Navigating the Transition: A Comprehensive Guide to Downgrading from Windows 11 to Windows 10
Related Articles: Navigating the Transition: A Comprehensive Guide to Downgrading from Windows 11 to Windows 10
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Transition: A Comprehensive Guide to Downgrading from Windows 11 to Windows 10. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Transition: A Comprehensive Guide to Downgrading from Windows 11 to Windows 10

While Windows 11 has been met with a mixed reception, some users may find themselves yearning for the familiarity and stability of its predecessor, Windows 10. This guide aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of the process of downgrading from Windows 11 to Windows 10, addressing potential concerns and outlining the steps involved.
Understanding the Rationale for Downgrading
The decision to revert to Windows 10 stems from various factors, each unique to the individual user. Some common reasons include:
- Hardware Compatibility: Windows 11 imposes stricter system requirements, potentially rendering older hardware incompatible. This can lead to performance issues and instability, compelling users to seek a more compatible operating system.
- Software Compatibility: Certain software applications may not be fully compatible with Windows 11, hindering productivity and workflow. The absence of essential software can be a significant deterrent for some users.
- User Interface Preference: Windows 11 introduces a redesigned user interface that may not resonate with all users. The familiar layout and functionalities of Windows 10 might be preferred for its simplicity and ease of use.
- Performance Concerns: Some users report experiencing performance degradation or increased resource consumption after upgrading to Windows 11. This can impact overall system responsiveness and affect the user experience.
