Installing Windows 11 on Unsupported Hardware: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Installing Windows 11 on Unsupported Hardware: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Installing Windows 11 on Unsupported Hardware: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Installing Windows 11 on Unsupported Hardware: A Comprehensive Guide
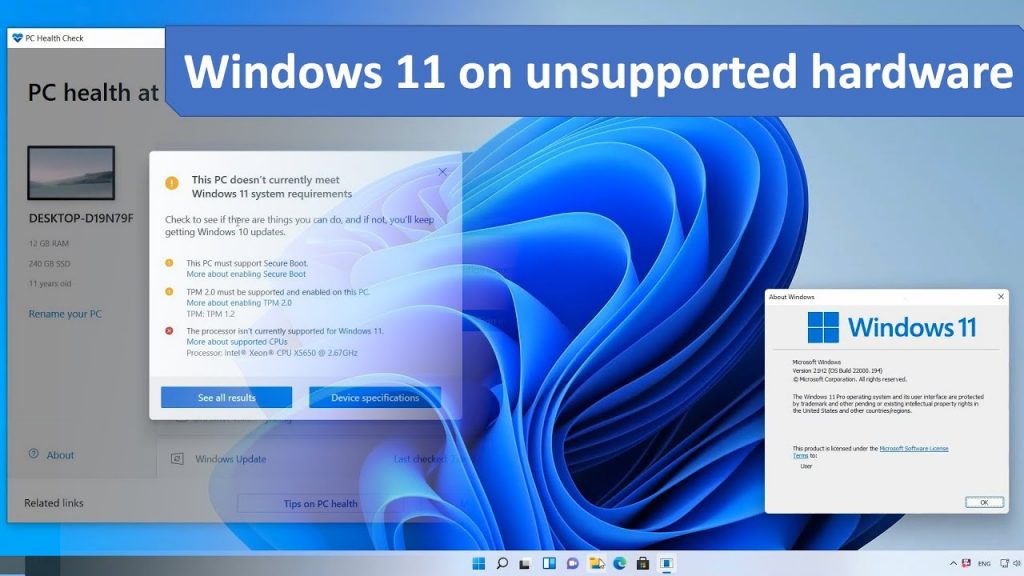
Windows 11, with its redesigned interface and enhanced security features, has attracted considerable attention. However, Microsoft has set specific hardware requirements for its installation, leaving many users with older machines unable to upgrade. This has led to a surge in interest in installing Windows 11 on computers that don’t officially meet the minimum requirements.
While this approach can be tempting, it comes with its own set of challenges and considerations. This article aims to provide a comprehensive guide to installing Windows 11 on unsupported hardware, outlining the risks, outlining the necessary steps, and addressing potential issues.
Understanding the Hardware Requirements and Risks:
Microsoft’s decision to establish minimum hardware requirements for Windows 11 is rooted in ensuring optimal performance, security, and compatibility. These requirements encompass factors such as:
- Processor: Windows 11 requires a 1 GHz or faster processor with at least two cores. This ensures sufficient processing power for the operating system and its applications.
- RAM: A minimum of 4 GB RAM is required to handle multitasking and run modern applications efficiently.
- Storage: A minimum of 64 GB storage is needed for the operating system files and user data.
- TPM 2.0: Trusted Platform Module (TPM) 2.0 is a security feature that protects sensitive data and prevents unauthorized access.
- Secure Boot: Secure Boot is a security protocol that verifies the authenticity of the operating system and its drivers before loading them.
Installing Windows 11 on unsupported hardware can lead to various issues, including:
- Performance Degradation: The lack of compatibility between the hardware and the operating system can result in reduced performance, slow boot times, and frequent crashes.
- Security Vulnerabilities: Unsupported hardware may lack the necessary security features, leaving the system vulnerable to malware and other threats.
- Driver Issues: Finding and installing compatible drivers for older hardware can be challenging and time-consuming.
- Limited Software Support: Some applications may not be compatible with Windows 11 on unsupported hardware.
- Lost Warranty: Attempting to install Windows 11 on unsupported hardware may void the manufacturer’s warranty.
Methods for Installing Windows 11 on Unsupported Hardware:
While Microsoft does not officially endorse installing Windows 11 on unsupported hardware, there are several methods that can be employed:
1. Bypassing the Hardware Requirements:
This method involves modifying the system’s registry or using third-party tools to trick Windows 11 setup into believing the hardware meets the minimum requirements.
- Registry Editing: This method involves manually modifying specific registry keys to bypass the hardware checks. However, it requires advanced knowledge and can potentially damage the system if not done correctly.
- Third-Party Tools: Several third-party tools, such as Rufus and Windows 11 Installation Assistant, can modify the installation media to bypass the hardware checks. These tools are generally easier to use but may also come with security risks.
2. Using a Custom Installation:
This method involves creating a bootable USB drive with the Windows 11 installation files and manually installing the operating system without relying on the standard setup process.
- Creating a Bootable USB Drive: This involves downloading the Windows 11 ISO file and using a tool like Rufus to create a bootable USB drive.
- Manual Installation: This requires booting from the USB drive and manually navigating the installation process, skipping the hardware checks.
3. Upgrading from Windows 10:
If your system is running Windows 10, you can attempt to upgrade to Windows 11 using the Windows Update feature. While this method may not always work, it can be a simpler alternative to manual installation.
