Navigating Windows 11’s Fast Startup: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Navigating Windows 11’s Fast Startup: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating Windows 11’s Fast Startup: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Navigating Windows 11’s Fast Startup: A Comprehensive Guide
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Navigating Windows 11’s Fast Startup: A Comprehensive Guide
- 3.1 Understanding Fast Startup
- 3.2 The Potential Downsides of Fast Startup
- 3.3 Managing Fast Startup Settings in Windows 11
- 3.4 FAQs Regarding Fast Startup in Windows 11
- 3.5 Tips for Optimizing Fast Startup
- 3.6 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Navigating Windows 11’s Fast Startup: A Comprehensive Guide
Windows 11, like its predecessors, incorporates a feature known as "Fast Startup" to expedite the boot process, significantly reducing the time it takes for the operating system to become operational. This feature, however, can sometimes lead to unexpected behavior or compatibility issues, prompting users to explore ways to modify or disable it. This article delves into the intricacies of fast startup settings in Windows 11, providing a comprehensive understanding of its functionalities, potential drawbacks, and effective methods for managing it.
Understanding Fast Startup
Fast Startup, a hybrid sleep mode, leverages the benefits of both hibernation and traditional shutdown. When enabled, Windows 11 does not completely shut down the system upon clicking the "Shut Down" button. Instead, it enters a state where the operating system kernel and essential drivers are loaded into the hibernation file. This file, stored on the hard drive, contains a snapshot of the system’s current state, allowing for a faster boot-up process.
When the computer is restarted, Windows 11 retrieves the saved state from the hibernation file and quickly loads it into memory, bypassing the lengthy process of loading the entire operating system from scratch. This results in a significantly reduced boot time, enhancing user experience.
The Potential Downsides of Fast Startup
While fast startup offers a noticeable improvement in boot times, it’s not without its drawbacks.
-
Potential for Data Loss: In rare cases, abrupt power outages during the shutdown process, while fast startup is enabled, can lead to data loss. This is because the system does not fully shut down, leaving some data in an unsaved state.
