Navigating the Post-Factory Reset Login Issue in Windows 10
Related Articles: Navigating the Post-Factory Reset Login Issue in Windows 10
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Post-Factory Reset Login Issue in Windows 10. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Navigating the Post-Factory Reset Login Issue in Windows 10
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Navigating the Post-Factory Reset Login Issue in Windows 10
- 3.1 Understanding the Root of the Problem
- 3.2 Troubleshooting and Solutions
- 3.3 FAQs
- 3.4 Tips for a Smooth Post-Factory Reset Experience
- 3.5 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Navigating the Post-Factory Reset Login Issue in Windows 10
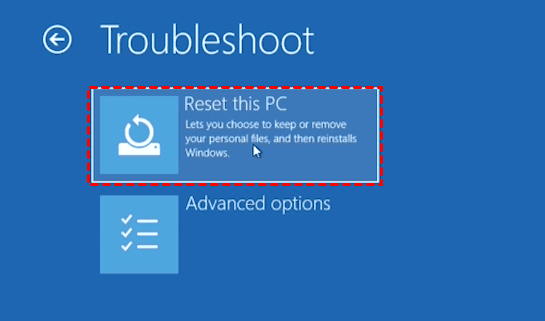
A factory reset is often seen as a solution for various Windows 10 problems, promising a fresh start and a clean slate. However, the process can sometimes lead to unexpected hurdles, particularly when it comes to logging in after the reset. This situation can be frustrating, leaving users locked out of their own system. This article delves into the common reasons behind this issue, offering comprehensive solutions and preventative measures to ensure a smooth post-factory reset experience.
Understanding the Root of the Problem
The inability to log in after a factory reset in Windows 10 can stem from a variety of factors, each requiring a specific approach for resolution. These include:
1. Incorrect or Forgotten Credentials:
The most common culprit is simply forgetting the password associated with the Microsoft account used during the reset. This scenario often arises when the user has multiple accounts or has not used the specific account in a while.
2. Account Deactivation or Suspension:
A deactivated or suspended Microsoft account, due to security reasons or inactivity, can prevent access to the system. This situation can occur even if the account credentials are correctly remembered.
3. Hardware Issues:
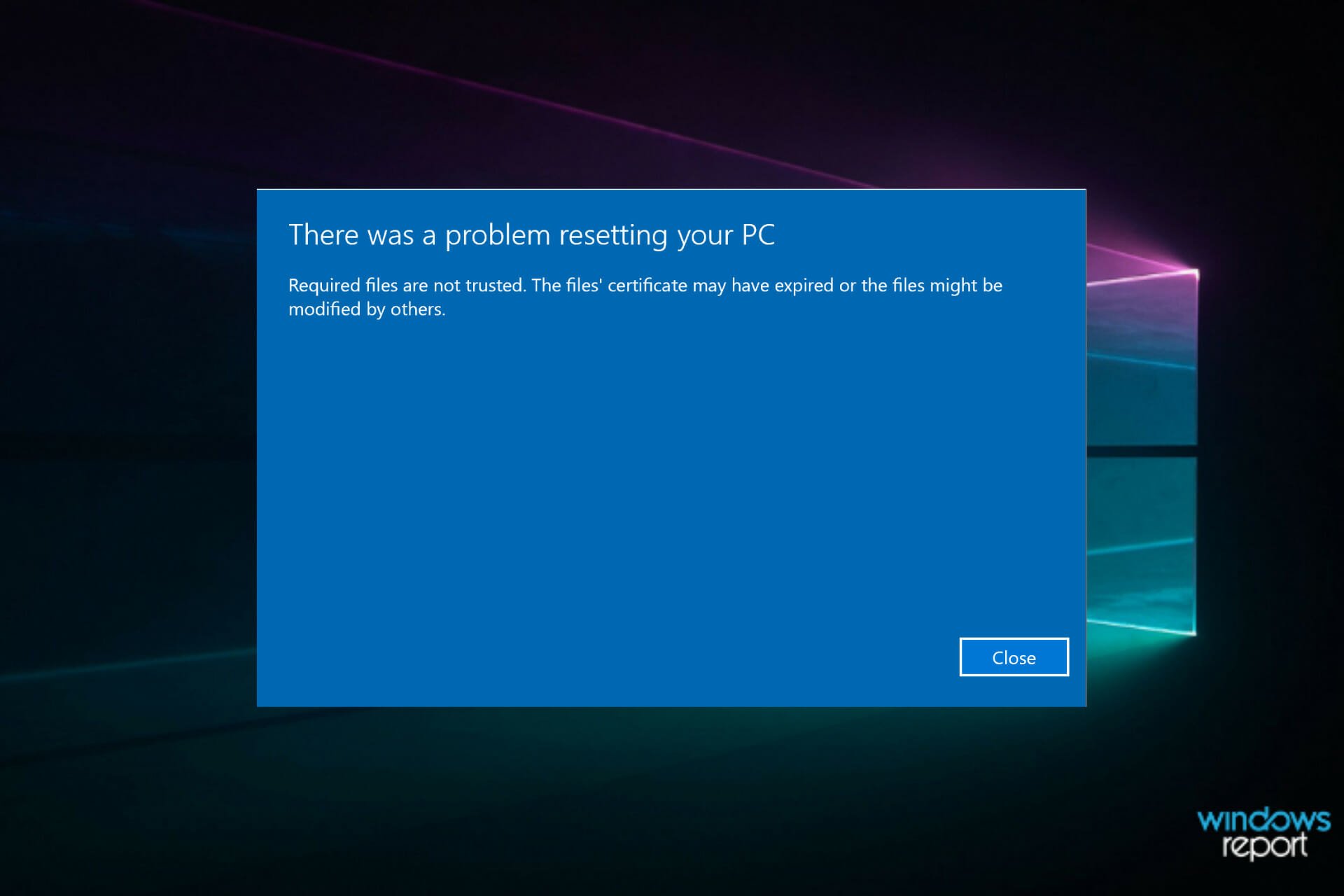
Problems with the hardware, particularly the hard drive, can hinder the reset process and cause login difficulties. A corrupted hard drive or a faulty drive controller can lead to data loss and system instability.
