Navigating the Labyrinth: Troubleshooting Windows 10 Boot Issues
Related Articles: Navigating the Labyrinth: Troubleshooting Windows 10 Boot Issues
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Labyrinth: Troubleshooting Windows 10 Boot Issues. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Labyrinth: Troubleshooting Windows 10 Boot Issues
The familiar Windows 10 logo, a beacon of productivity and entertainment, can vanish without warning, leaving users stranded in a boot purgatory. A computer refusing to load Windows 10 can be a frustrating and perplexing experience. However, understanding the potential causes and employing systematic troubleshooting techniques can empower users to address the issue effectively.
Understanding the Boot Process
Before delving into troubleshooting, it is essential to grasp the fundamental steps involved in the boot process. This process is a complex sequence of events, commencing with the power-on and culminating in the Windows desktop.
-
Power-On Self Test (POST): When the computer is powered on, the BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) performs a self-test, checking the hardware components for functionality.
-
Boot Device Selection: The BIOS then searches for a bootable device (usually a hard drive or an external storage device). The boot order, determining the priority of devices, can be configured in the BIOS settings.
-
Operating System Loading: If a bootable device is found, the BIOS loads the operating system’s boot files, initiating the loading process.
-
Windows Startup: Windows loads essential system files, checks for updates, and prepares the user interface, ultimately presenting the familiar desktop.
Common Culprits Behind Windows 10 Boot Failures
A multitude of factors can disrupt this intricate sequence, leading to a failed Windows 10 boot. The most common culprits include:
1. Hardware Malfunctions:
- Hard Drive Failure: A failing hard drive can lead to corrupted data, including the boot files, rendering the operating system inaccessible.
- RAM Issues: Faulty RAM modules can cause system instability and prevent Windows from loading properly.
- Loose Connections: Loose connections within the computer, such as those involving the hard drive, RAM, or motherboard, can disrupt the boot process.
- Power Supply Problems: A malfunctioning power supply can deprive the computer of sufficient power, causing intermittent failures or complete shutdowns.
2. Software Glitches:
- Corrupted Boot Files: Essential system files, including the boot manager, can become corrupted due to software errors, malware infections, or improper updates.
- Conflicting Drivers: Outdated or incompatible drivers can clash with the operating system, preventing a successful boot.
- Malware Infections: Malicious software can damage or disrupt the boot process, rendering Windows inaccessible.
- Improper Updates: Incomplete or faulty Windows updates can cause boot failures.
3. User Error:
- Incorrect BIOS Settings: Modifying BIOS settings without proper knowledge can lead to boot issues.
- Accidental Deletion of System Files: Deleting or modifying critical system files can severely disrupt the boot process.
Troubleshooting Windows 10 Boot Problems: A Step-by-Step Guide
Addressing boot failures requires a systematic approach, gradually eliminating potential causes. The following steps provide a comprehensive guide to troubleshooting Windows 10 boot issues:
1. Check for Basic Issues:
- Verify Power Supply: Ensure the power supply is connected correctly and functioning properly. Check for any loose connections.
- Examine Hardware: Visually inspect the internal components for loose connections, dust accumulation, or signs of damage.
- Test RAM: Run a memory test using the BIOS’s built-in diagnostic tools or a dedicated memory testing software.