-
Compatibility Issues: Some applications or hardware devices might not function as expected when fast startup is enabled. This can lead to errors, crashes, or unexpected behavior.
-
Slower Wake-up Times: Although fast startup generally reduces boot times, it can sometimes lead to longer wake-up times from sleep mode.
-
Increased Disk Usage: The hibernation file, which stores the saved system state, can occupy a significant amount of disk space. This can be a concern for users with limited storage capacity.
Managing Fast Startup Settings in Windows 11
Understanding the potential drawbacks of fast startup, users might opt to disable or modify its settings. Windows 11 provides a straightforward interface for managing fast startup settings:
-
Accessing Power Options: Navigate to the "Start" menu and type "Power Options." Select the "Power & Sleep" option from the search results.
-
Choosing "Additional Power Settings": In the "Power & Sleep" window, click on "Additional power settings" located in the right-hand pane.
-
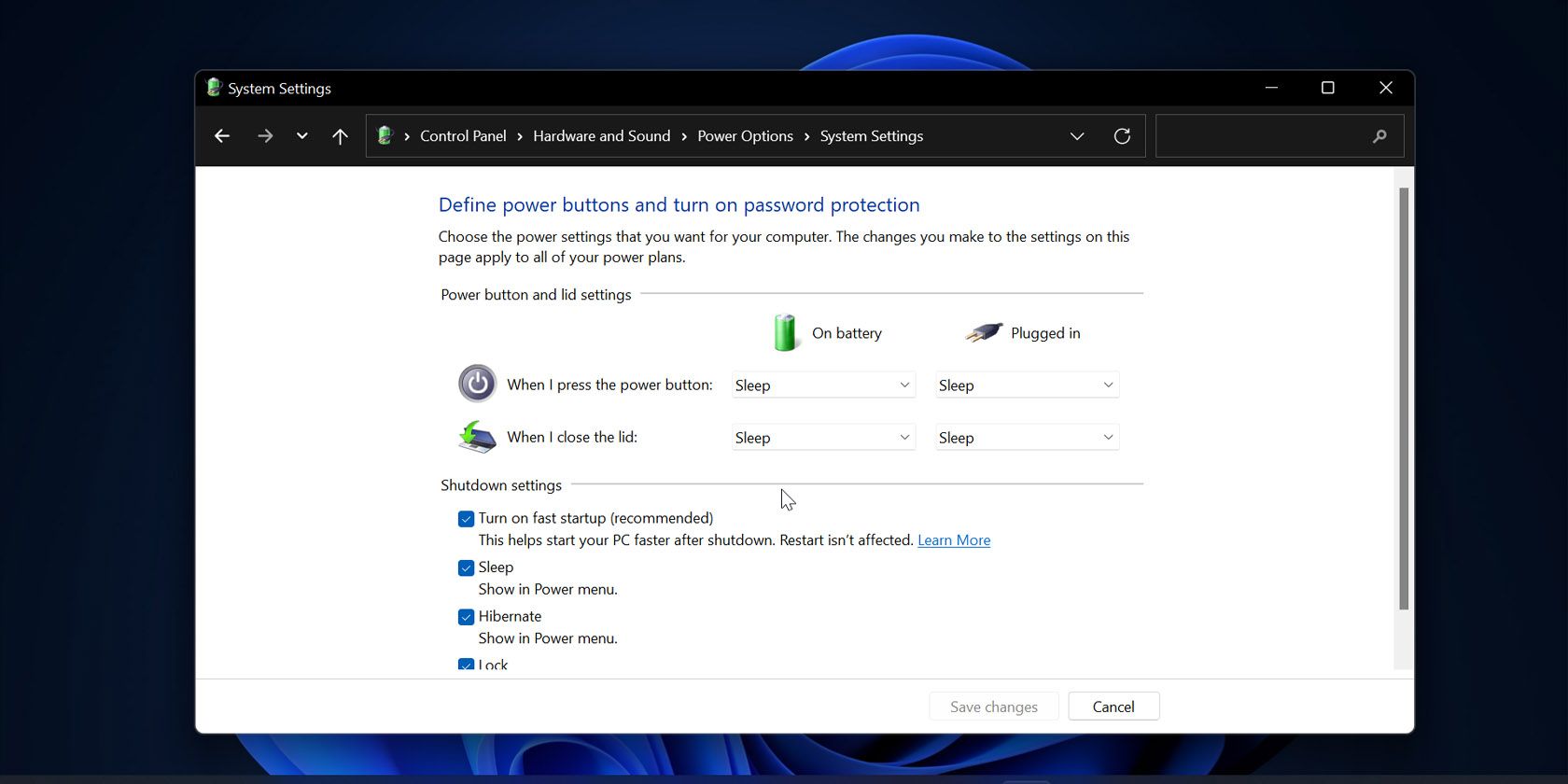
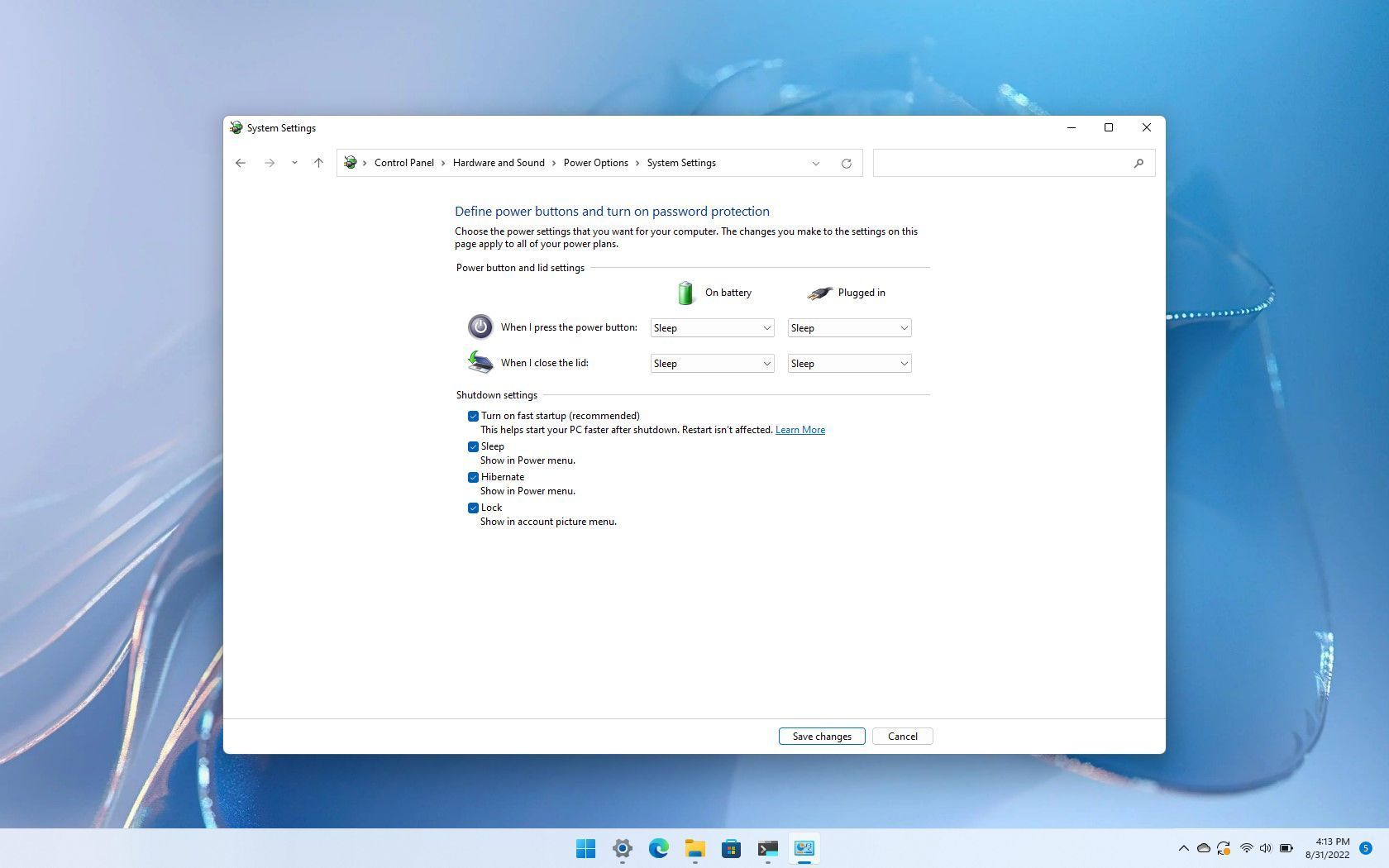
Modifying Startup Settings: In the "Power Options" window, click on "Choose what the power buttons do" on the left-hand side.
-
Enabling or Disabling Fast Startup: Click on "Change settings that are currently unavailable." Scroll down to the "Shutdown settings" section and uncheck the box labeled "Turn on fast startup (recommended)." Click "Save changes" to apply the modifications.
FAQs Regarding Fast Startup in Windows 11
1. Is Fast Startup Enabled by Default in Windows 11?
Yes, fast startup is enabled by default in Windows 11. This is intended to enhance the user experience by reducing boot times.
2. Can Fast Startup Be Disabled Without Losing Data?
Disabling fast startup does not result in data loss. The hibernation file, containing the saved system state, is deleted when fast startup is disabled, ensuring no data is lost.
3. What are the Alternatives to Fast Startup?
While fast startup offers a convenient way to expedite the boot process, users can explore alternative methods to achieve similar results:
-
Enable SSDs: Using a Solid State Drive (SSD) significantly speeds up boot times due to its faster read and write speeds compared to traditional hard disk drives (HDDs).
-
Optimize Startup Programs: Reducing the number of programs that launch automatically at startup can improve boot times. Users can manage startup programs through the Task Manager.
