Navigating the Transition: Downgrading from Windows 11 to Windows 10
Related Articles: Navigating the Transition: Downgrading from Windows 11 to Windows 10
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Transition: Downgrading from Windows 11 to Windows 10. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Transition: Downgrading from Windows 11 to Windows 10
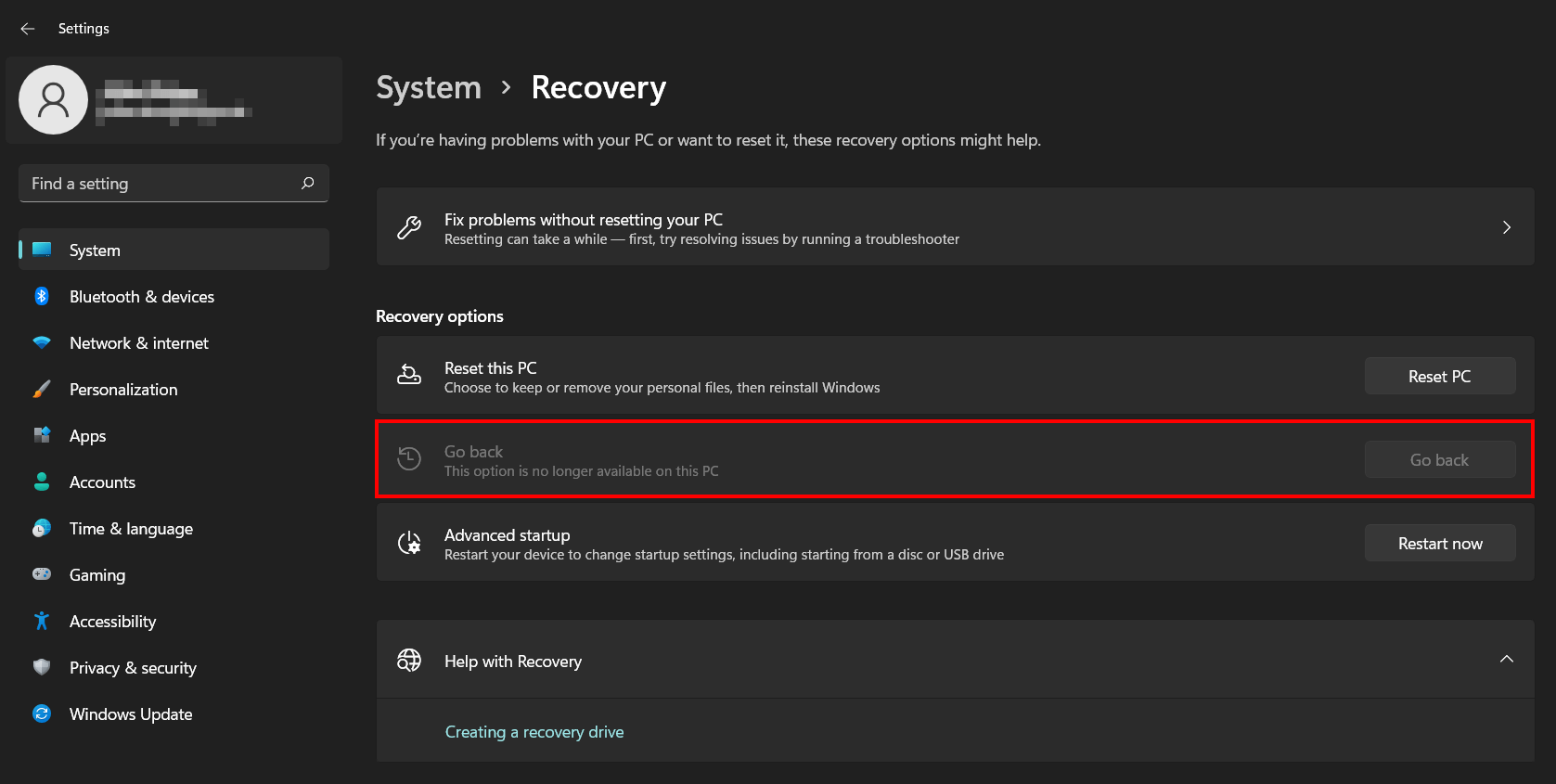
The release of Windows 11 brought a wave of excitement and anticipation. However, for some users, the new operating system hasn’t lived up to expectations, leading them to seek a return to the familiar terrain of Windows 10. This decision, while seemingly straightforward, requires careful consideration and a methodical approach. This article aims to demystify the process of downgrading from Windows 11 to Windows 10, outlining the steps involved, potential challenges, and crucial considerations.