- Security and Stability Issues: While Windows 11 boasts enhanced security features, some users might encounter unforeseen security vulnerabilities or system instability. Downgrading to Windows 10 could offer a more stable and secure environment.
The Downgrade Process: A Step-by-Step Guide
The process of downgrading from Windows 11 to Windows 10 involves a series of steps, requiring careful execution and a backup of essential data.
1. System Requirements and Compatibility:
- Verify that your computer meets the minimum system requirements for Windows 10. Refer to Microsoft’s official website for detailed specifications.
- Ensure that your hardware drivers are compatible with Windows 10. Check the manufacturer’s website for the latest driver updates.
2. Data Backup:
- Create a complete backup of your important files, including documents, photos, videos, and other critical data. This is crucial as the downgrade process might erase existing data.
- Consider using a reliable backup solution like external hard drives, cloud storage services, or specialized backup software.
3. Windows 10 Installation Media:
- Obtain a bootable USB drive or DVD containing a valid Windows 10 installation image. This can be downloaded from Microsoft’s website.
- Ensure that the installation media matches the version of Windows 10 you wish to install (Home, Pro, Enterprise).
4. Downgrade Procedure:
- Clean Install: The most thorough approach involves performing a clean install of Windows 10, erasing all existing data and reinstalling the operating system. This ensures a fresh start and eliminates potential compatibility issues.
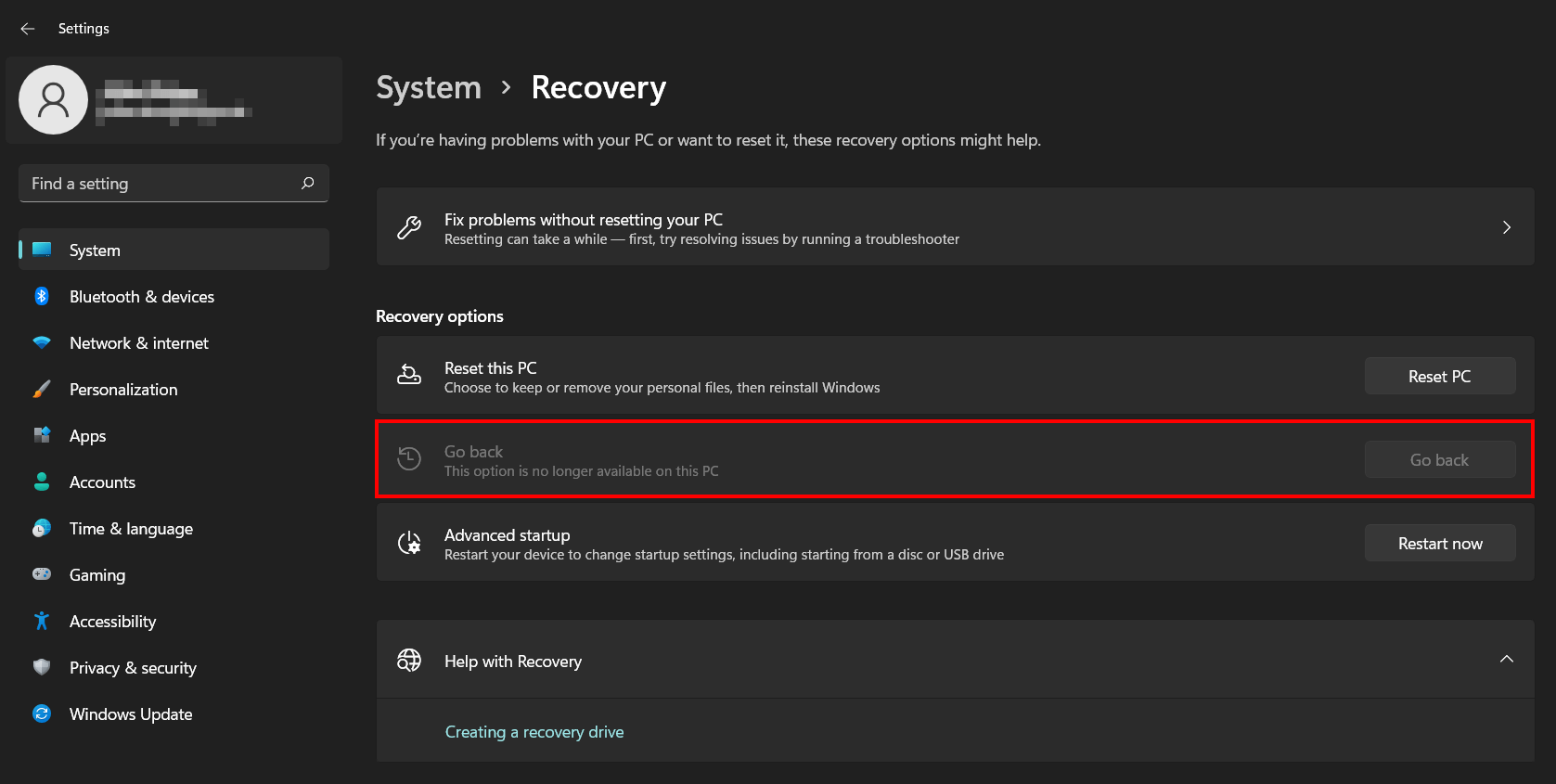
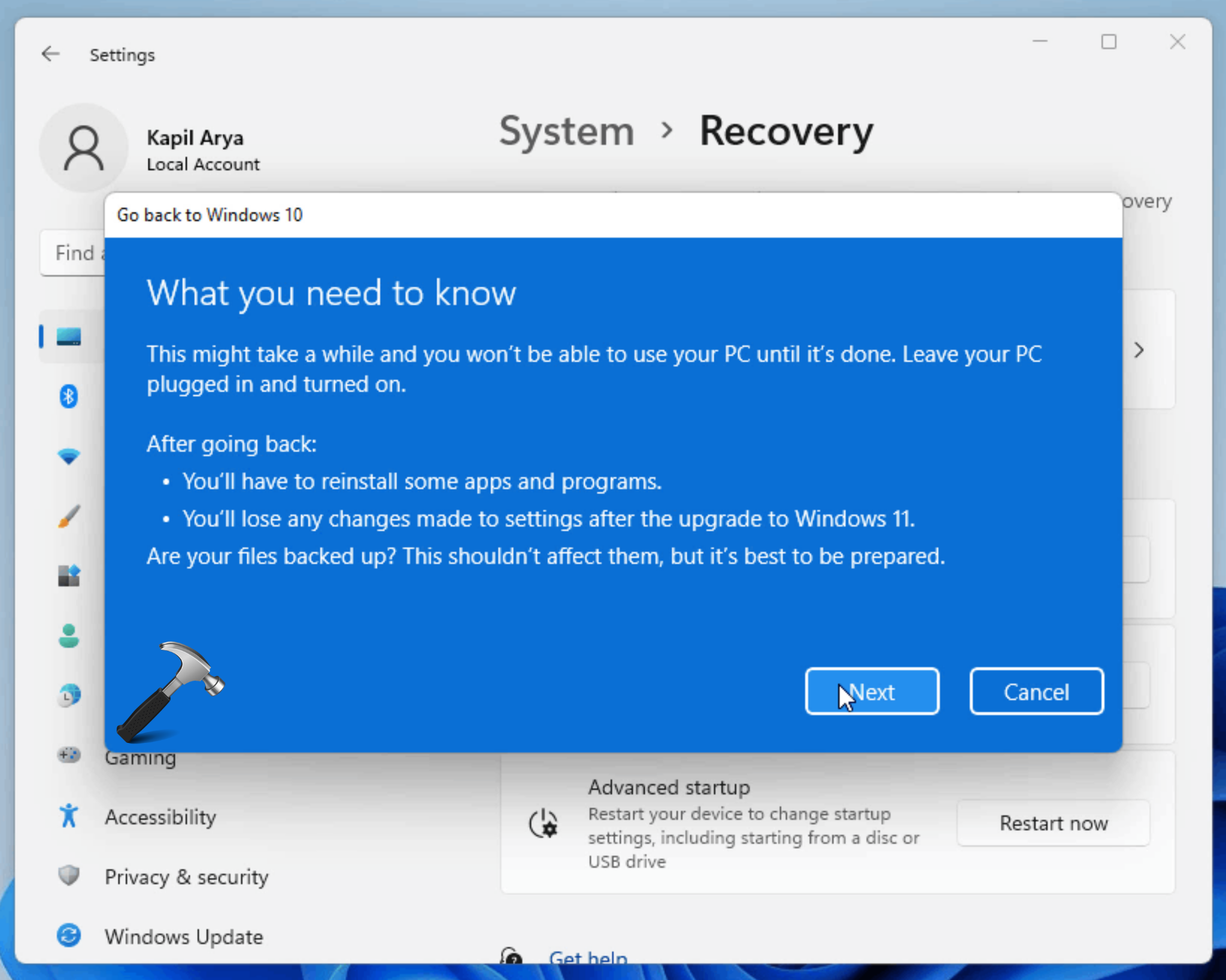
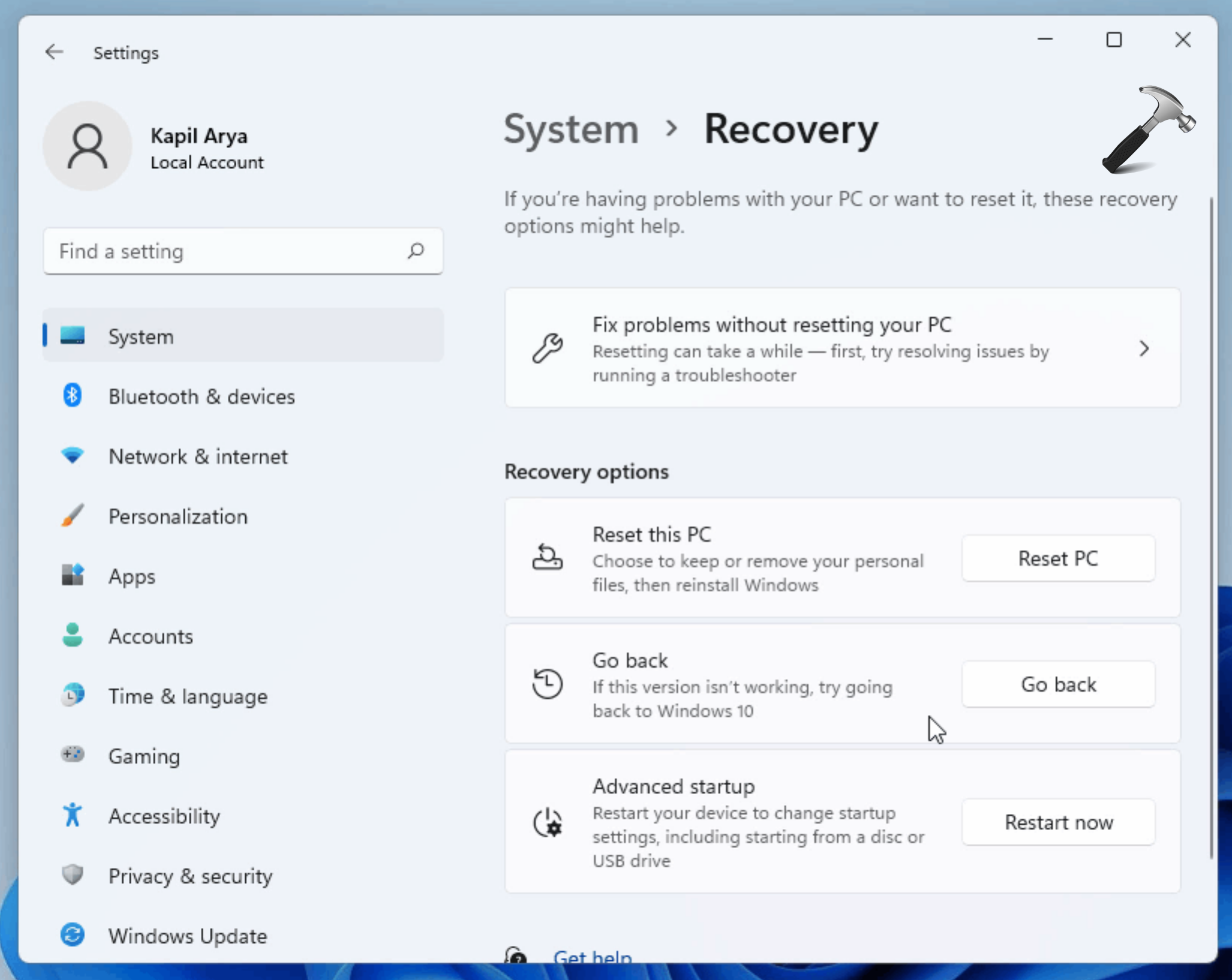
