Navigating the Ext4 Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Accessing Linux Filesystems on Windows 11
Related Articles: Navigating the Ext4 Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Accessing Linux Filesystems on Windows 11
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Ext4 Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Accessing Linux Filesystems on Windows 11. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Ext4 Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Accessing Linux Filesystems on Windows 11
![How to Access and Read EXT4 Partition and Data on Windows 11/10 [2024 Updated]](https://www.easeus.com/images/en/screenshot/partition-manager/mount-ext4-on-windows-via-diskinternal-linux-reader-2.jpg)
The world of operating systems is vast and diverse, with each platform employing its own unique file system to organize and manage data. Windows, the dominant operating system for personal computers, relies on the NTFS (New Technology File System) for its primary storage needs. Conversely, Linux, a powerful open-source operating system, utilizes the Ext4 file system, known for its robust features and performance. This difference in file systems presents a challenge for users who wish to seamlessly access data stored on Linux partitions from their Windows 11 machines.
While Windows 11 does not natively support Ext4, the need to access data stored on Linux partitions remains a common requirement for various scenarios. This need arises when users:
- Dual-boot Windows 11 and Linux: Many users opt for a dual-boot setup, allowing them to leverage the strengths of both operating systems. Accessing data shared between these systems becomes crucial.
- Use external drives formatted with Ext4: External hard drives or USB drives formatted with Ext4, often used for backups or data transfers, require access from Windows.
- Work with Linux-based virtual machines: Virtual machines running Linux distributions on Windows 11 may require access to data stored on the host machine.
Fortunately, various methods exist to bridge this gap and enable Windows 11 to read and even write to Ext4 partitions, providing users with the flexibility they need to navigate the cross-platform data access landscape.
Understanding the Ext4 File System:
Before delving into the methods for accessing Ext4, it’s crucial to understand its core characteristics and why Windows 11’s native support is lacking:
- Journaling File System: Ext4 is a journaling file system, meaning it logs changes to the file system before they are physically applied. This ensures data integrity and recovery in case of system crashes or power outages.
-
Advanced Features: Ext4 offers several advanced features, including:
- Extents: Improves file allocation efficiency.
- Large File Support: Supports files exceeding 16TB in size.
- Online File System Checks: Allows for filesystem checks while the system is running.