Understanding the Decision:
Before embarking on the downgrade journey, it’s essential to understand the rationale behind this choice. While Windows 11 boasts new features and a refined aesthetic, it also introduces compatibility issues, performance concerns, and a learning curve for users accustomed to the Windows 10 interface.
Factors influencing the decision to downgrade include:
- Hardware incompatibility: Windows 11 has specific hardware requirements that may not be met by older systems, leading to performance issues or outright incompatibility.
- Software compatibility: Certain software applications may not be compatible with Windows 11, hindering productivity and functionality.
- User preference: Some users find the new interface and features of Windows 11 less intuitive or appealing compared to Windows 10.
- Performance concerns: Windows 11 may experience performance issues on older or less powerful systems, impacting responsiveness and overall user experience.
The Downgrade Process:
Downgrading from Windows 11 to Windows 10 is a multi-step process that involves careful planning and execution. The process can be broadly categorized into three key phases:
1. Preparation:
- Backup: Prior to any system alterations, it is imperative to create a complete backup of all important data. This includes files, documents, applications, and system settings. This backup serves as a safety net in case of unexpected issues during the downgrade process.
- Compatibility Check: Verify the compatibility of existing hardware and software with Windows 10. Ensure all drivers and applications are compatible with the older operating system.
- Product Key: Locate the Windows 10 product key. This key is crucial for activating Windows 10 after the downgrade. If the product key is unavailable, it may be necessary to contact Microsoft for assistance.
- System Requirements: Confirm that the system meets the minimum requirements for Windows 10. This includes processor, RAM, storage space, and graphics card specifications.
2. Downgrade Execution:
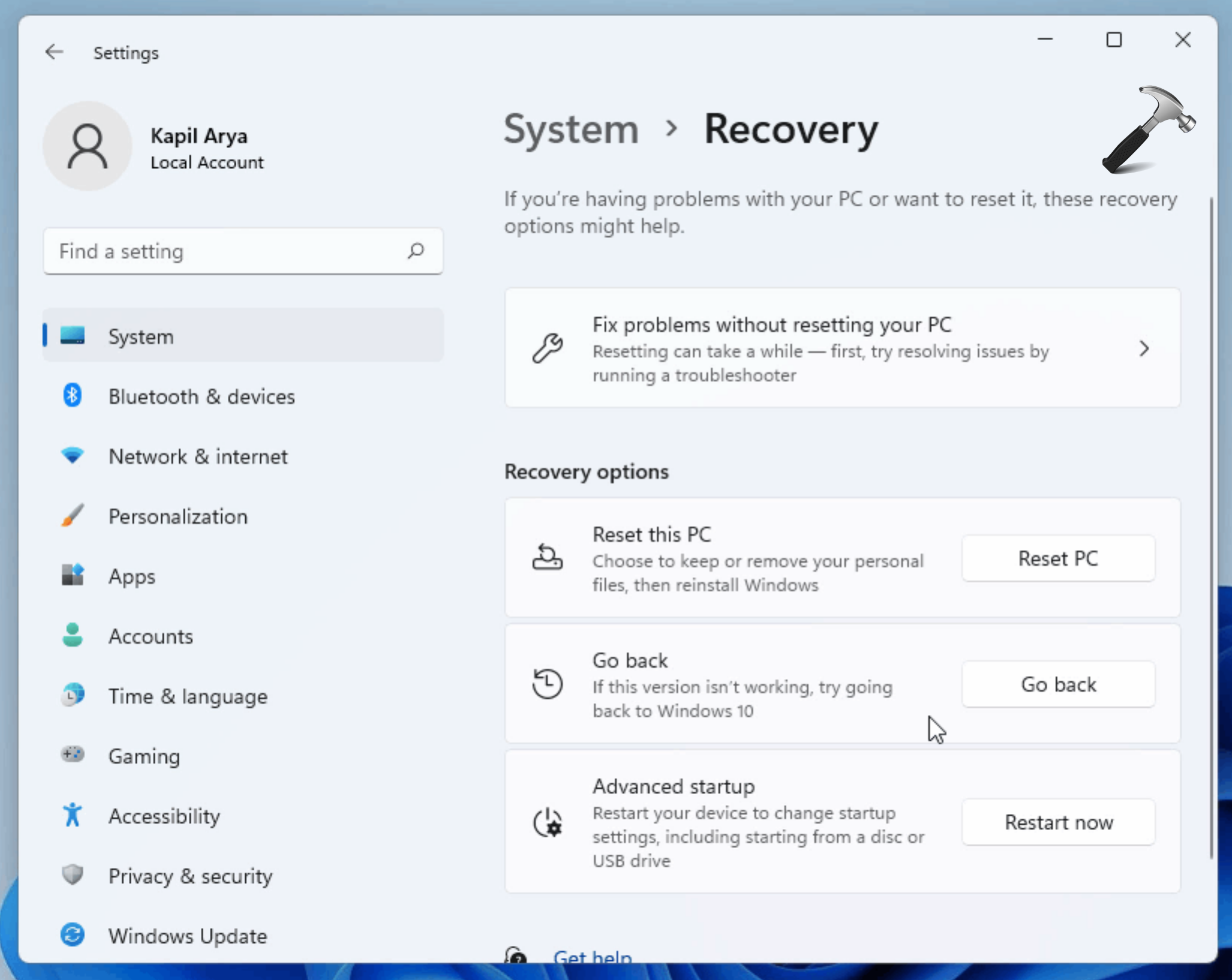
- Clean Installation: The most reliable way to downgrade is through a clean installation of Windows 10. This involves formatting the hard drive and installing Windows 10 from scratch.