- Upgrade to Windows 10: If a clean install is not desired, Microsoft offers a downgrade option through the "Windows 10 Go Back" feature. This feature allows users to revert to their previous Windows 10 installation within a specific timeframe.
- Using a Recovery Drive: If you have a recovery drive created during the Windows 11 installation process, you can utilize it to restore your system to a previous state, effectively downgrading to Windows 10.
5. Post-Downgrade Configuration:
- After the downgrade process is complete, update your system drivers to ensure optimal performance.
- Install essential software applications and restore your backed-up data.
- Configure your system settings and personalize your user experience according to your preferences.
Potential Challenges and Considerations
The downgrade process may present certain challenges:
- Data Loss: While backup procedures mitigate data loss, there’s always a risk of accidental data deletion during the process.
- Software Compatibility: Some software applications might require specific versions or configurations for optimal functionality in Windows 10.
- Driver Issues: Certain hardware drivers may not be fully compatible with Windows 10, leading to performance issues or device malfunctions.
- System Performance: While Windows 10 might offer improved performance compared to Windows 11, it’s essential to ensure your system meets the minimum requirements for optimal performance.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Is it possible to downgrade from Windows 11 to Windows 10 without losing data?
A: While a clean install typically erases all data, using the "Windows 10 Go Back" feature or a recovery drive might preserve your existing data. However, it’s highly recommended to create a backup before attempting the downgrade process.
Q: How long does the downgrade process take?
