Navigating Windows 10 Troubles: A Comprehensive Guide to Safe Mode
Related Articles: Navigating Windows 10 Troubles: A Comprehensive Guide to Safe Mode
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating Windows 10 Troubles: A Comprehensive Guide to Safe Mode. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating Windows 10 Troubles: A Comprehensive Guide to Safe Mode

Windows 10, despite its robustness, can sometimes encounter issues that hinder its smooth operation. These issues can range from minor inconveniences like sluggish performance to major system malfunctions that prevent the operating system from booting correctly. In such scenarios, a valuable troubleshooting tool emerges: Safe Mode.
Safe Mode is a diagnostic environment that loads Windows with a minimal set of drivers and programs. This stripped-down state allows users to troubleshoot problems that may arise due to conflicting or corrupted drivers, malware infections, or faulty software installations. By booting into Safe Mode, users can isolate the root cause of the issue and address it effectively.
Understanding the Significance of Safe Mode:
Safe Mode serves as a critical troubleshooting tool for several reasons:
- Identifying and Resolving Software Conflicts: When encountering system instability or crashes, Safe Mode helps pinpoint the culprit. By excluding unnecessary drivers and programs, users can determine if a specific application or driver is causing the issue.
- Removing Malware: Malware often interferes with system processes, making it difficult to remove through conventional methods. Safe Mode, with its limited environment, allows users to run anti-malware scans and eliminate persistent threats.
- Troubleshooting Driver Issues: Drivers are software programs that enable communication between the operating system and hardware components. Corrupted or incompatible drivers can lead to system errors. Safe Mode facilitates driver updates or rollbacks, resolving conflicts and restoring stability.
- Performing System Repairs: Certain system repairs, like restoring system files or reinstalling Windows, require a clean environment. Safe Mode provides this environment, minimizing interference from other programs and ensuring a smooth repair process.
Accessing Safe Mode in Windows 10: A Step-by-Step Guide
There are multiple ways to access Safe Mode in Windows 10. The most common methods involve utilizing the "F" keys during the boot process. Here’s a breakdown of each method:
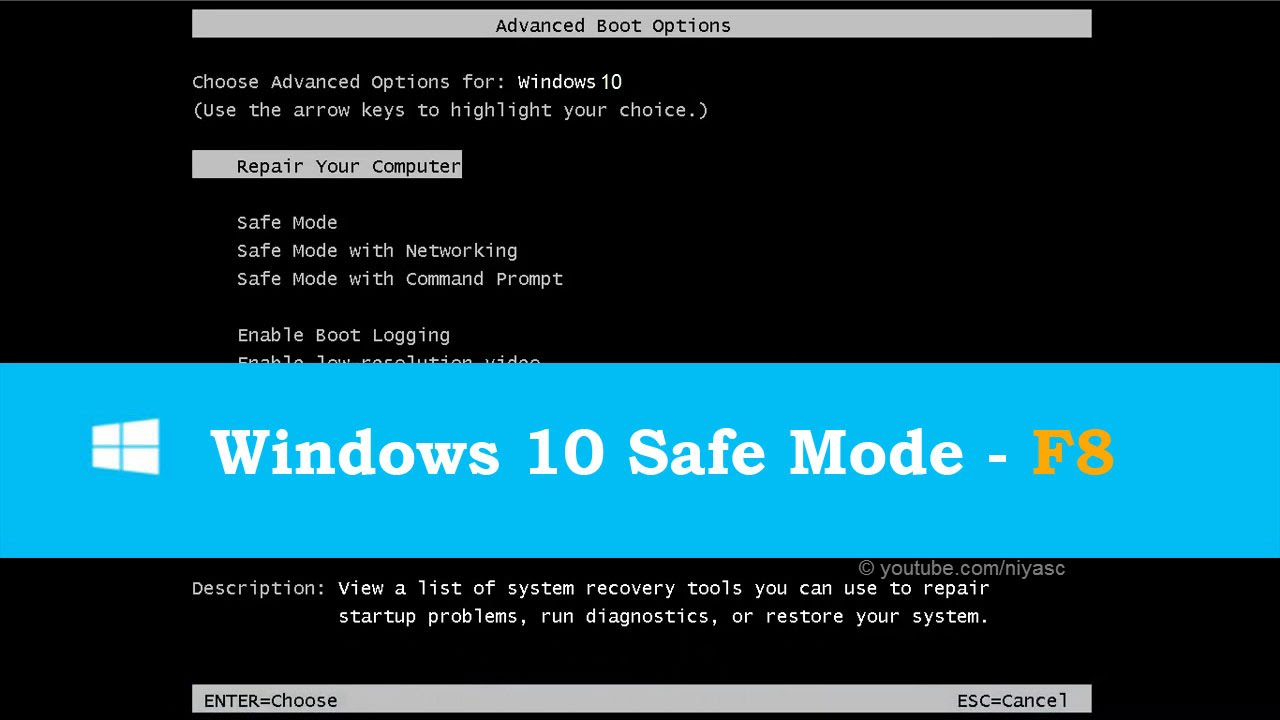
Method 1: Using the "F8" Key (Legacy Boot)
- Restart the Computer: Power down the computer and restart it.