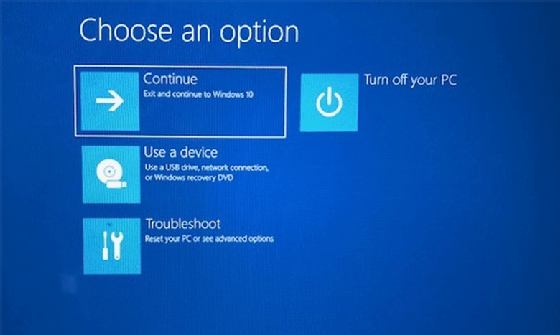
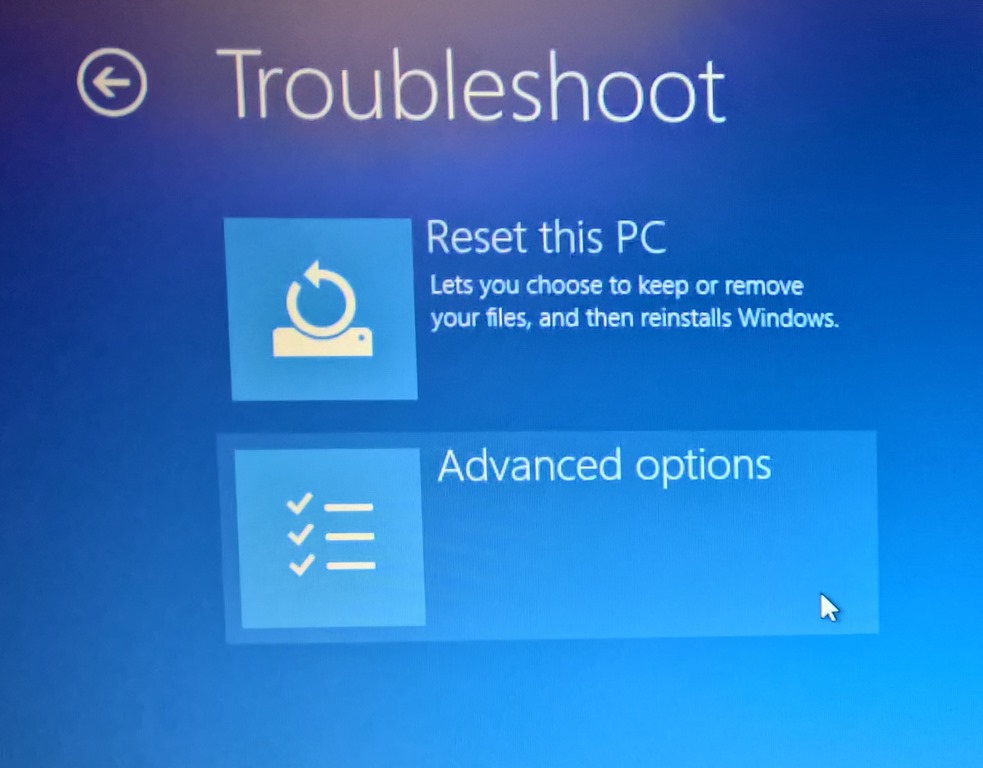
2. Utilize the Windows Recovery Environment:
- Access the Recovery Environment: Restart the computer and repeatedly press the appropriate key (usually F2, F8, or Del) to enter the BIOS setup. Access the boot options and choose the "Boot from CD/DVD" or "Boot from USB" option, depending on the recovery media.
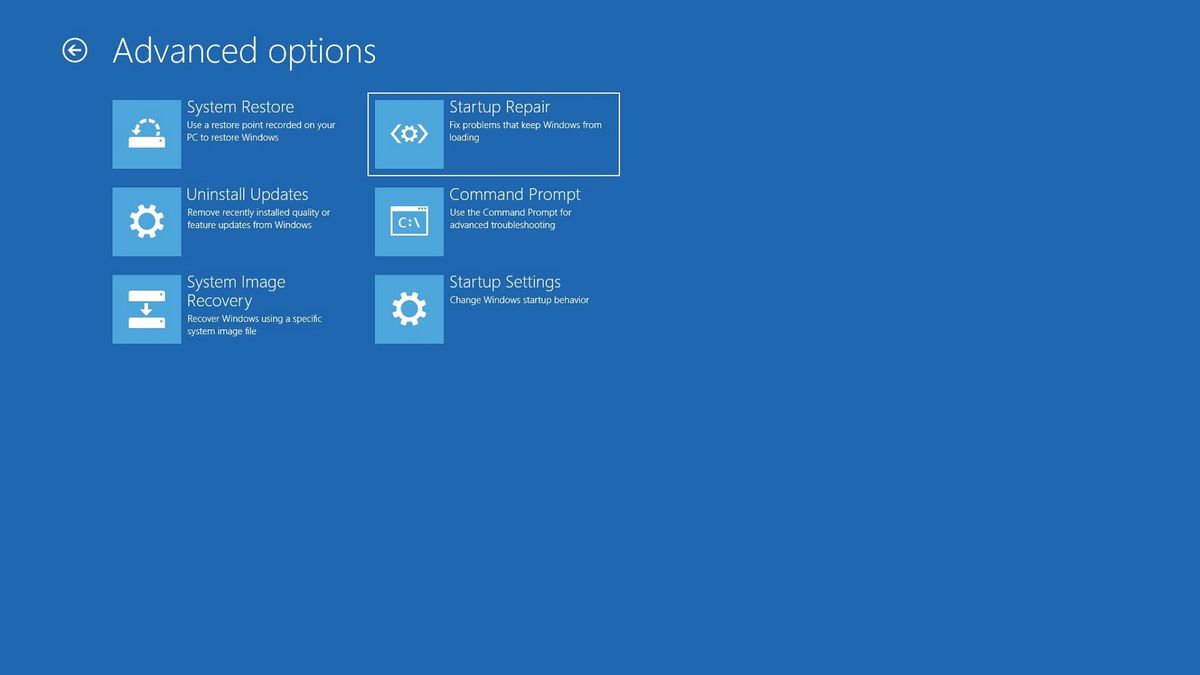
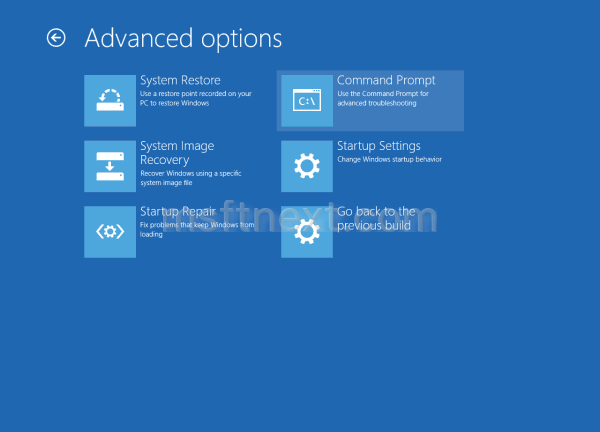
- Repair Boot Files: Utilize the "Startup Repair" or "Automatic Repair" options in the recovery environment to attempt automatic repair of corrupted boot files.
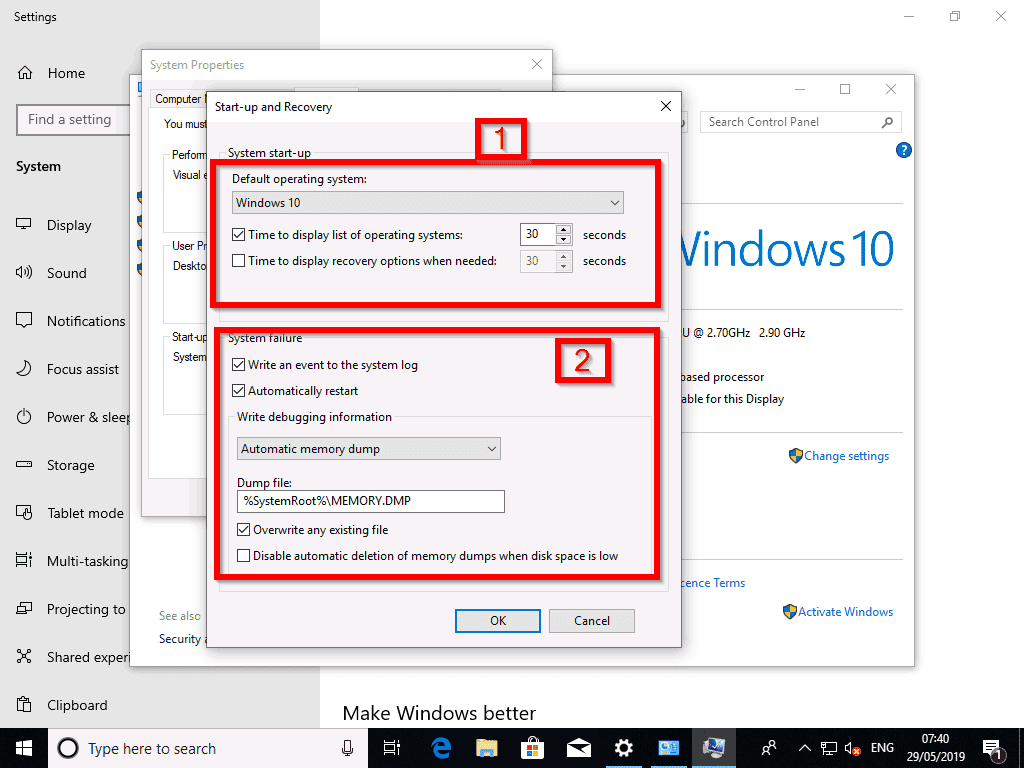
- System Restore: If possible, restore the system to a previous point in time before the boot issues arose.
3. Consider Advanced Troubleshooting:
- Boot into Safe Mode: Attempt to boot into Safe Mode, a diagnostic mode that loads only essential drivers and services. This can help isolate the cause of the boot failure.
- Perform a Clean Boot: Disable all non-essential startup programs and services to determine if a specific software conflict is preventing Windows from loading.
- Use a Live CD or USB Drive: Boot from a live operating system, such as a Linux distribution, to access the hard drive and potentially repair corrupted files or recover data.
