Navigating Windows 11 Compatibility: A Comprehensive Guide to Unsupported CPUs
Related Articles: Navigating Windows 11 Compatibility: A Comprehensive Guide to Unsupported CPUs
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating Windows 11 Compatibility: A Comprehensive Guide to Unsupported CPUs. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating Windows 11 Compatibility: A Comprehensive Guide to Unsupported CPUs
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/22908708/windows_11_unsupported.jpg)
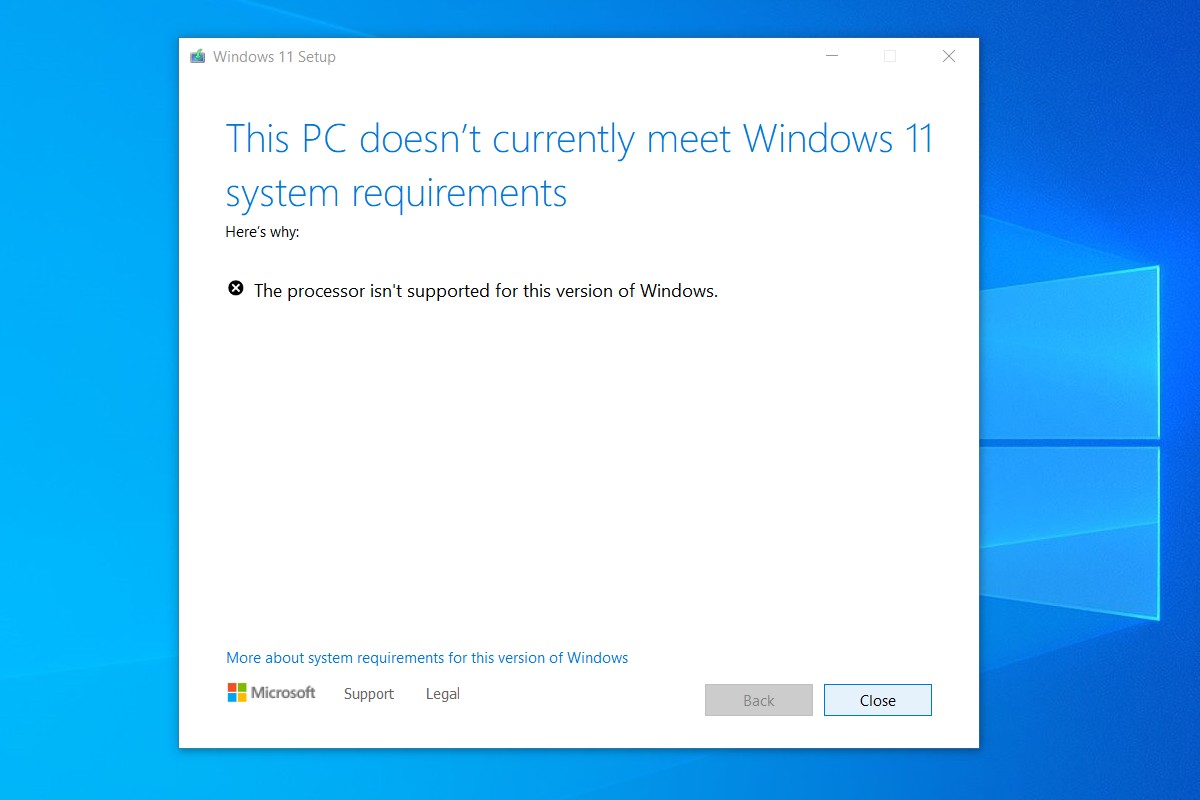
Microsoft’s Windows 11 operating system arrived with a set of stringent hardware requirements, including a CPU compatibility check. This check, designed to ensure optimal performance and security, has left many users with older processors facing a roadblock. While Microsoft’s official stance discourages installing Windows 11 on unsupported CPUs, the reality is that numerous users have successfully bypassed this restriction. This article delves into the intricacies of this issue, providing a comprehensive understanding of the challenges, potential solutions, and the implications of installing Windows 11 on unsupported processors.
Understanding the Compatibility Requirements
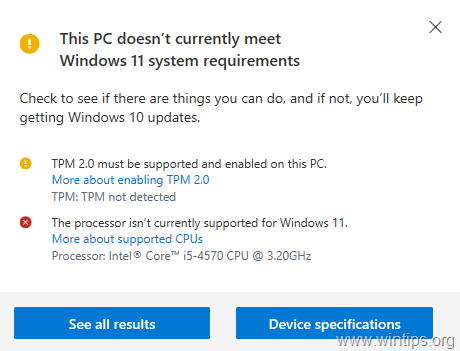
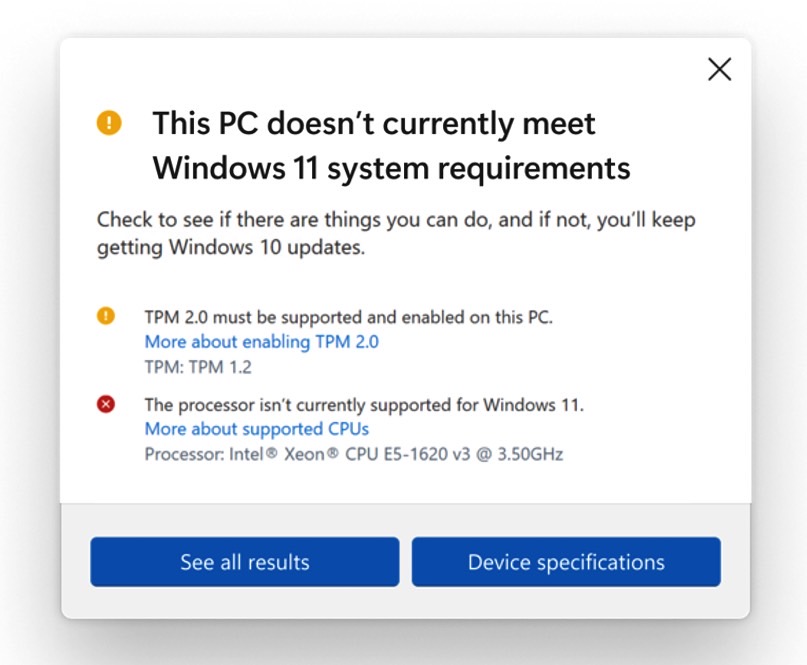
At its core, Windows 11’s compatibility check focuses on the processor’s architecture and capabilities. Microsoft mandates a CPU with a minimum of two cores, a clock speed of 1 GHz, and support for specific instruction sets like Secure Boot, TPM 2.0, and virtualization. These requirements are intended to provide a foundation for the operating system’s security features, performance optimization, and compatibility with modern hardware.