A: The duration of the downgrade process varies depending on the chosen method and system configuration. A clean install might take longer than using the "Windows 10 Go Back" feature or a recovery drive.
Q: What happens to my Windows 11 license after downgrading?
A: Your Windows 11 license will remain valid after downgrading to Windows 10. You can activate Windows 10 using the same product key.
Q: Can I upgrade back to Windows 11 after downgrading to Windows 10?
A: Yes, you can upgrade back to Windows 11 from Windows 10 using the Windows Update feature. However, ensure that your system meets the minimum requirements for Windows 11.
Tips for a Smooth Downgrade
- Thorough Backup: Create a comprehensive backup of your data before attempting the downgrade process.
- Check System Requirements: Ensure that your hardware meets the minimum system requirements for Windows 10.
- Update Drivers: Ensure that your hardware drivers are compatible with Windows 10.
- Use Official Media: Download the Windows 10 installation media from Microsoft’s official website.
- Seek Professional Assistance: If you encounter difficulties or have concerns about the downgrade process, consider seeking professional assistance from a qualified technician.
Conclusion
Downgrading from Windows 11 to Windows 10 can be a viable solution for users facing compatibility issues, performance concerns, or a preference for the familiar Windows 10 interface. However, it’s essential to approach the process with caution, carefully considering the potential challenges and ensuring a thorough backup of essential data. By following the outlined steps and taking necessary precautions, users can navigate the downgrade process effectively and transition back to a more suitable operating system.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Transition: A Comprehensive Guide to Downgrading from Windows 11 to Windows 10. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!