Navigating the Compatibility Landscape: Can 7th Generation Processors Power Windows 11?
Related Articles: Navigating the Compatibility Landscape: Can 7th Generation Processors Power Windows 11?
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Compatibility Landscape: Can 7th Generation Processors Power Windows 11?. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Compatibility Landscape: Can 7th Generation Processors Power Windows 11?
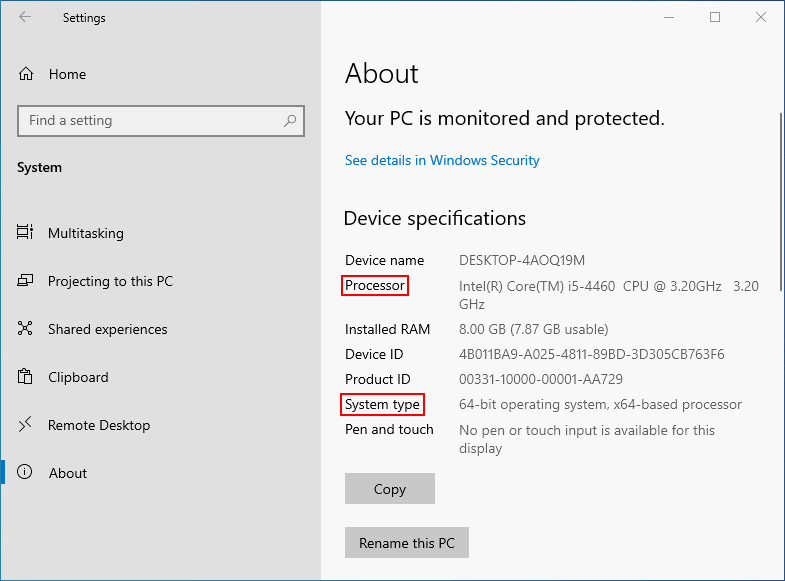
The release of Windows 11 sparked widespread curiosity and debate, particularly regarding its compatibility with older hardware. A significant point of contention centered around the processor requirements, with Microsoft outlining specific guidelines for supported CPUs. This led to questions about the fate of devices equipped with 7th generation Intel Core processors, a popular choice in computers released around 2016-2017.
While the official Windows 11 system requirements initially seemed to exclude 7th generation Intel Core processors, the reality is more nuanced. The key determining factor is not simply the processor generation but the underlying architecture and security features.
Understanding the Architecture: A Look Beneath the Surface
The 7th generation Intel Core processors, codenamed Kaby Lake, are based on the Skylake architecture. This architecture introduced significant advancements, including support for the Trusted Platform Module (TPM) 2.0, a critical security feature that became a mandatory requirement for Windows 11.
The Trusted Platform Module (TPM) 2.0: A Security Foundation
TPM 2.0 is a dedicated security chip embedded on the motherboard, designed to enhance system security by protecting sensitive data and verifying the integrity of the operating system. Its presence is crucial for Windows 11, as it strengthens the platform’s defenses against malware and unauthorized access.
TPM 2.0: The Key to Windows 11 Compatibility
While the 7th generation Intel Core processors themselves do not inherently guarantee compatibility with Windows 11, the presence of TPM 2.0 on the motherboard is the crucial factor. If your device equipped with a 7th generation Intel Core processor features TPM 2.0, you have a strong chance of successfully installing and running Windows 11.
Beyond the Processor: Other Factors to Consider
While TPM 2.0 is paramount, other system specifications play a role in Windows 11 compatibility. These include:
- RAM: Windows 11 requires at least 4GB of RAM, although 8GB is recommended for optimal performance.
- Storage: A minimum of 64GB of storage is necessary, with SSDs being preferred for faster loading times.
- Display: A display with a resolution of at least 1280 x 768 pixels is required.
- Secure Boot: This feature, enabled in the BIOS, helps prevent unauthorized software from loading during startup.
Verifying Compatibility: A Comprehensive Approach
Before attempting to install Windows 11 on a device with a 7th generation Intel Core processor, it’s essential to verify compatibility. Here are the recommended steps:
- Check the PC Health Check App: Microsoft offers a dedicated PC Health Check app that can assess your system’s readiness for Windows 11. Download and run the app to receive a detailed report outlining potential compatibility issues.
- Examine BIOS Settings: Access your BIOS settings and look for options related to TPM 2.0. Ensure it is enabled and configured correctly.
- Explore Device Manager: Open Device Manager and check for any entries related to TPM. If a TPM device is listed, it indicates its presence on your motherboard.
