Enabling Hibernate Mode in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Enabling Hibernate Mode in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Enabling Hibernate Mode in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Enabling Hibernate Mode in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Enabling Hibernate Mode in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide
- 3.1 Understanding the Benefits of Hibernation
- 3.2 Enabling Hibernation Mode: A Step-by-Step Guide
- 3.3 Troubleshooting: When Hibernation Mode Is Unavailable
- 3.4 Optimizing Hibernation Mode: Tips and Best Practices
- 3.5 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Enabling Hibernate Mode in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide

Hibernate mode is a power-saving feature that allows your Windows 11 computer to enter a state of deep sleep, saving energy and preserving your work. Unlike sleep mode, which retains a minimal amount of power to maintain your system’s state, hibernation saves the entire contents of your RAM to your hard drive, allowing your computer to shut down completely without losing any unsaved data. This makes it an ideal option for extended periods of inactivity, such as overnight or when you need to transport your laptop.
This guide provides a detailed explanation of how to enable hibernation mode in Windows 11, addressing common concerns and offering helpful tips for optimal usage.
Understanding the Benefits of Hibernation
Enabling hibernation mode presents several advantages:
- Energy Conservation: By completely shutting down the system, hibernation mode significantly reduces power consumption compared to sleep mode. This is particularly beneficial for laptops, extending battery life and reducing environmental impact.
- Data Preservation: Hibernation saves the entire contents of your RAM to your hard drive, ensuring no data loss occurs when the computer is powered off. This is crucial for unsaved work, open applications, and system settings.
- Fast Startup: When you restart your computer from hibernation, the saved RAM data is quickly loaded back into memory, allowing for a faster startup compared to a cold boot.
Enabling Hibernation Mode: A Step-by-Step Guide
-
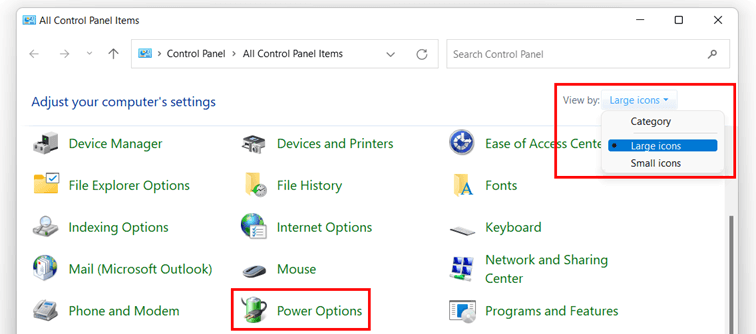
Access Control Panel: Start by opening the Control Panel. You can do this by searching for "Control Panel" in the Windows search bar or by pressing the Windows key + R, typing "control," and pressing Enter.
-
Navigate to Power Options: Within the Control Panel, locate and click on "Power Options."
-
Select "Choose what the power buttons do": In the left-hand pane of the Power Options window, click on "Choose what the power buttons do."
