Navigating Windows 10 Troubles: A Guide to Safe Mode Access from BIOS
Related Articles: Navigating Windows 10 Troubles: A Guide to Safe Mode Access from BIOS
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating Windows 10 Troubles: A Guide to Safe Mode Access from BIOS. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating Windows 10 Troubles: A Guide to Safe Mode Access from BIOS
Windows 10, despite its robust nature, can occasionally encounter issues that disrupt its smooth operation. These issues can range from minor performance glitches to severe system crashes, hindering user productivity and potentially compromising data integrity. In such scenarios, a powerful troubleshooting tool emerges: Safe Mode.
Safe Mode is a diagnostic environment that boots Windows 10 with a minimal set of drivers and services. This stripped-down environment eliminates potential conflicts caused by third-party applications, faulty drivers, or malware, allowing users to address the underlying problem without the interference of extraneous software.
Accessing Safe Mode directly from the BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) provides a more advanced level of control and is particularly useful when the system is unable to boot into Windows normally. This method empowers users to troubleshoot issues that may prevent the standard Safe Mode options from being accessible within the operating system itself.
Understanding the BIOS and its Role in Safe Mode Access
The BIOS is a firmware program embedded on the motherboard of a computer. It acts as the initial software that runs when the computer is powered on, responsible for initializing hardware components and setting up the system for boot-up. This process includes identifying the boot order, which dictates the sequence in which the system searches for a bootable operating system.
When a system fails to boot into Windows normally, accessing the BIOS becomes crucial. By adjusting the boot order within the BIOS settings, users can prioritize booting from a recovery drive or other external media, thereby bypassing the malfunctioning Windows installation and gaining access to troubleshooting tools.
The Importance of Safe Mode Access from BIOS
-
Troubleshooting Severe System Issues: Safe Mode access from BIOS is essential when Windows 10 is unable to load normally, rendering the standard Safe Mode options within the operating system inaccessible. This scenario could arise due to a corrupt boot sector, a failed driver update, or a malware infection that prevents the system from reaching the login screen.
-
Addressing Boot-Related Problems: Boot-related issues, such as a malfunctioning hard drive, a corrupted boot sector, or a faulty boot configuration, can prevent Windows from loading properly. By accessing Safe Mode from BIOS, users can perform essential system repairs and restore a functional boot environment.
-
Restoring System Files: Safe Mode from BIOS allows users to access recovery tools and potentially restore system files that have become corrupted or damaged. This is particularly useful when facing issues related to system updates, driver installations, or malware infections.
-
Performing Clean Boot: A clean boot, which involves starting Windows with only essential services and drivers enabled, can help isolate the cause of a specific problem. Accessing Safe Mode from BIOS enables users to perform a clean boot and identify the culprit behind system instability or performance issues.
Steps to Access Safe Mode from BIOS
-
Restart the Computer: Begin by restarting your computer.
-
Access the BIOS: During the initial boot-up sequence, look for a key prompt on the screen (usually F2, F10, Del, or Esc) that instructs you how to enter the BIOS setup. Press the corresponding key repeatedly until the BIOS screen appears.
-
Navigate to Boot Settings: Within the BIOS menu, navigate to the "Boot" or "Boot Order" section. The exact menu options may vary depending on the motherboard manufacturer.
-
Adjust Boot Order: Locate the entry for your Windows 10 installation and prioritize it as the first boot device. If you are using a recovery drive or a USB stick, prioritize that as the first boot device.
-
Save Changes and Exit: Once you have adjusted the boot order, save the changes and exit the BIOS setup. This typically involves pressing the F10 key or selecting "Save & Exit" from the menu.
-
Boot from Recovery Media: The computer will now attempt to boot from the prioritized device. If you selected a recovery drive or a USB stick, you will be presented with a recovery environment or a boot menu.