- Press and Hold "F8": As the computer starts, repeatedly press and hold the "F8" key. This will bring up the Advanced Boot Options menu.
- Select "Safe Mode": Use the arrow keys to navigate to "Safe Mode" and press Enter.
- Wait for Windows to Load: The computer will boot into Safe Mode.
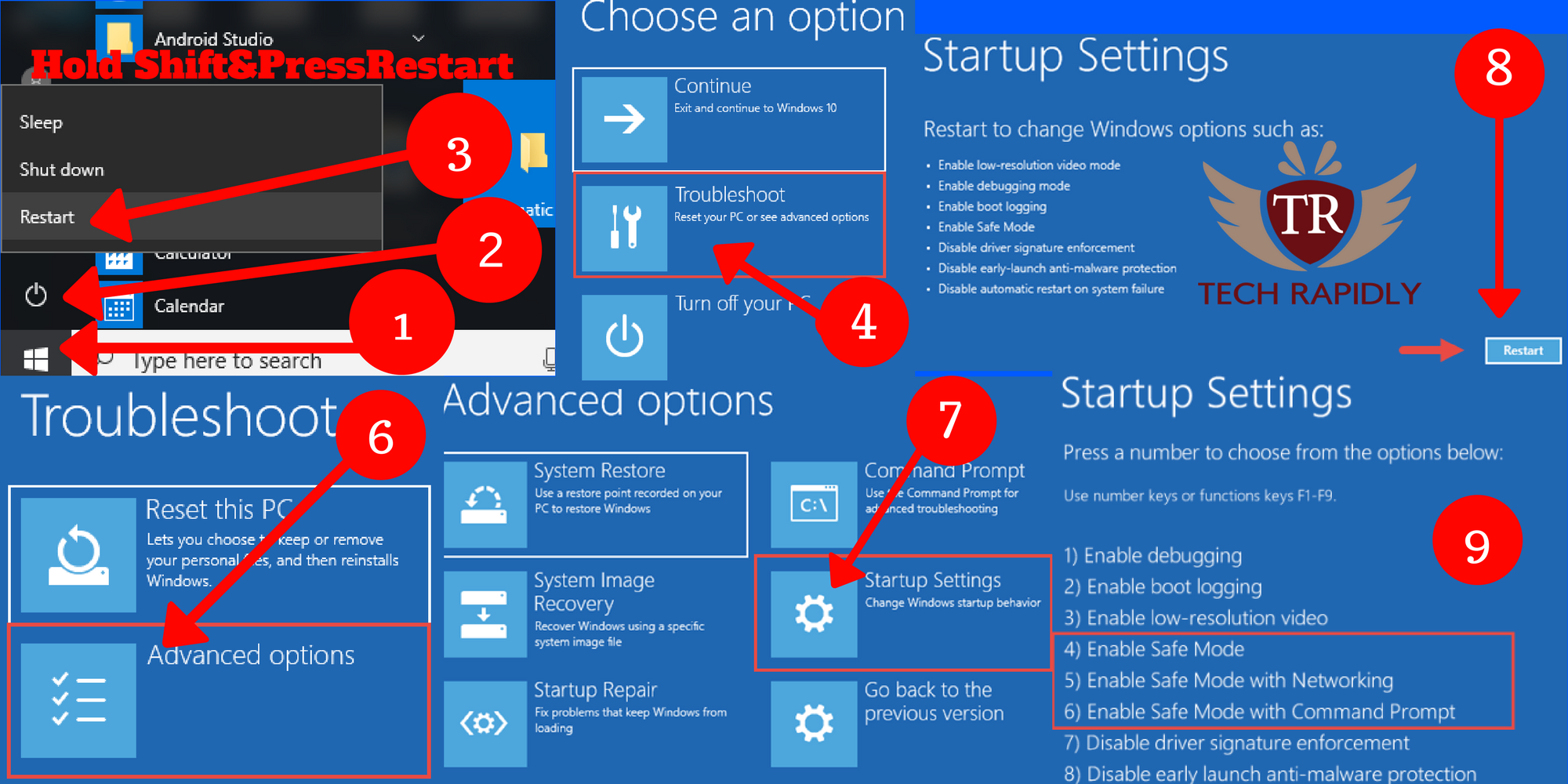
Method 2: Using the "Shift" Key and "Restart" Option (Modern Boot)
- Open the "Start" Menu: Click the Windows icon in the taskbar.