- Open Source: Ext4 is open-source software, allowing for community-driven development and improvements.
- Windows Compatibility: Windows 11 does not natively support Ext4 due to its proprietary nature and the lack of a standard driver for this file system.
Methods for Accessing Ext4 Partitions on Windows 11:
Several methods allow Windows 11 users to access and manage Ext4 partitions:
1. Third-Party File System Drivers:
- Ext2Fsd: This popular open-source driver provides read and write access to Ext2, Ext3, and Ext4 file systems on Windows. It’s known for its stability and wide compatibility.
- Ext4 NTFS: This driver offers similar functionality to Ext2Fsd, providing read and write access to Ext4 partitions.
- Paragon ExtFS: A commercial solution offering robust features, including read and write access, file system repair, and advanced options for managing Ext4 partitions.
2. Using Linux-Based Tools:
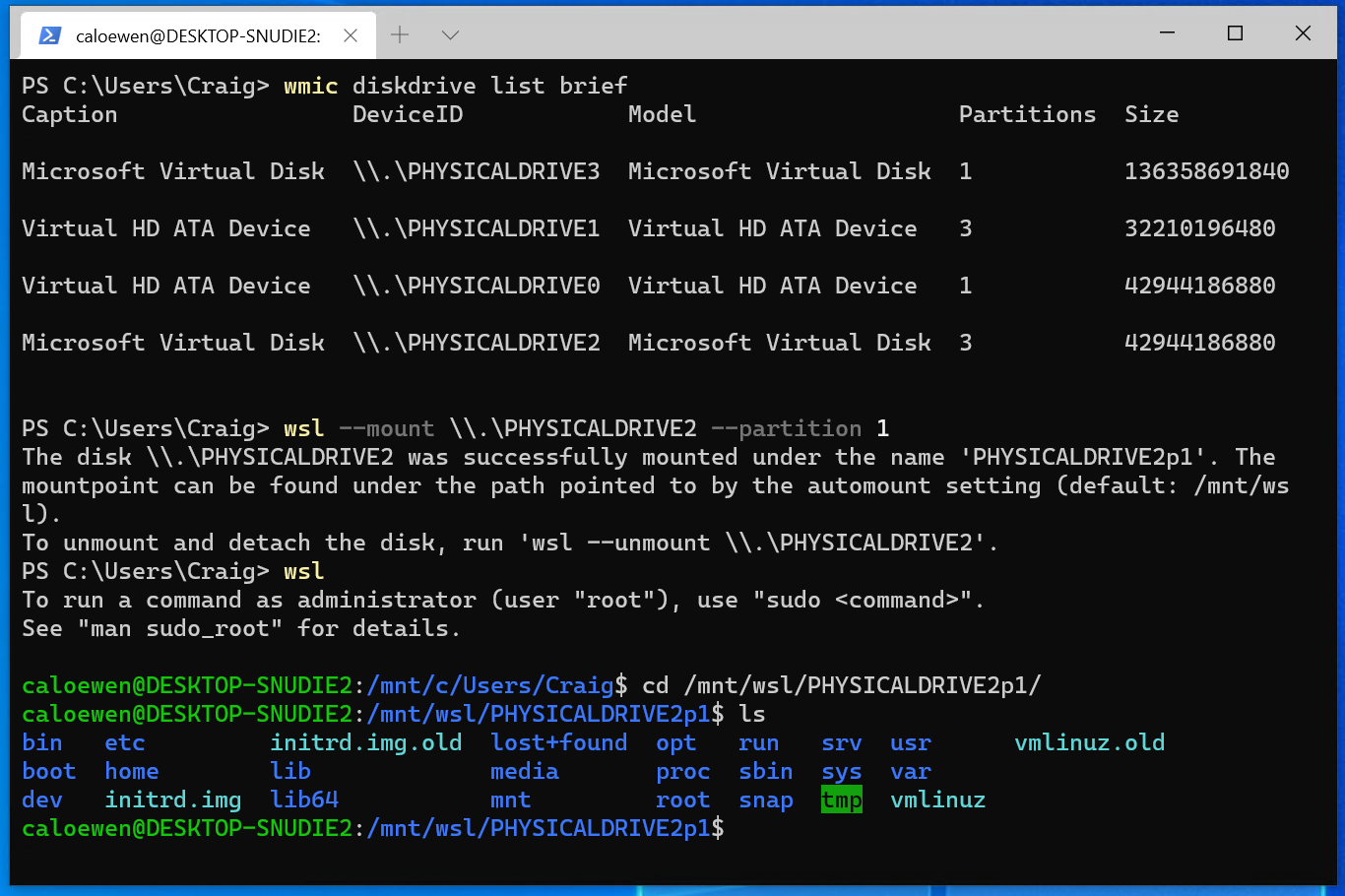
- Virtual Machines: Running a Linux distribution within a virtual machine environment like VirtualBox or VMware provides a native environment for accessing Ext4 partitions. This method allows users to directly mount and manage these partitions within the Linux virtual machine.
- Live CD/USB: Booting into a Linux live environment from a CD or USB drive provides temporary access to Ext4 partitions. This approach is useful for quickly accessing data or performing file transfers.
3. Cloud Storage Solutions:
- Cloud-Based Storage Services: Uploading data from the Ext4 partition to cloud storage services like Google Drive, Dropbox, or OneDrive allows for easy access from Windows 11. This approach, while requiring an internet connection, ensures data accessibility across multiple devices.
4. File Transfer Methods:
- FTP Clients: Using an FTP client like FileZilla allows users to transfer data between Windows 11 and an Ext4 partition accessible through an FTP server.
- Network Sharing: Configuring the Ext4 partition to be shared on a network allows for access from other devices, including Windows 11 machines.
Choosing the Right Approach:
The best approach for accessing Ext4 partitions on Windows 11 depends on individual needs and preferences. Consider the following factors:
- Read-Only or Read-Write Access: If you only need to read files from an Ext4 partition, using a third-party driver or a Linux-based solution might suffice. However, if you need to write data to the partition, a driver specifically designed for write access is essential.
- Frequency of Access: If you frequently need to access the Ext4 partition, installing a driver might be the most convenient option. However, for occasional access, using a virtual machine or a live CD/USB might be more suitable.
- Security Considerations: Ensure that the third-party drivers you choose are reputable and from trusted sources to avoid security vulnerabilities.