-
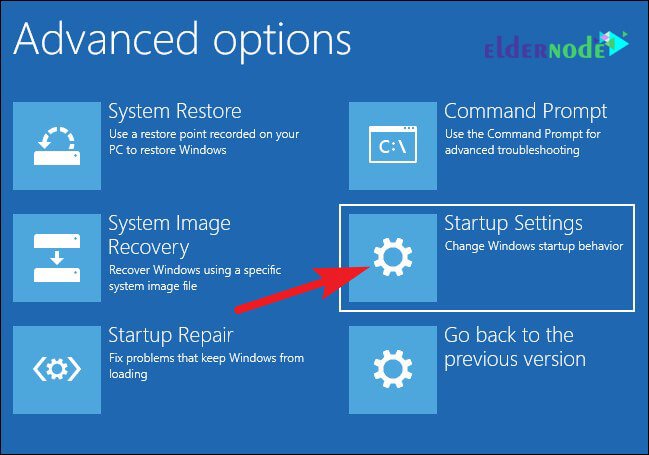
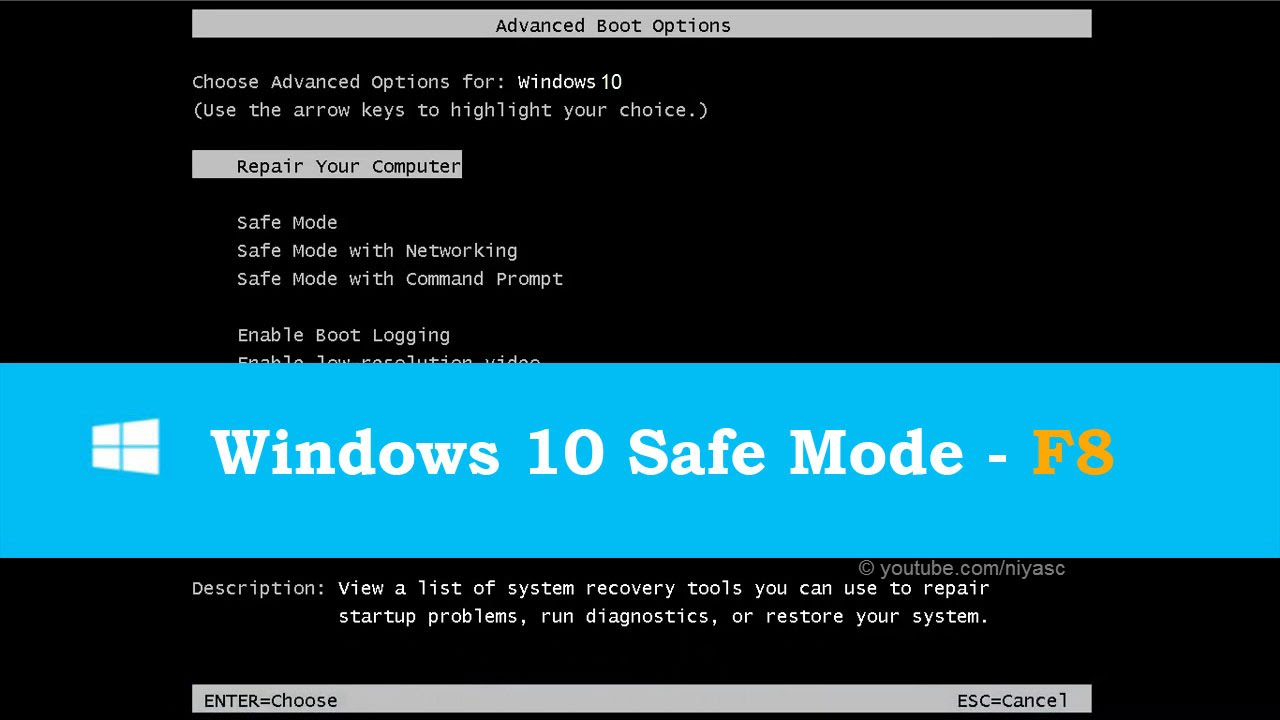
Select Safe Mode: Within the recovery environment, select "Troubleshoot" followed by "Advanced Options." You will find "Startup Settings" within this menu. Choose "Startup Settings" and press F10 to restart the system. You will then be presented with a list of startup options, including Safe Mode. Select the appropriate Safe Mode option using the number keys.
FAQs: Addressing Common Queries
Q: What is the difference between Safe Mode and Safe Mode with Networking?
A: Safe Mode provides a basic environment with limited services and drivers. Safe Mode with Networking allows access to the internet and network drives, making it suitable for troubleshooting issues related to network connectivity or online services.
Q: Why is it necessary to access Safe Mode from BIOS in some cases?
A: When Windows 10 is unable to load properly, accessing Safe Mode from BIOS becomes necessary as the standard Safe Mode options within the operating system are inaccessible. This allows users to bypass the malfunctioning Windows installation and access troubleshooting tools.
Q: What if I forget the key to access the BIOS?
A: Refer to your motherboard’s user manual or search online for the specific model to identify the key used to access the BIOS setup.
Q: Can I use Safe Mode from BIOS to fix a corrupted boot sector?
A: Yes, Safe Mode from BIOS allows access to the command prompt, where you can utilize tools like "bootrec.exe" to repair the boot sector and restore the boot environment.
Q: Is it safe to use Safe Mode from BIOS frequently?
A: Safe Mode is intended for troubleshooting purposes and should not be used as a regular operating environment. Frequent use can impact system performance and may not address the underlying issue.
Tips for Effective Troubleshooting in Safe Mode
-
Identify the Problem: Before entering Safe Mode, carefully assess the symptoms of the issue to narrow down the potential causes.
-
Perform a Clean Boot: If you suspect a third-party application or driver is causing problems, perform a clean boot to isolate the culprit.
-
Run System File Checker: Utilize the System File Checker (SFC) tool to scan for and repair corrupted system files.
-
Check for Malware: If you suspect a malware infection, run a full system scan with a reputable antivirus program.
-
Update Drivers: Ensure that all drivers are up-to-date, especially those related to the problematic hardware component.
-
Restore System: If the issue persists, consider restoring the system to a previous restore point or performing a clean installation of Windows 10.
Conclusion
Accessing Safe Mode from BIOS provides a powerful troubleshooting tool for addressing a wide range of Windows 10 issues, particularly those that prevent the system from booting normally. By understanding the BIOS and its role in boot order, users can gain access to recovery tools and diagnose system problems effectively. This advanced troubleshooting technique empowers users to resolve critical issues, restore system functionality, and maintain a stable and reliable computing experience.



![How to Start Windows 10 Safe Mode From BIOS [Solved]](https://techrapidly.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/02/How-to-Start-Windows-10-Safe-Mode-From-BIOS-Solved.png)



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating Windows 10 Troubles: A Guide to Safe Mode Access from BIOS. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!