-
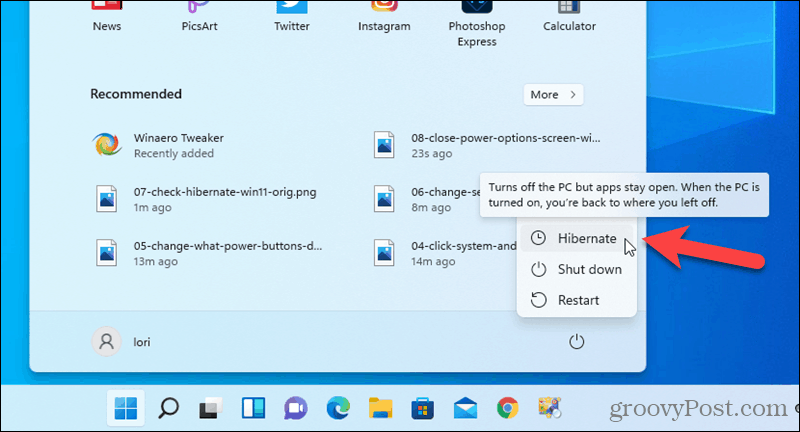
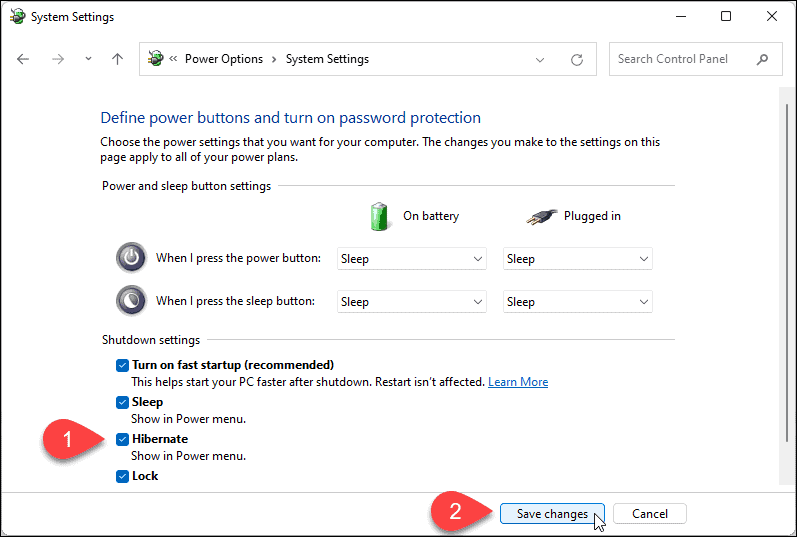
Enable "Hibernate": At the bottom of the window, check the box next to "Hibernate."
-
Confirm Changes: Click "Save Changes" to apply the settings and enable hibernation mode.
Troubleshooting: When Hibernation Mode Is Unavailable
If the "Hibernate" option remains unavailable or grayed out in the Power Options menu, the following reasons could be contributing factors:
-
Insufficient Disk Space: Hibernation requires enough free disk space to store the contents of your RAM. If your hard drive is close to full, hibernation may be disabled. Consider deleting unnecessary files or freeing up space on your hard drive.
-
Disabled Feature: In some cases, hibernation may be disabled in the system’s advanced settings. To check this, follow these steps:
- Press Windows key + R and type "powercfg.cpl" in the Run dialog box.
- Click "Change settings that are currently unavailable."
- In the "Advanced settings" tab, expand the "Sleep" option and then the "Hibernate after" option.
- Ensure that the "Hibernate after" option is not set to "Never."
-
Outdated Drivers: Outdated drivers for your computer’s hardware, especially for the power management components, can interfere with hibernation functionality. Consider updating your drivers to the latest versions.
-
System Configuration Issues: Certain system configurations or software settings may prevent hibernation from working properly. If the above troubleshooting steps fail, consider consulting Microsoft’s support resources or a qualified technician for further assistance.
Optimizing Hibernation Mode: Tips and Best Practices
- Regular Disk Cleanup: Regularly clean up your hard drive to ensure sufficient free space for hibernation. This will prevent hibernation from being disabled due to insufficient disk space.
- Consider Disk Defragmentation: Defragmenting your hard drive can improve overall system performance, including hibernation speed.
- Use a Power Plan: Windows 11 offers various power plans that can be customized to optimize your system’s power consumption. Consider using a power plan that prioritizes energy efficiency when hibernation is desired.
- Disable Fast Startup (Windows 10): Fast startup is a feature in Windows 10 that speeds up boot times by storing a portion of the system’s state in a file on your hard drive. However, it can sometimes conflict with hibernation mode. If you’re experiencing issues with hibernation, consider disabling Fast Startup in Windows 10.
- Monitor Battery Life: Hibernation can extend battery life, but it’s essential to monitor your battery’s charge level. If your battery is low, consider using sleep mode instead to conserve power.
Conclusion
Enabling hibernation mode in Windows 11 offers a powerful tool for energy conservation, data preservation, and fast startup times. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can easily enable hibernation on your Windows 11 computer and enjoy the benefits it offers. Remember to troubleshoot potential issues and optimize your system’s settings for optimal hibernation performance.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Enabling Hibernate Mode in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!