Benefits of Accessing Ext4 Partitions on Windows 11:
Accessing Ext4 partitions from Windows 11 offers several advantages:
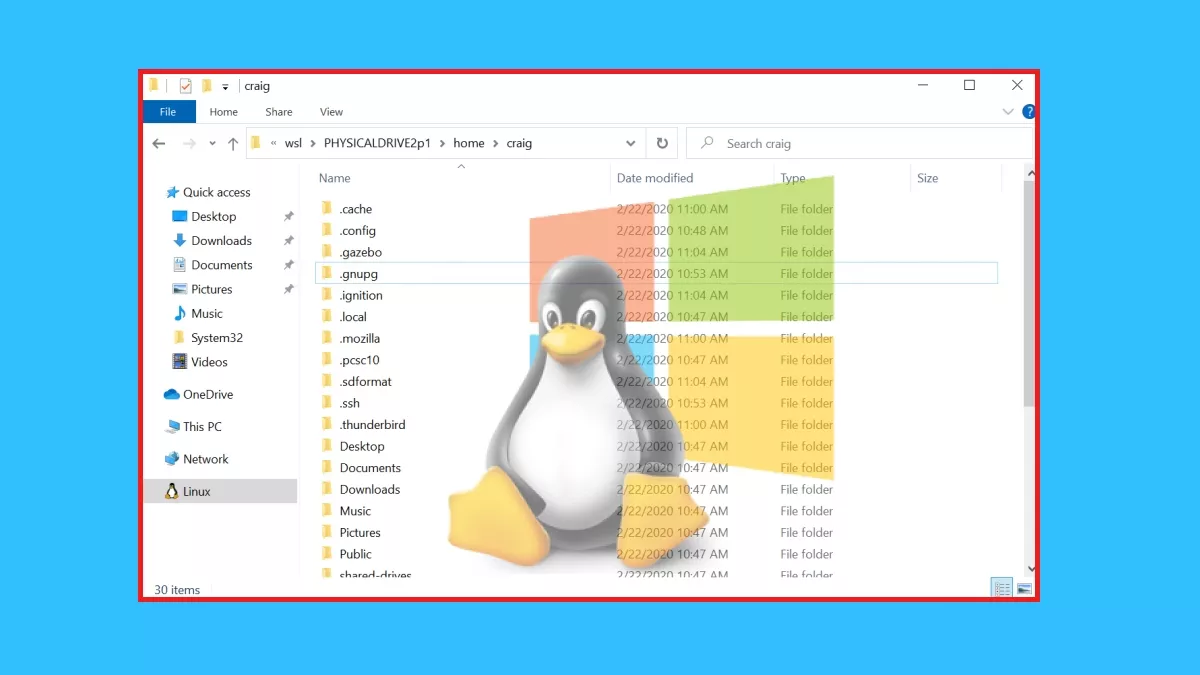
- Cross-Platform Data Sharing: Enables seamless data exchange between Windows and Linux systems, simplifying workflows and reducing data duplication.
- Data Recovery: Allows users to access data stored on damaged or corrupted Ext4 partitions for recovery purposes.
- Flexibility: Provides users with the ability to leverage the strengths of both Windows and Linux environments.
- Enhanced Productivity: Streamlines workflows by enabling users to manage data across different operating systems without the need for complex data migration processes.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
Q1: Can I format an Ext4 partition in Windows 11?
A1: While Windows 11 does not natively support Ext4 formatting, third-party tools like GParted (available on Linux live environments) can be used to format partitions to Ext4. However, it’s generally recommended to format partitions using the native tools of the target operating system.
Q2: Are there any risks associated with using third-party drivers?
A2: As with any software, there are potential risks associated with using third-party drivers. Always download drivers from reputable sources and ensure they are updated regularly to mitigate security vulnerabilities.
Q3: Can I use Ext4 partitions for system files on Windows 11?
A3: While it’s possible to install Windows 11 on an Ext4 partition using advanced techniques, it’s not recommended. Windows 11 is optimized for NTFS, and using Ext4 for system files can lead to instability and compatibility issues.
Q4: What if I need to access a large number of Ext4 partitions?
A4: For managing multiple Ext4 partitions, using a driver like Ext2Fsd or Paragon ExtFS might be more efficient than relying on virtual machines or live CDs.
Q5: Are there any performance implications for accessing Ext4 partitions from Windows 11?
A5: Performance can vary depending on the chosen method. Third-party drivers generally offer comparable performance to native access, while virtual machines might experience some overhead due to the virtualization layer.
Tips for Accessing Ext4 Partitions on Windows 11:
- Backup Data: Before making any changes to an Ext4 partition, back up your data to prevent accidental loss.
- Choose Reputable Drivers: Select drivers from trusted sources like the official websites of developers or well-known software repositories.
- Update Drivers Regularly: Keep your drivers updated to benefit from bug fixes and security patches.
- Use Virtual Machines for Complex Operations: For complex tasks like formatting or partitioning, consider using a virtual machine to avoid potential issues with the host operating system.
- Utilize Cloud Storage for Data Accessibility: Leverage cloud storage services for easy access to data stored on Ext4 partitions across multiple devices.
Conclusion:
While Windows 11 does not natively support Ext4, various methods allow users to access and manage data stored on these partitions. Understanding the available options and their pros and cons is crucial for choosing the most suitable approach based on individual needs and preferences. By leveraging these methods, users can seamlessly integrate Ext4 partitions into their Windows 11 workflows, enhancing cross-platform data sharing and maximizing productivity.
![How to Access Linux EXT4 Partition and Data on Windows 11/10/8/7 [2023 Updated] - EaseUS](https://www.easeus.com/images/en/screenshot/partition-manager/explore-partition-2.png)





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Ext4 Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Accessing Linux Filesystems on Windows 11. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!