- Using a USB Drive: Create a bootable USB drive containing the Windows 10 installation media. This can be downloaded from Microsoft’s official website.
- Boot from USB: During system startup, change the boot order in the BIOS to prioritize the USB drive. This will initiate the Windows 10 installation process.
- Installation: Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the installation. This includes selecting the desired language, region, and keyboard layout.
- Product Key Activation: Enter the Windows 10 product key during the installation process to activate the operating system.
3. Post-Downgrade:
- Driver Installation: Install the necessary drivers for hardware components like graphics cards, sound cards, and network adapters. These drivers can be obtained from the manufacturer’s website or through Windows Update.
- Software Installation: Reinstall applications that were previously installed on the system.
- Data Restoration: Restore the backed-up data from the backup created in the preparation phase.
- System Optimization: Run system optimization tools to ensure the system is running efficiently. This includes checking for updates, clearing temporary files, and defragmenting the hard drive.
Potential Challenges:
While the downgrade process is generally straightforward, certain challenges may arise:
- Driver Compatibility: Some hardware drivers may not be readily available for Windows 10, potentially requiring manual searching and installation.
- Software Compatibility: Certain software applications may not be compatible with Windows 10, requiring alternative solutions or updates.
- Data Loss: If backups are not properly created or restored, data loss may occur during the downgrade process.
- Activation Issues: Activation issues may arise if the Windows 10 product key is lost or invalid.
FAQs:
Q: Can I downgrade from Windows 11 to Windows 10 without losing my data?
A: While it is possible to perform a downgrade without data loss, it is highly recommended to create a complete backup of all important data before proceeding. This will ensure data recovery in case of unexpected issues.
Q: Can I downgrade to a previous version of Windows 10?
A: Downgrading to a previous version of Windows 10 is not possible through the standard downgrade process. A clean installation of Windows 10 will install the latest version available at the time.
Q: What if I don’t have my Windows 10 product key?
A: If you do not have your Windows 10 product key, you may need to contact Microsoft for assistance in recovering it or purchasing a new key.
Q: Can I upgrade back to Windows 11 after downgrading to Windows 10?
A: Yes, you can upgrade back to Windows 11 after downgrading to Windows 10. However, it’s essential to ensure that your system meets the minimum requirements for Windows 11.
Tips:
- Thorough Backup: Prioritize creating a complete backup of all important data before initiating the downgrade process.
- Compatibility Verification: Confirm the compatibility of hardware and software with Windows 10 prior to the downgrade.
- Clean Installation: For the most reliable outcome, opt for a clean installation of Windows 10.
- Driver Updates: Install the latest drivers for all hardware components after the downgrade.
- Software Updates: Update all software applications to ensure compatibility with Windows 10.
- System Optimization: Run system optimization tools to improve system performance after the downgrade.
Conclusion:
Downgrading from Windows 11 to Windows 10 is a decision that should be made with careful consideration. While the process can be technically challenging, following the outlined steps and taking necessary precautions can ensure a smooth transition. Remember to prioritize data backup, driver compatibility, and system optimization for a seamless and successful downgrade experience.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Transition: Downgrading from Windows 11 to Windows 10. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!