and Reliability
Successfully saving a static IP address is essential for maintaining stable and reliable network communication. While various factors can contribute to configuration failures, understanding the underlying causes and following a systematic troubleshooting approach can effectively resolve the issue. By addressing potential conflicts, verifying network settings, and implementing best practices, network administrators can ensure smooth and efficient operation, enabling devices to communicate consistently and predictably.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Network Connectivity Issues: When Static IP Address Configuration Fails. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!