- Select "Power": Click the power icon, located at the bottom left corner of the Start Menu.
- Hold "Shift" and Click "Restart": While holding the Shift key, click the "Restart" option.
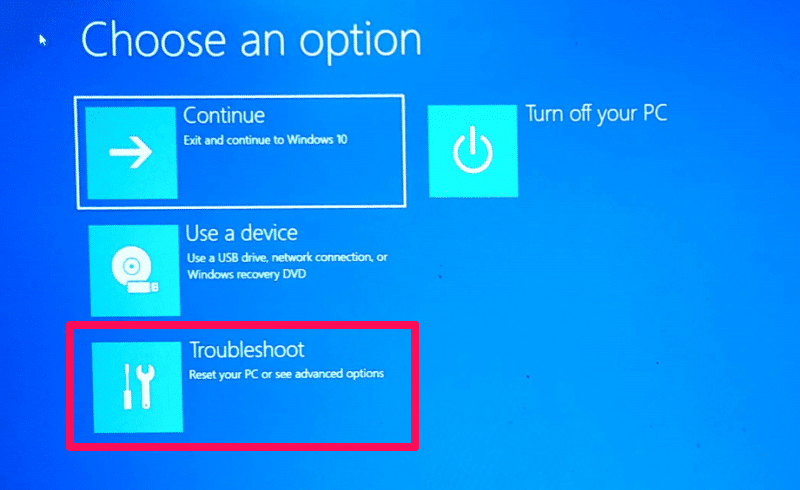
- Choose "Troubleshoot": In the blue screen, select "Troubleshoot".
- Select "Advanced Options": Click on "Advanced Options".
- Select "Startup Settings": Choose "Startup Settings".
- Click "Restart": Click the "Restart" button to reboot the computer.
- Select "Safe Mode": After the computer restarts, you’ll see a list of boot options. Select "Safe Mode" using the number keys.
Method 3: Using the "Command Prompt" (Advanced)
- Access the "Troubleshoot" Menu: Follow steps 1-5 from Method 2.
- Open "Command Prompt": Select "Command Prompt" from the Advanced Options menu.
- Enter "bcdedit /set default bootmenupolicy legacy": This command switches the boot mode to legacy.
- Restart the Computer: Reboot the computer.
- Use "F8" Key: After restarting, use the "F8" key to access the Advanced Boot Options menu, as described in Method 1.
Important Considerations:
- Legacy Boot vs. Modern Boot: The availability of the "F8" key method depends on the boot mode. If your computer uses UEFI/GPT, the "F8" key may not work. In such cases, the "Shift" and "Restart" method is recommended.
- Timing is Crucial: Pressing the "F8" key repeatedly and quickly is essential for accessing the Advanced Boot Options menu.
- Safe Mode Variations: Safe Mode offers variations like Safe Mode with Networking and Safe Mode with Command Prompt. These options provide additional features for troubleshooting.
FAQs: Unraveling Common Queries Regarding Safe Mode
Q1: What is the difference between Safe Mode and Normal Mode?
Safe Mode operates with a limited set of drivers and programs, while Normal Mode runs the full operating system with all drivers and applications enabled.
Q2: How long does it take to boot into Safe Mode?
The boot time for Safe Mode is typically longer than Normal Mode due to the reduced number of loaded components.
Q3: Can I access the internet in Safe Mode?
Depending on the Safe Mode variation selected, internet access may or may not be available. Safe Mode with Networking provides internet connectivity.
Q4: Can I use Safe Mode to recover lost data?
Safe Mode is not designed for data recovery. Data recovery tools should be used for this purpose.
Q5: Can I install software in Safe Mode?
Installing software in Safe Mode is generally not recommended as it may lead to conflicts or instability.
Tips for Effective Safe Mode Utilization:
- Document the Issue: Before entering Safe Mode, note down the specific problem you’re experiencing.
- Run Anti-Malware Scans: Use a reliable anti-malware program to scan for and remove any potential threats.
- Update or Rollback Drivers: If driver conflicts are suspected, update or rollback drivers through Device Manager.
- Restore System Files: If necessary, use the System Restore feature to revert to a previous system state.
- Reinstall Windows: If all else fails, reinstalling Windows can resolve persistent issues.
Conclusion: Empowering Users to Overcome Windows 10 Challenges
Safe Mode serves as a powerful tool for troubleshooting various Windows 10 problems. Its ability to isolate issues, remove malware, and facilitate system repairs empowers users to overcome challenges and restore their systems to optimal performance. By understanding the different methods of accessing Safe Mode and its variations, users can effectively navigate troubleshooting scenarios and ensure the smooth operation of their Windows 10 environment.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating Windows 10 Troubles: A Comprehensive Guide to Safe Mode. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!