4. Boot Sector Errors:
Errors in the boot sector, the part of the hard drive that contains essential information for booting the system, can prevent Windows 10 from loading correctly, making it impossible to log in.
5. Corrupted System Files:
Despite the reset, corrupted system files might persist, interfering with the login process. This scenario can occur if the reset was interrupted or if the system files were damaged before the reset.
6. Incorrect Time and Date Settings:
While seemingly minor, incorrect time and date settings can lead to unexpected errors, including login issues. This can occur due to a faulty system clock or a recent power outage.
7. Conflicting Software:
Some software, especially security programs or system utilities, can interfere with the reset process and cause login problems. This can happen if the software is not compatible with the new system configuration.
8. Network Connectivity Issues:
A stable internet connection is crucial for successful login after a factory reset. Connectivity problems can prevent the system from verifying the user’s account and granting access.
9. UEFI/BIOS Settings:
The system’s UEFI/BIOS settings, which control the boot order and other hardware configurations, can affect the login process. Incorrect settings might prevent the system from booting correctly, leading to login issues.
Troubleshooting and Solutions
Navigating the login issue after a factory reset requires a methodical approach, systematically eliminating possible causes and applying appropriate solutions. The following steps can help resolve the problem:
1. Verify Account Credentials:
- Double-check the email address and password: Ensure that the entered credentials are correct and match the Microsoft account used during the reset.
- Attempt password recovery: If the password is forgotten, use the Microsoft account recovery process to reset it.
- Check for account status: Access the Microsoft account website to verify the account status and ensure it is not deactivated or suspended.
2. Troubleshoot Hardware Issues:
- Run a hardware diagnostic: Utilize the built-in hardware diagnostics tool to check for any hardware errors or malfunctions.
