Navigating Windows 11 Compatibility: Exploring the Capabilities of 8th Generation Intel Processors
Related Articles: Navigating Windows 11 Compatibility: Exploring the Capabilities of 8th Generation Intel Processors
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating Windows 11 Compatibility: Exploring the Capabilities of 8th Generation Intel Processors. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating Windows 11 Compatibility: Exploring the Capabilities of 8th Generation Intel Processors

The release of Windows 11 ushered in a new era for personal computing, boasting enhanced features and a refined user interface. However, with this advancement came a set of system requirements, including a specific focus on processor compatibility. This has led to a common question: Can 8th generation Intel processors run Windows 11?
The answer, while not universally affirmative, is generally positive. However, understanding the nuances of compatibility is crucial. This article delves into the intricacies of Windows 11’s system requirements, specifically focusing on 8th generation Intel processors, providing a comprehensive guide for users seeking to upgrade or build a new PC.
Windows 11’s System Requirements: A Foundation for Understanding
Windows 11, like its predecessors, demands specific hardware capabilities to ensure optimal performance and stability. These requirements, outlined by Microsoft, are divided into two categories:
- Minimum System Requirements: These represent the bare minimum hardware specifications necessary for Windows 11 to function. Devices meeting these requirements may experience limited performance and feature availability.
- Recommended System Requirements: These specifications aim to provide a smoother and more robust user experience, enabling the full potential of Windows 11’s features.
The Role of the Processor: A Vital Component in Compatibility
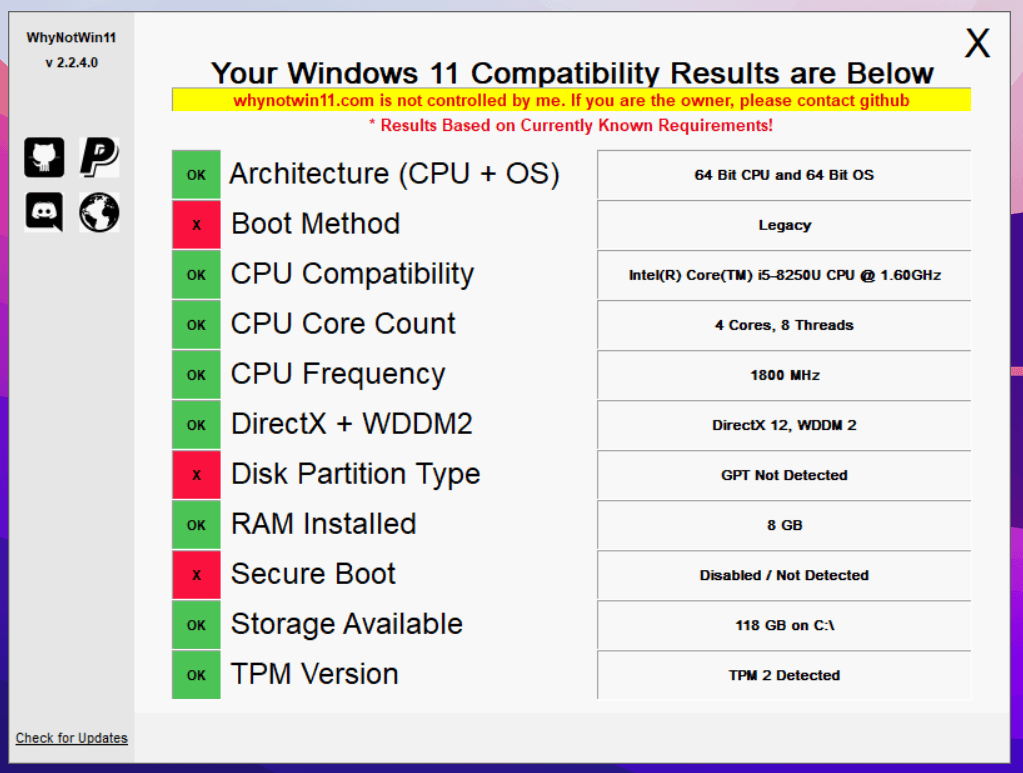
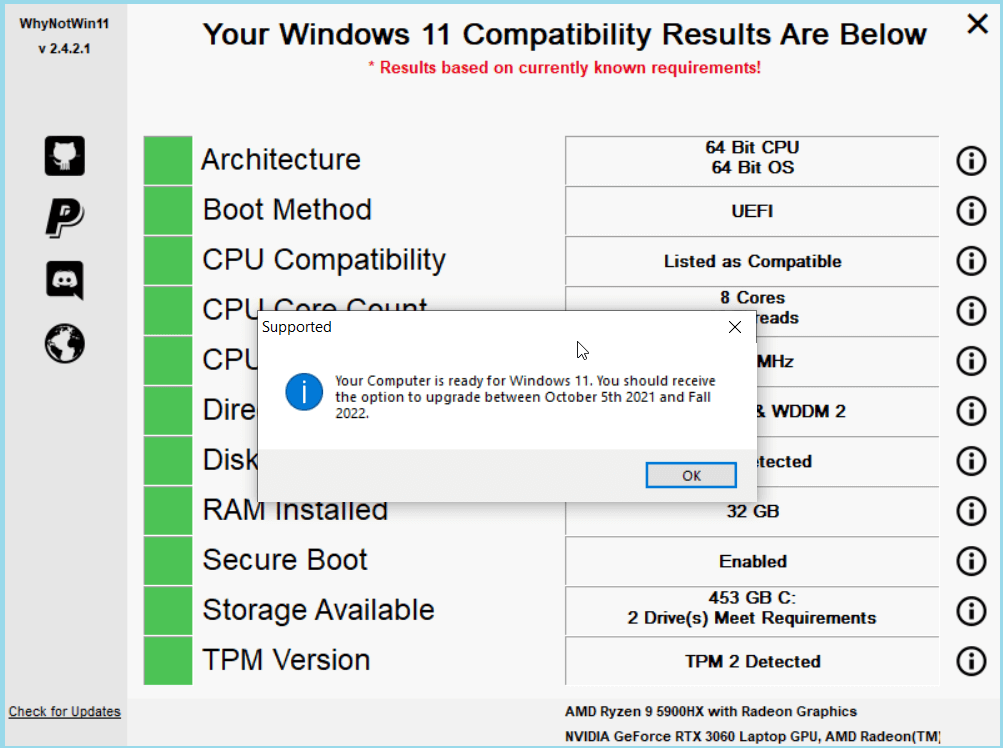
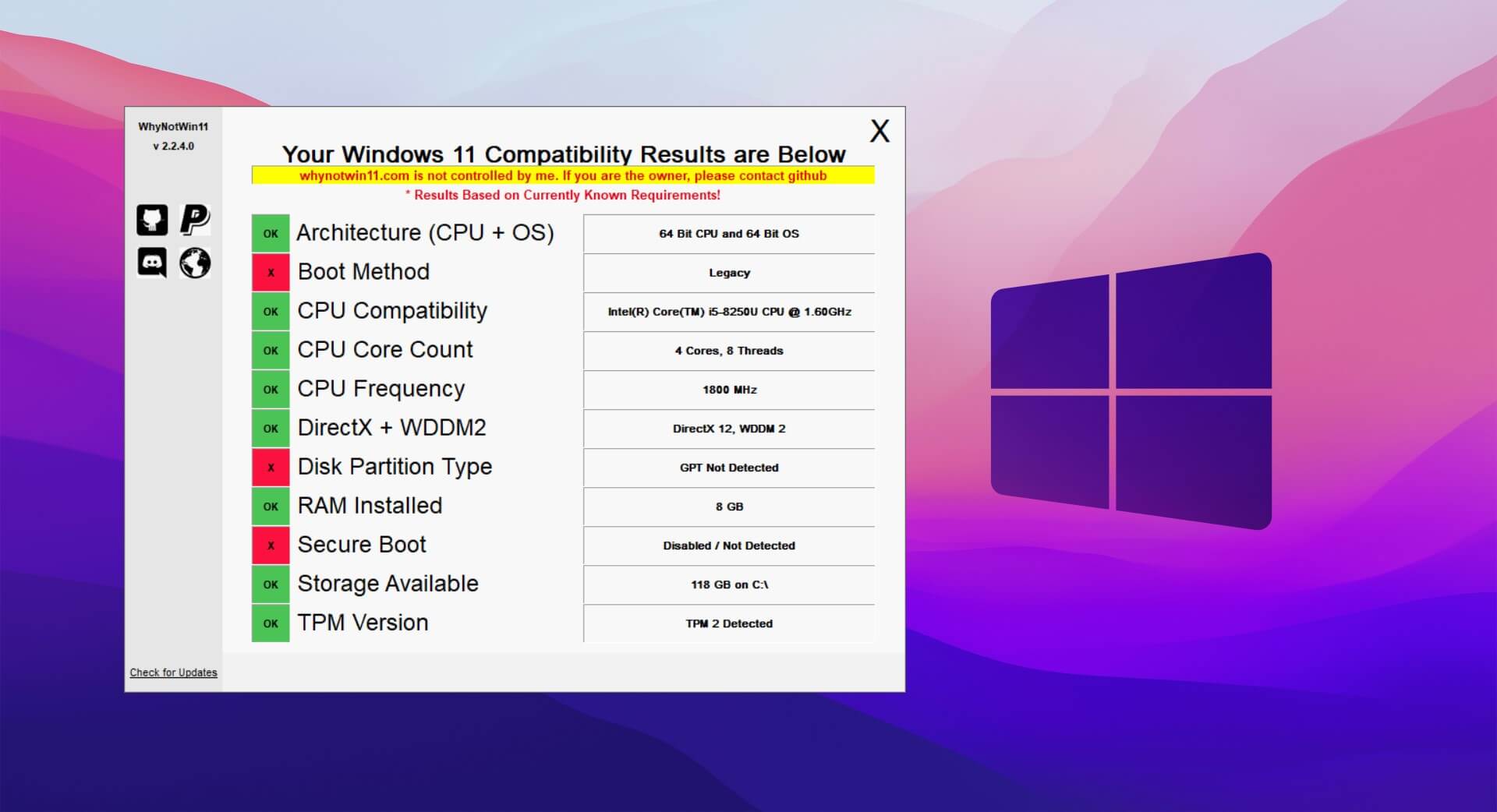
Among the various system requirements, the processor plays a pivotal role in determining compatibility with Windows 11. Microsoft has explicitly stated that the operating system requires a processor that supports Secure Boot and TPM 2.0. These features, essential for enhanced security, are generally found in processors released after 2016.