The Limitations of Unsupported CPUs
While installing Windows 11 on an unsupported CPU may seem appealing, it’s essential to understand the potential drawbacks. These include:
- Performance Degradation: Older processors may struggle to keep pace with Windows 11’s demands, leading to sluggish performance, frequent freezes, and application crashes.
- Security Risks: Unsupported CPUs may lack the necessary security features, rendering the system vulnerable to malware and exploits.
- Lack of Updates: Microsoft may not provide security updates or bug fixes for unsupported hardware, leaving systems exposed to potential vulnerabilities.
- Driver Compatibility Issues: Drivers for older hardware might not be fully compatible with Windows 11, leading to device malfunctions or instability.
- Limited Feature Support: Some features and applications may not function optimally or at all on unsupported hardware.
Methods for Installing Windows 11 on Unsupported CPUs
Despite the official limitations, several methods allow users to install Windows 11 on unsupported CPUs. These methods involve circumventing the compatibility check, but they come with the aforementioned risks:
- Registry Editing: This method involves modifying specific registry entries to bypass the compatibility check. However, it requires advanced technical knowledge and can potentially damage the operating system if not done correctly.
- Using a USB Installation Media: Creating a bootable USB drive with a modified Windows 11 installation file allows users to bypass the compatibility check during installation. However, this method may still encounter driver compatibility issues.
- Disabling the TPM and Secure Boot: This method involves disabling the Trusted Platform Module (TPM) and Secure Boot features in the BIOS, effectively circumventing the compatibility check. However, disabling these security features significantly compromises the system’s security.
The Importance of Informed Decision-Making
The decision to install Windows 11 on an unsupported CPU is a complex one. Users must weigh the potential benefits against the inherent risks. Consider the following factors:
- System Performance: If the system’s performance is already sluggish, installing Windows 11 may exacerbate the issue.
- Security Concerns: The lack of security updates and the vulnerability to exploits should be carefully considered, especially for users handling sensitive data.
- Driver Compatibility: Ensure that drivers for all essential hardware components are compatible with Windows 11.
- Alternatives: Explore alternative operating systems like Linux, which may offer better compatibility with older hardware.
FAQs
Q: Is it legal to install Windows 11 on an unsupported CPU?
A: While Microsoft’s terms of service may not explicitly prohibit installing Windows 11 on unsupported hardware, it is strongly discouraged. Users may encounter issues with updates and support, and potential security risks.
Q: What are the potential consequences of installing Windows 11 on an unsupported CPU?
A: The potential consequences include performance degradation, security vulnerabilities, driver compatibility issues, and limited feature support.
Q: Can I upgrade from Windows 10 to Windows 11 on an unsupported CPU?
A: The upgrade process will likely fail due to the compatibility check.
Q: Is it possible to use a virtual machine to run Windows 11 on an unsupported CPU?
A: While virtual machines can help run different operating systems, the performance may be significantly impacted, and the virtual machine itself may require a compatible CPU.
Tips for Users with Unsupported CPUs
- Consider upgrading your CPU: If performance is a primary concern, upgrading to a compatible CPU is the most reliable solution.
- Explore alternative operating systems: Linux distributions are generally more compatible with older hardware and offer a robust alternative to Windows 11.
- Use Windows 10: Windows 10 remains a viable option for users with unsupported CPUs, as it offers better compatibility and security updates.
- Consult with a technical expert: Seek guidance from a qualified IT professional before attempting to install Windows 11 on an unsupported CPU.
Conclusion
Installing Windows 11 on an unsupported CPU is a decision that should be made with careful consideration. While it is technically possible to bypass the compatibility check, users must be aware of the potential risks and limitations. For optimal performance, security, and compatibility, it is highly recommended to ensure that the CPU meets the minimum requirements specified by Microsoft. If an upgrade is not feasible, explore alternative operating systems or stick with Windows 10 for a more stable and secure experience.

![�� How to Install Windows 11 with an Unsupported CPU Step-by-Step [100% Updates Work] - YouTube](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/06xCjCFghic/maxresdefault.jpg)

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating Windows 11 Compatibility: A Comprehensive Guide to Unsupported CPUs. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!