- Check for loose connections: Ensure all cables and connections are securely plugged in, especially those related to the hard drive.
- Replace the hard drive (if necessary): If hardware diagnostics indicate a faulty hard drive, consider replacing it with a new one.
3. Repair Boot Sector Errors:
- Use a bootable USB drive: Create a bootable USB drive with a Windows installation media.
- Access the command prompt: Boot from the USB drive and access the command prompt.
- Run the "bootrec" command: Execute the "bootrec /fixmbr" and "bootrec /fixboot" commands to repair the boot sector.
4. Repair Corrupted System Files:
- Run a system file checker (SFC) scan: Execute the "sfc /scannow" command in the command prompt to check and repair corrupted system files.
- Use a system image backup (if available): If a system image backup was created before the reset, restore the system to a previous point in time.
5. Correct Time and Date Settings:
- Access the date and time settings: Open the Windows settings and navigate to "Time & Language."
- Synchronize with an internet time server: Enable automatic time synchronization to ensure accurate time and date settings.
6. Remove Conflicting Software:
- Boot into Safe Mode: Start the system in Safe Mode to prevent conflicting software from loading.
- Uninstall conflicting software: Identify and uninstall any software that might be interfering with the login process.
7. Ensure Network Connectivity:
- Check the internet connection: Verify that the system has a stable internet connection.
- Troubleshoot network problems: If necessary, troubleshoot any network connectivity issues.
- Temporarily disable firewalls and antivirus software: Deactivate firewalls and antivirus software to eliminate potential conflicts.
8. Adjust UEFI/BIOS Settings:
- Access the UEFI/BIOS settings: Restart the system and access the UEFI/BIOS settings by pressing the appropriate key (usually F2 or Del).
- Check boot order: Ensure that the hard drive is listed as the first boot device.
- Disable secure boot (if necessary): In some cases, disabling secure boot might resolve the issue.
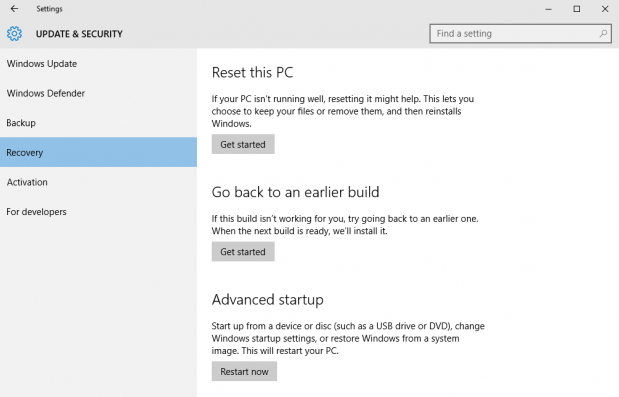
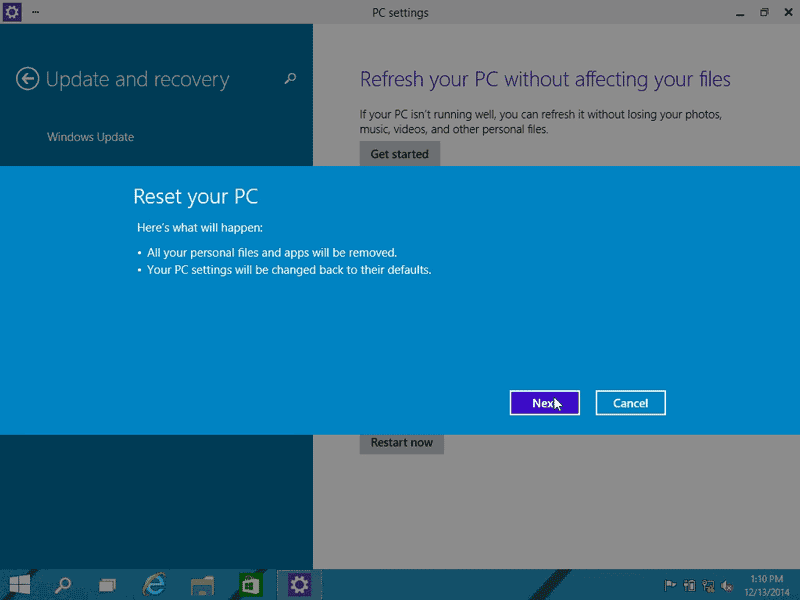
9. Reset Windows 10 (if all else fails):
- Perform a clean install: If all other solutions fail, consider performing a clean install of Windows 10. This will erase all data and reinstall the operating system from scratch.