-
Disable Unnecessary Services: Disabling unnecessary services can enhance system performance and reduce boot times. Users can manage services through the "Services" window (accessible by typing "services.msc" in the "Run" dialog box).
4. How Can I Monitor Disk Usage by the Hibernation File?
The hibernation file is typically located in the root directory of the system drive (usually C:). Its file name is "hiberfil.sys." You can monitor its size using file explorer or disk management tools.
5. Can I Manually Delete the Hibernation File?
Deleting the "hiberfil.sys" file manually is not recommended. This file is critical for fast startup functionality, and deleting it can cause unexpected behavior.
Tips for Optimizing Fast Startup
While fast startup is a valuable feature for improving boot times, users can further optimize its performance through these tips:
-
Keep the Hibernation File Clean: Regularly cleaning and defragmenting the hard drive can improve the efficiency of the hibernation file, leading to faster boot times.
-
Monitor System Resources: Ensure sufficient system resources, such as RAM and disk space, are available for fast startup to function optimally.
-
Update Drivers: Regularly updating device drivers, especially those related to storage devices, can enhance system performance and potentially improve fast startup speeds.
-
Avoid Unnecessary Programs: Minimizing the number of applications running in the background can reduce the load on the system and improve boot times.
Conclusion
Fast startup in Windows 11 offers a significant boost to boot times, enhancing the user experience. However, its potential drawbacks, including data loss risks and compatibility issues, require careful consideration. By understanding the nuances of fast startup and its management options, users can optimize their system performance while mitigating potential risks.
Ultimately, the decision to enable or disable fast startup depends on individual needs and preferences. By carefully evaluating the benefits and drawbacks, users can make informed choices to ensure a smooth and efficient computing experience.


![How to Enable or Turn On Fast Startup on Windows 11 [Tutorial] - YouTube](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/aO2eIvIHUlU/maxresdefault.jpg)



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating Windows 11’s Fast Startup: A Comprehensive Guide. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!