Installing Windows 11 on Unsupported Hardware: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Installing Windows 11 on Unsupported Hardware: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Installing Windows 11 on Unsupported Hardware: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Installing Windows 11 on Unsupported Hardware: A Comprehensive Guide
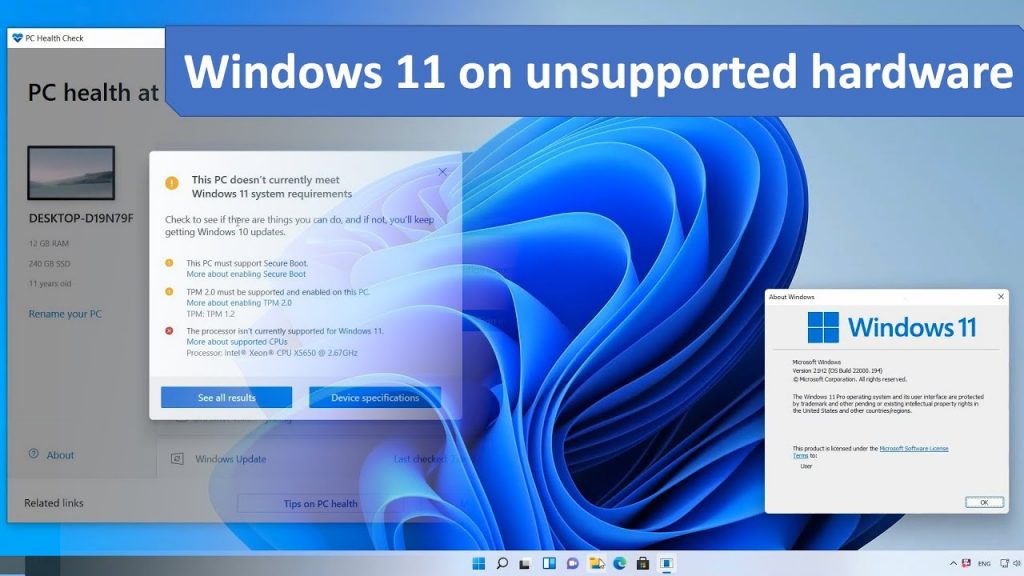
While Microsoft officially outlines specific system requirements for Windows 11, many users find themselves with computers that technically do not meet these criteria. This can be frustrating, especially considering the numerous benefits Windows 11 offers, including enhanced security, improved performance, and a modern interface.
This guide aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of how to install Windows 11 on unsupported hardware, outlining the process, potential challenges, and essential considerations.
Understanding the Restrictions
Microsoft’s decision to set specific hardware requirements for Windows 11 stems from a desire to ensure optimal performance and security. The requirements include:
- Processor: 1 GHz or faster with 2 or more cores
- RAM: 4 GB
- Storage: 64 GB or larger
- System Firmware: UEFI, Secure Boot capable
- TPM: TPM 2.0
- Display: 9-inch display with HD resolution (720p)
While these requirements are generally beneficial, they can exclude older computers, even those capable of running Windows 11 smoothly.
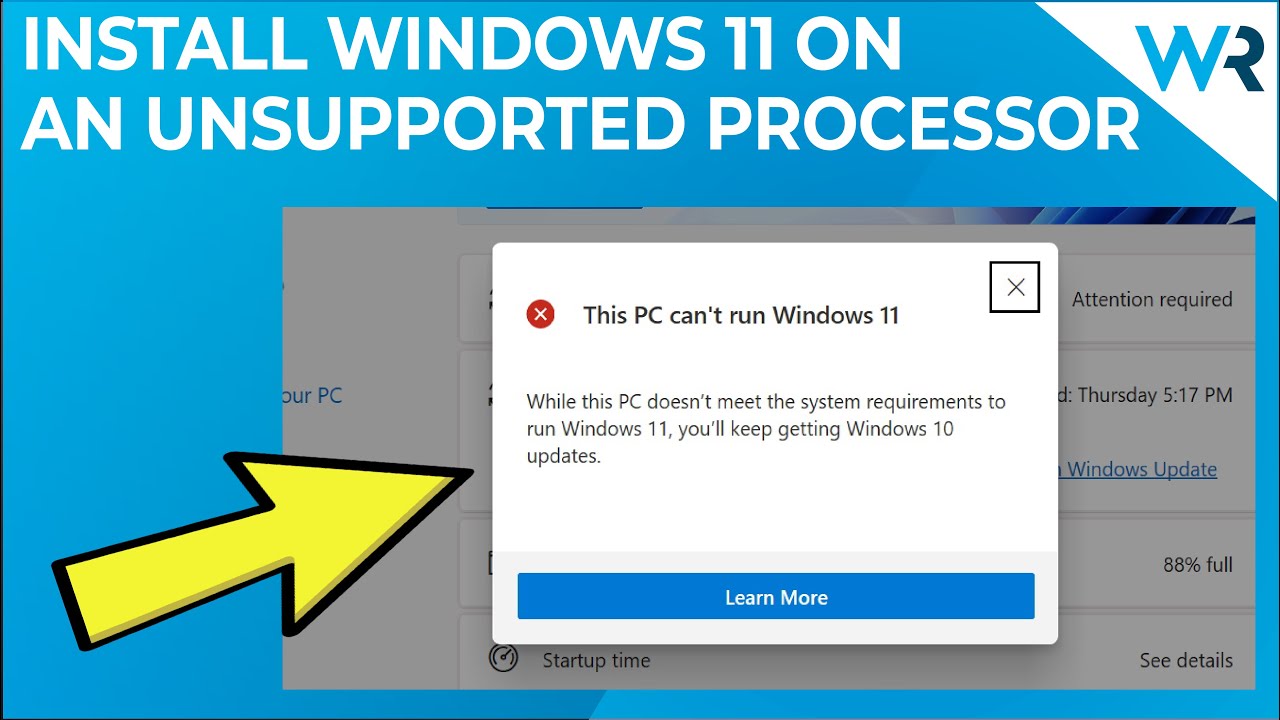
The "Unsupported" Reality
Many computers, particularly those manufactured before 2017, might not meet all the Windows 11 requirements. This doesn’t necessarily mean they are incapable of running the operating system. It simply means they are not officially supported by Microsoft.
Installing Windows 11 on Unsupported Hardware
Installing Windows 11 on unsupported hardware is possible, but it requires a workaround. This involves bypassing the system checks that Microsoft implements during installation.
The Process:
- Download Windows 11 Installation Media: Obtain an ISO image of Windows 11 from the official Microsoft website. This can be done by using the Media Creation Tool.
- Create a Bootable USB Drive: Use a tool like Rufus or the Windows USB/DVD Download Tool to create a bootable USB drive from the downloaded ISO image.
- Bypass System Checks: This is the crucial step. You can use a registry hack, a tool like Rufus, or a third-party program like "NTLite" to bypass the system checks.
- Start Installation: Boot your computer from the USB drive and follow the on-screen instructions to install Windows 11.
Potential Challenges:
- Driver Compatibility: While the installation might be successful, you may encounter driver issues with certain hardware components.
- Security Risks: Bypassing security checks could potentially expose your computer to vulnerabilities.
- Performance Issues: Although the installation might proceed without errors, performance might be subpar compared to supported hardware.
- Updates: You might not receive regular security updates from Microsoft.
Tips for Success:
- Research Thoroughly: Before attempting the installation, research your specific computer model and its compatibility with Windows 11.
- Back Up Data: Always back up your important data before making any significant changes to your computer.
- Consider Alternatives: If your computer is significantly old or lacks essential components, consider alternative operating systems like Linux or a lightweight version of Windows.
- Seek Professional Assistance: If you are unsure about the process or encounter difficulties, consider seeking assistance from a computer technician.
FAQs
Q: Is it safe to install Windows 11 on unsupported hardware?
A: While possible, it comes with risks. You might encounter driver issues, security vulnerabilities, and performance problems. It’s crucial to weigh the potential benefits against these risks.
Q: What are the benefits of installing Windows 11 on unsupported hardware?
A: Access to newer features, a modern interface, and potential performance improvements. However, these benefits are not guaranteed and may be outweighed by the risks.
Q: Will I receive security updates for Windows 11 on unsupported hardware?
A: It’s highly unlikely. Microsoft prioritizes updates for supported devices.
Q: Can I upgrade from Windows 10 to Windows 11 on unsupported hardware?
A: No, the upgrade process will likely fail as the system checks will prevent the upgrade.
Q: What if I encounter driver issues after installing Windows 11?
A: You can try manually installing drivers from the manufacturer’s website. However, compatibility issues may still persist.
Conclusion
Installing Windows 11 on unsupported hardware is possible but comes with risks. While it might offer access to newer features and a modern interface, the potential for driver issues, security vulnerabilities, and performance problems should be carefully considered. It’s crucial to weigh the benefits against the risks and make an informed decision. If you are unsure about the process or encounter difficulties, seeking professional assistance is strongly recommended.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Installing Windows 11 on Unsupported Hardware: A Comprehensive Guide. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!