FAQs
Q: What if I can’t remember my Microsoft account password?
A: Utilize the Microsoft account recovery process to reset your password. You will need to provide information associated with the account, such as your email address or phone number, to verify your identity.
Q: Is there a way to bypass the login screen after a factory reset?
A: Bypassing the login screen without valid credentials is not recommended and can compromise system security. It is crucial to use the appropriate recovery methods to regain access.
Q: Can I use a local account instead of a Microsoft account?
A: While it’s possible to create a local account after a factory reset, it is recommended to use a Microsoft account for better security and integration with other Microsoft services.
Q: What if my hard drive is faulty?
A: If the hard drive is faulty, it needs to be replaced. Contact a qualified technician or consult the manufacturer’s support for assistance.
Q: What is the best way to prevent login issues after a factory reset?
A: To prevent login issues after a factory reset, ensure you have a strong password for your Microsoft account, keep the account active, and regularly back up your important data.
Tips for a Smooth Post-Factory Reset Experience
- Back up important data: Before performing a factory reset, ensure that all critical data is backed up to an external drive or cloud storage.
- Use a strong password: Choose a strong and unique password for your Microsoft account to prevent unauthorized access.
- Keep the account active: Regularly log in to your Microsoft account to avoid inactivity-related deactivation.
- Update Windows regularly: Ensure that your Windows 10 installation is up-to-date with the latest updates to fix security vulnerabilities and improve system stability.