- Consult Manufacturer’s Website: Visit the manufacturer’s website for your specific device model and search for information regarding Windows 11 compatibility.
Potential Workarounds: Expanding Compatibility Horizons
Even if your device does not meet the official Windows 11 system requirements, there are potential workarounds to explore:
- BIOS Update: Some motherboard manufacturers may release BIOS updates that enable TPM 2.0 support on older devices.
- Third-Party TPM Modules: While not ideal, external TPM modules can be purchased and connected to your motherboard to provide the necessary security feature.
- Windows 10: A Stable Alternative: If compatibility issues persist, consider staying with Windows 10, which continues to receive security updates and support.
Navigating the Compatibility Landscape: A Detailed Guide
1. Understanding the Processor Generation:
The processor generation is not the sole determinant of Windows 11 compatibility. While newer generations typically offer improved performance and features, the underlying architecture and security features are crucial.
2. The Significance of TPM 2.0:
TPM 2.0 is a security chip embedded on the motherboard, playing a critical role in verifying system integrity and protecting sensitive data. Its presence is a prerequisite for Windows 11 compatibility.
3. Verifying TPM 2.0 Support:
Access your BIOS settings and look for options related to TPM 2.0. Ensure it is enabled and configured correctly. Additionally, check Device Manager for entries related to TPM.
4. Exploring Compatibility Tools:
Utilize the PC Health Check app to assess your system’s readiness for Windows 11. This tool provides a comprehensive report outlining potential compatibility issues.
5. Consulting Manufacturer’s Resources:
Visit the manufacturer’s website for your specific device model to find information regarding Windows 11 compatibility. They may provide updates or specific guidelines for your device.
6. Exploring Workarounds:
If your device does not meet the official requirements, consider BIOS updates, third-party TPM modules, or staying with Windows 10.
7. Weighing the Benefits of Windows 11:
Windows 11 offers a refined user interface, improved security features, and enhanced performance. However, consider whether these benefits outweigh the potential compatibility challenges.
8. Understanding the Long-Term Support:
Windows 11 is supported for several years, ensuring continued security updates and feature enhancements. However, older devices may eventually reach the end of their support lifecycle.
9. Evaluating Upgrade Costs:
Upgrading to a newer device may be necessary to ensure compatibility with Windows 11. Consider the cost of a new system versus the potential benefits of the latest operating system.
10. Making Informed Decisions:
Ultimately, the decision of whether to upgrade to Windows 11 depends on your individual needs, device specifications, and budget. Weigh the benefits and challenges carefully before making a decision.
FAQs: Addressing Common Concerns
Q: Can I upgrade to Windows 11 without TPM 2.0?
A: While Microsoft has relaxed the requirement for TPM 2.0 in some cases, it is generally recommended for optimal security and performance. Without TPM 2.0, your system may not be able to access all the features and security enhancements of Windows 11.
Q: How can I check if my motherboard has TPM 2.0?
A: Access your BIOS settings and look for options related to TPM 2.0. Alternatively, open Device Manager and check for entries related to TPM.
Q: What are the benefits of using Windows 11?
A: Windows 11 offers a modern user interface, improved security features, enhanced performance, and integration with the latest hardware.
Q: Can I install Windows 11 on a virtual machine?
A: Yes, you can install Windows 11 on a virtual machine, but the performance may be limited depending on your system resources.
Q: What happens if I don’t upgrade to Windows 11?
A: Windows 10 will continue to receive security updates and support for several years. However, you may miss out on the new features and enhancements offered by Windows 11.
Tips: Maximizing Compatibility and Performance
- Keep your drivers updated: Ensure that all your device drivers are up to date to ensure optimal compatibility and performance.
- Disable unnecessary programs: Close unnecessary programs and services running in the background to free up system resources.
- Optimize your storage: Consider upgrading to an SSD or defragmenting your hard drive to improve performance.
- Clean your system: Regularly clean your system of unnecessary files and temporary data to optimize performance and free up storage space.
Conclusion: A Balanced Perspective on Compatibility
The compatibility of 7th generation Intel Core processors with Windows 11 is not a simple yes or no answer. The presence of TPM 2.0 is the key factor, but other system specifications also play a role. While older devices may not meet the official requirements, workarounds exist, and Windows 10 remains a viable option. Ultimately, the decision to upgrade to Windows 11 should be based on a careful assessment of your individual needs, device specifications, and budget. By understanding the nuances of compatibility and exploring available options, you can make an informed decision that best suits your computing needs.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Compatibility Landscape: Can 7th Generation Processors Power Windows 11?. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!