Important Considerations and Tips:
- Backup Your Data: Before attempting any installation process, ensure you have a complete backup of your data. This will prevent data loss in case of any unforeseen issues.
- Research Thoroughly: Thoroughly research the risks and limitations associated with installing Windows 11 on unsupported hardware before proceeding.
- Use Reliable Sources: Download the Windows 11 installation files from official Microsoft sources to avoid malware and other security risks.
- Seek Professional Help: If you are unsure about the process or concerned about potential risks, seek professional assistance from a qualified technician.
- Consider Alternatives: If you are experiencing performance issues or compatibility problems with your current operating system, consider upgrading your hardware or opting for a lighter operating system like Linux.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Q: What are the risks of installing Windows 11 on unsupported hardware?
A: Installing Windows 11 on unsupported hardware can lead to various issues, including performance degradation, security vulnerabilities, driver issues, limited software support, and potential warranty voidance.
Q: Can I install Windows 11 on my older computer without meeting the minimum requirements?
A: While it is possible to bypass the hardware checks, it is not recommended as it can lead to various issues and may not provide the optimal performance or security.
Q: Is it safe to use third-party tools to bypass the hardware requirements?
A: Third-party tools can be helpful but may come with security risks. It is essential to research and choose reputable tools from trusted sources.
Q: What if I encounter problems during the installation process?
A: If you encounter problems, it is advisable to seek professional assistance from a qualified technician.
Q: How can I ensure my data is safe during the installation process?
A: It is crucial to have a complete backup of your data before attempting any installation process.
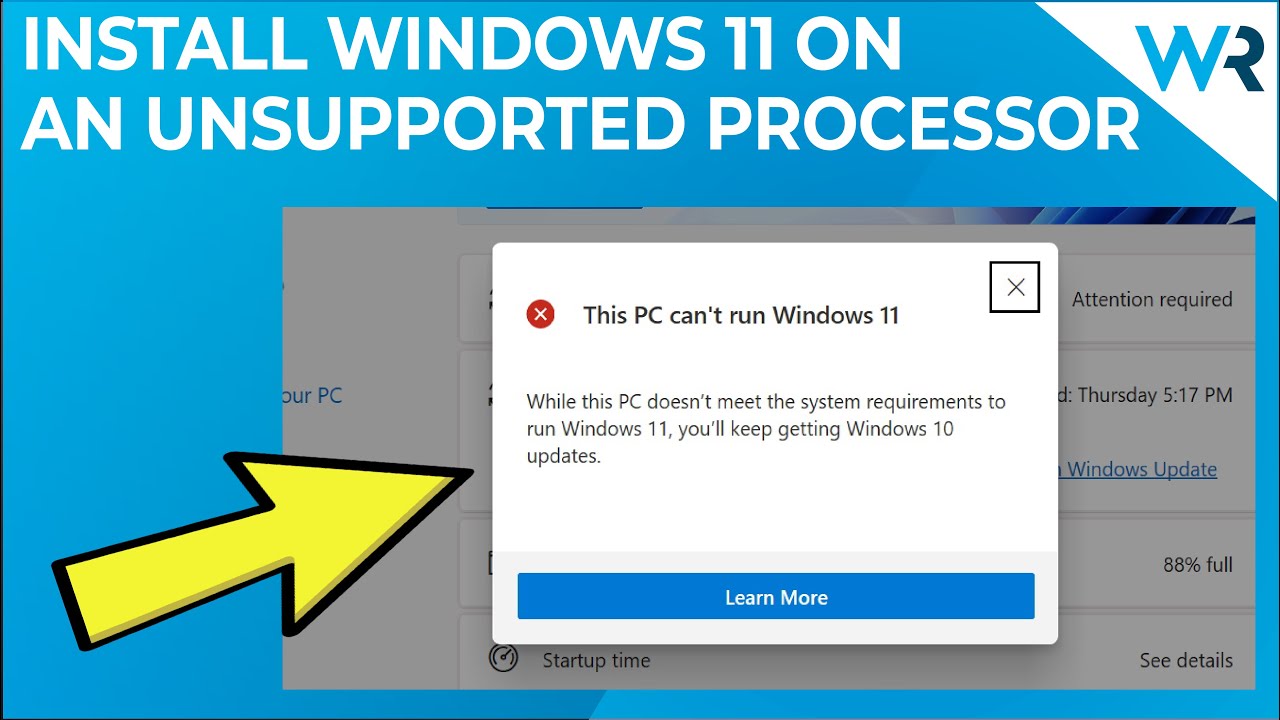
Q: Is there a way to check if my computer meets the minimum requirements for Windows 11?
A: Microsoft provides a PC Health Check app that can assess your computer’s compatibility with Windows 11.
Conclusion:
Installing Windows 11 on unsupported hardware can be tempting, but it is not without its risks. While it may be possible to bypass the hardware checks, it is crucial to weigh the potential benefits against the risks and limitations. If you are considering this approach, it is essential to research thoroughly, understand the implications, and proceed with caution.
In many cases, upgrading your hardware or exploring alternative operating systems may be more practical and secure solutions for older computers. Ultimately, the decision to install Windows 11 on unsupported hardware should be based on a comprehensive understanding of the potential consequences and a careful assessment of your specific needs and resources.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Installing Windows 11 on Unsupported Hardware: A Comprehensive Guide. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!