8th Generation Intel Processors: A Detailed Examination
8th generation Intel processors, commonly referred to as "Coffee Lake" and "Kaby Lake Refresh," were launched in 2017 and 2018, respectively. While these processors were released after the 2016 cutoff, not all models within the 8th generation meet the specific requirements for Windows 11.
Understanding the Compatibility Landscape: Unveiling the Specifics
The key determining factor for compatibility with Windows 11 is the presence of Secure Boot and TPM 2.0 within the specific 8th generation Intel processor model.
- Secure Boot: This security feature, enabled in the BIOS, ensures that only trusted software can load during system startup.
- TPM 2.0: This hardware-based security module provides cryptographic keys and encryption for secure data storage and operations.
Identifying Compatibility: A Step-by-Step Guide
To determine whether your specific 8th generation Intel processor supports Windows 11, follow these steps:
- Identify Your Processor: Access your computer’s system information. You can usually find this by searching for "System Information" in the Windows search bar. Look for the "Processor" or "CPU" entry.
-
Check for Secure Boot and TPM 2.0:
- Secure Boot: Access your BIOS settings (usually by pressing F2 or Del during startup) and navigate to the "Security" or "Boot" section. Look for an option called "Secure Boot" and ensure it is enabled.
- TPM 2.0: In the BIOS, locate the "Security" or "Trusted Platform Module" section. Confirm that TPM 2.0 is enabled or present.
- Utilize Online Resources: Several websites and tools can help identify processor compatibility with Windows 11. Search online for "Windows 11 compatibility checker" or "Intel processor compatibility list."
Navigating Compatibility Challenges: Solutions and Workarounds
In scenarios where your 8th generation Intel processor lacks Secure Boot or TPM 2.0, several options exist:
- BIOS Update: Some motherboard manufacturers may release BIOS updates that enable Secure Boot and TPM 2.0 on older processors. Check your motherboard manufacturer’s website for available updates.
- Virtualization: If you cannot enable Secure Boot or TPM 2.0, you may consider running Windows 11 in a virtual machine environment. This approach allows you to run Windows 11 without directly interacting with your hardware.
- Windows 10 as an Alternative: If upgrading to Windows 11 is not a priority, Windows 10 remains a viable option for computers with 8th generation Intel processors. Microsoft continues to provide security updates and support for Windows 10.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions
Q: What are the minimum system requirements for Windows 11?
A: The minimum system requirements for Windows 11 include a 1 GHz or faster processor with 2 or more cores, 4 GB RAM, 64 GB storage, and a compatible graphics card. However, these minimum requirements may not guarantee a smooth user experience.
Q: Can I upgrade from Windows 10 to Windows 11 on an 8th generation Intel processor?
A: While the upgrade process may initiate, Windows 11 will likely prompt you to update your BIOS or acquire a compatible processor if your current configuration does not meet the requirements.
Q: What are the benefits of using Windows 11?
A: Windows 11 offers several benefits, including a refined user interface, improved performance, enhanced security features, and support for the latest hardware and software.
Tips for Optimizing Windows 11 Performance on 8th Generation Intel Processors
- Ensure Driver Updates: Keep your device drivers up-to-date to ensure optimal compatibility and performance.
- Monitor Resource Usage: Regularly monitor your system’s resource usage (CPU, RAM, storage) to identify potential bottlenecks and optimize settings.
- Disable Unnecessary Background Processes: Disable unnecessary background processes and applications to free up system resources.
- Optimize Power Settings: Adjust power settings to prioritize performance or energy efficiency based on your needs.
Conclusion: A Balanced Perspective on Compatibility
The compatibility of 8th generation Intel processors with Windows 11 is a complex issue that depends on the specific processor model and the availability of Secure Boot and TPM 2.0. While some 8th generation processors may meet the requirements, others may require BIOS updates or alternative solutions.
Ultimately, the decision to upgrade to Windows 11 should be based on a careful evaluation of your hardware, the available resources, and your individual needs. By understanding the intricacies of compatibility and utilizing the available resources, users can make informed decisions about their computing environment.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating Windows 11 Compatibility: Exploring the Capabilities of 8th Generation Intel Processors. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!