- Check for compatibility: Before installing any software, ensure it is compatible with your Windows 10 version and hardware configuration.
Conclusion
The inability to log in after a factory reset in Windows 10 can be a frustrating experience. However, by understanding the underlying causes and applying the appropriate troubleshooting steps, users can effectively resolve the issue and regain access to their system. By following the recommended tips and preventative measures, users can minimize the risk of encountering login problems after a factory reset, ensuring a smooth and hassle-free experience.
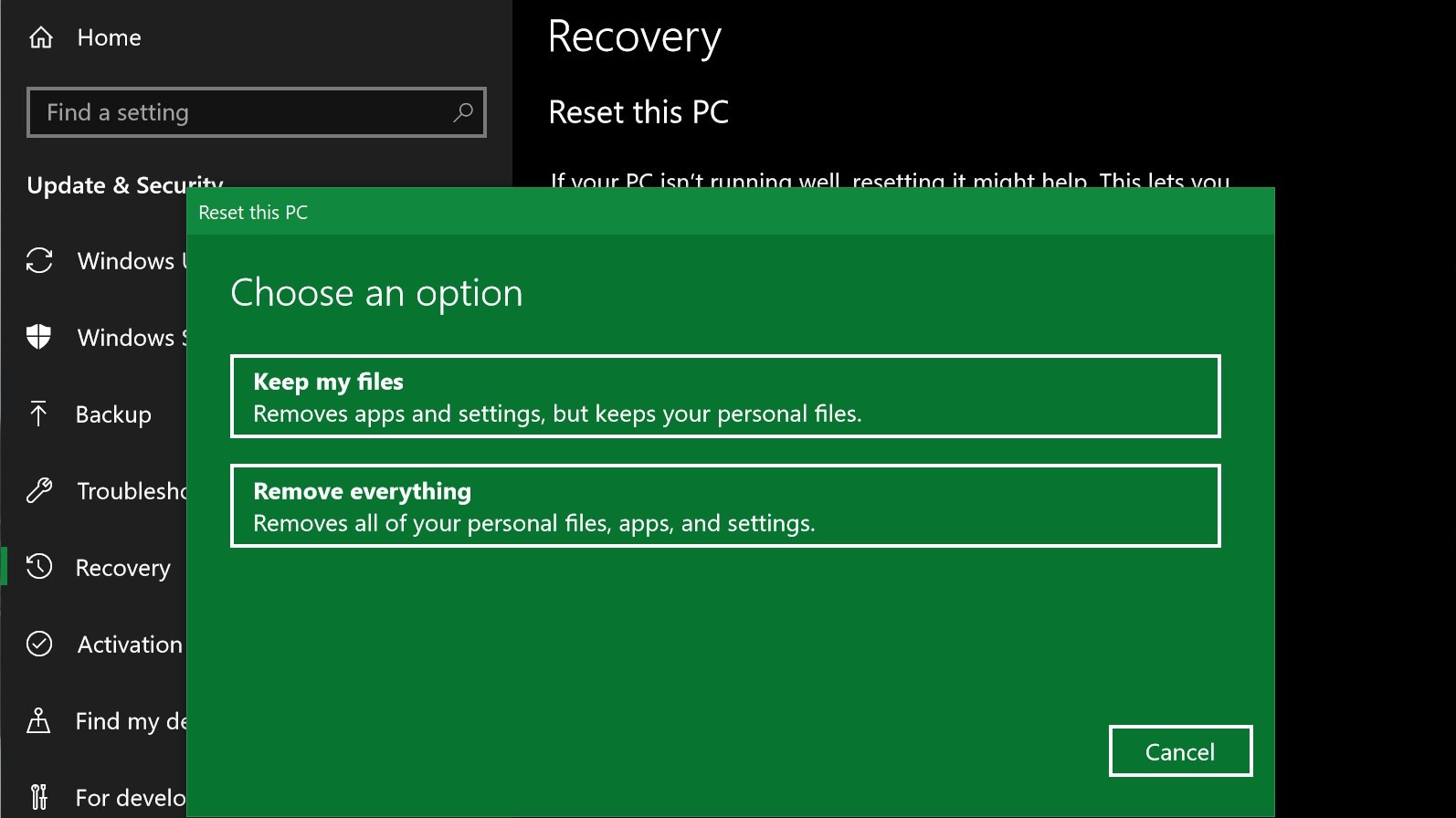
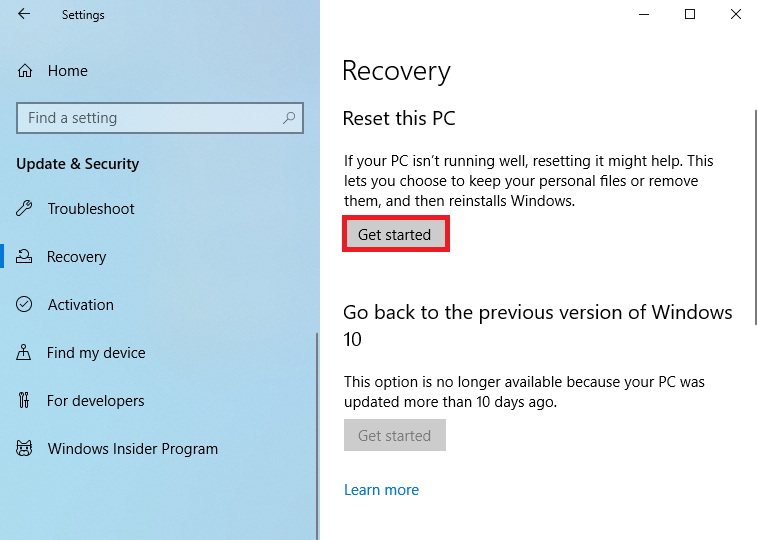
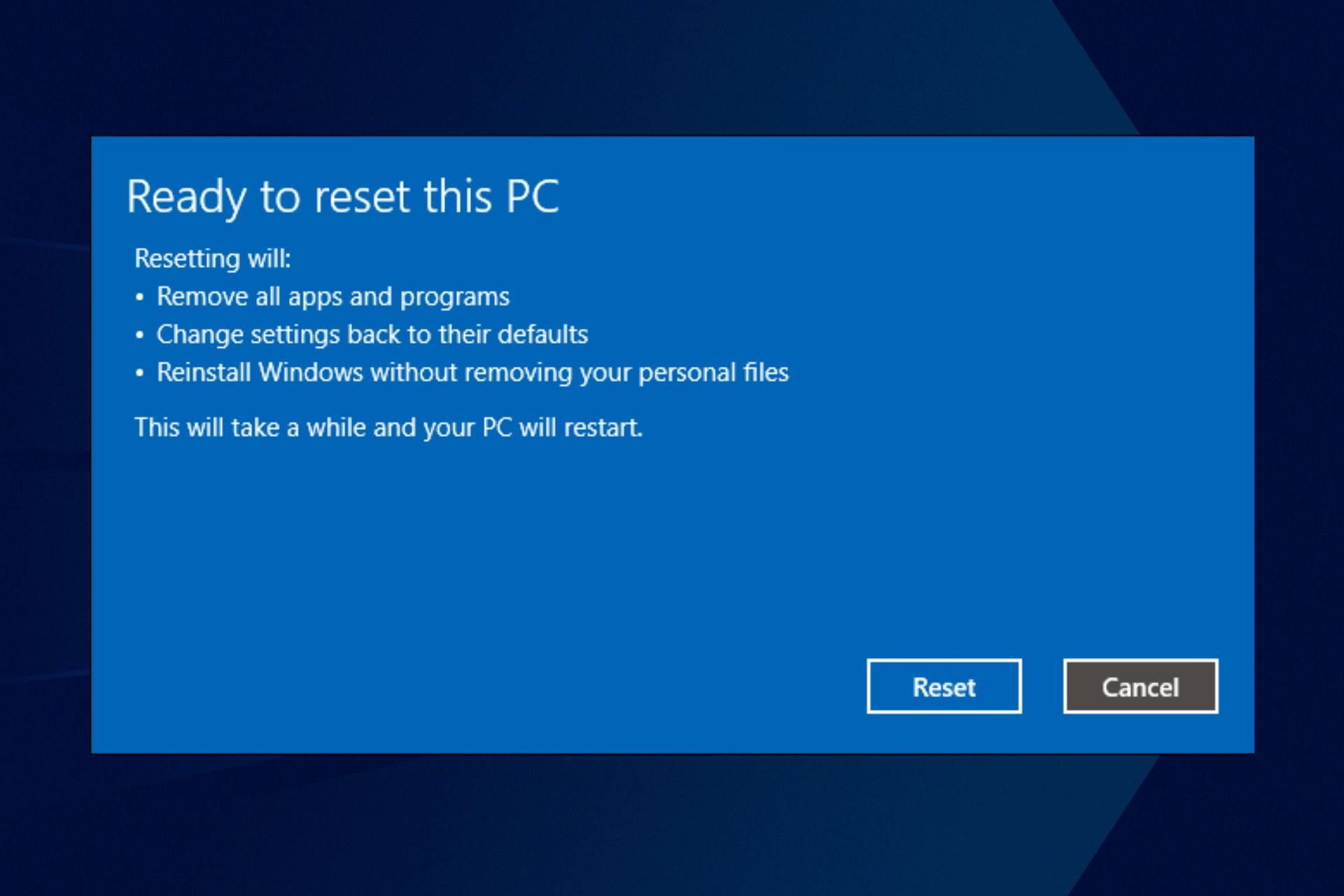


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Post-Factory Reset Login Issue in Windows 10. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!