- Reinstall Windows: If all other troubleshooting steps fail, consider reinstalling Windows 10. However, this will erase all data on the hard drive, so ensure a backup is available.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions
1. What does a "blue screen of death" indicate?
A "blue screen of death" (BSOD) is a critical error screen that appears during the boot process, indicating a fatal system failure. The error message displayed on the screen can provide clues about the cause of the issue.
2. How can I access the BIOS settings?
During the boot process, repeatedly press the appropriate key (usually F2, F8, or Del) to enter the BIOS setup. The specific key may vary depending on the computer manufacturer.
3. What is a "bootable USB drive?"
A bootable USB drive contains an operating system or recovery tools that can be used to boot the computer and access the recovery environment. It can be created using software like Rufus or the Windows Media Creation Tool.
4. What are the risks of reinstalling Windows?
Reinstalling Windows will erase all data on the hard drive. Therefore, it is crucial to create a backup of all important files before proceeding.
5. How can I prevent future boot problems?
- Regularly back up important data.
- Keep the operating system and drivers updated.
- Scan for malware regularly.
- Avoid unnecessary modifications to system files.
- Monitor system health using built-in tools or third-party software.
Tips for Avoiding Windows 10 Boot Issues:
- Regular Updates: Install all recommended Windows updates promptly.
- Driver Maintenance: Keep drivers updated, particularly for critical hardware components like the graphics card and network adapter.
- Malware Protection: Install and maintain a reliable antivirus program.
- System Maintenance: Regularly clean the computer’s internal components, such as the fan and heat sink, to prevent overheating and system instability.
- Disk Cleanup: Use the built-in disk cleanup tool to remove temporary files and other unnecessary data, freeing up disk space and improving performance.
Conclusion:
Windows 10 boot failures can be a challenging experience, but with a systematic approach and a basic understanding of the boot process, users can effectively troubleshoot and resolve these issues. By implementing preventative measures and maintaining a proactive approach to system health, users can minimize the risk of future boot problems and ensure a smooth and reliable computing experience. Remember, while the journey through boot failures can be arduous, understanding the intricacies of the boot process and employing the right troubleshooting techniques can empower users to navigate this labyrinth successfully.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Labyrinth: Troubleshooting Windows 10 Boot Issues. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!