Enabling Hibernate Mode in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Enabling Hibernate Mode in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Enabling Hibernate Mode in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Enabling Hibernate Mode in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide

Hibernate mode is a power-saving feature in Windows 11 that allows users to completely shut down their computers while preserving the current state of all open applications and documents. This feature is particularly useful for users who wish to conserve battery life on laptops or who want to ensure their work is saved without needing to manually save everything before shutting down. This guide provides a detailed explanation of how to enable hibernation mode in Windows 11, along with its benefits and potential considerations.
Understanding Hibernate Mode
When a computer enters hibernation mode, it saves the contents of the computer’s RAM (Random Access Memory) to a file on the hard drive, called the "hiberfil.sys" file. This file acts as a snapshot of the system’s current state. Once the computer is shut down, all power is cut off, and the system enters a low-power state. When the computer is restarted, it loads the saved state from the "hiberfil.sys" file, restoring the system to its previous state, including all open applications and documents.
Benefits of Using Hibernate Mode
Hibernate mode offers several advantages over simply shutting down or using sleep mode:
- Power Conservation: Hibernate mode consumes significantly less power than sleep mode, especially on laptops. This can extend battery life considerably, making it ideal for users who frequently work on the go.
- Data Preservation: Unlike sleep mode, which maintains the system’s state in RAM, hibernate mode saves the system’s state to the hard drive. This ensures that all unsaved data is preserved even if the computer is unplugged or experiences a power outage.
- Faster Startup: While not as fast as resuming from sleep mode, hibernation mode offers a faster startup than a cold boot. The system can load from the saved state on the hard drive, eliminating the need to load the operating system from scratch.
Enabling Hibernate Mode in Windows 11
Enabling hibernation mode in Windows 11 is a straightforward process:
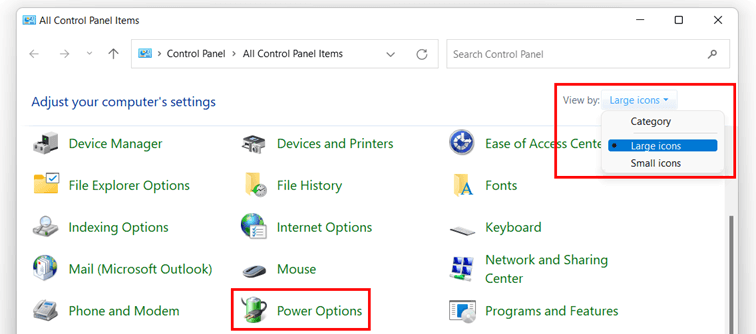
- Open the Control Panel: You can access the Control Panel by searching for it in the Windows search bar.
- Navigate to Power Options: Within the Control Panel, click on "Power Options."
- Choose "Choose what the power buttons do": In the left-hand menu, select "Choose what the power buttons do."
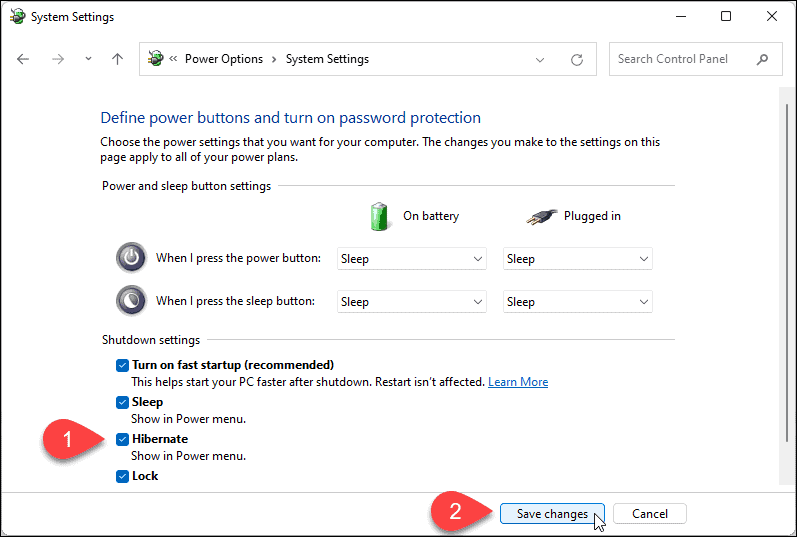
- Click "Change settings that are currently unavailable": This option unlocks additional settings, including the ability to enable hibernation.
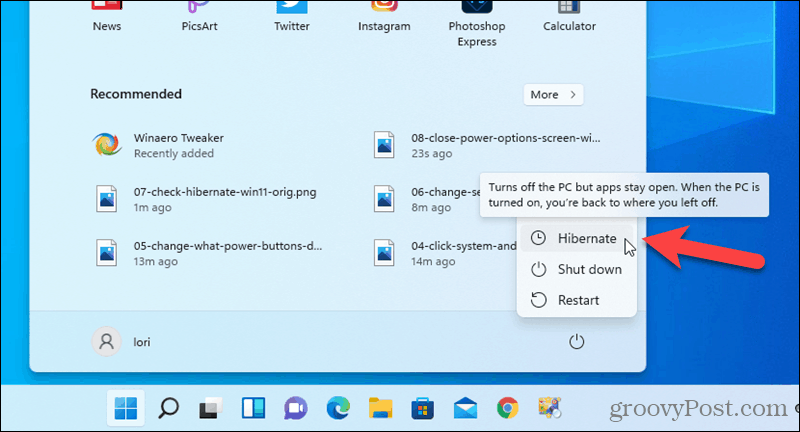
- Check the "Hibernate" box: Locate the "Hibernate" option and check the box next to it.
- Save Changes: Click "Save Changes" to apply the new settings.
Considerations for Using Hibernate Mode
While hibernate mode offers several advantages, there are a few considerations to keep in mind:
- Hard Drive Space: The "hiberfil.sys" file can be quite large, especially if you have a lot of RAM. This file requires storage space on your hard drive, so ensure you have sufficient space available.
- Startup Time: While faster than a cold boot, hibernation mode still takes longer to start than resuming from sleep mode.
- Compatibility: Not all devices may support hibernation mode. If you are using an older computer or device, hibernation mode might not be available.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: Is hibernation mode the same as sleep mode?
A: No, hibernation mode and sleep mode are distinct. Sleep mode maintains the system’s state in RAM, while hibernation mode saves the state to the hard drive. Hibernate mode consumes less power than sleep mode but takes longer to resume.
Q: How much space does the "hiberfil.sys" file take up?
A: The size of the "hiberfil.sys" file is typically equal to the amount of RAM installed in the computer. For example, a computer with 8 GB of RAM will have a "hiberfil.sys" file that is approximately 8 GB in size.
Q: Can I disable hibernation mode?
A: Yes, you can disable hibernation mode by following the same steps outlined above for enabling it, but unchecking the "Hibernate" box instead.
Q: Why is hibernation mode not available on my computer?
A: Hibernate mode may not be available if your computer does not have enough hard drive space or if your device does not support it.
Tips for Using Hibernate Mode Effectively
- Regularly Clean Up Hard Drive Space: Ensure sufficient hard drive space is available for the "hiberfil.sys" file to function properly.
- Consider Using Sleep Mode for Quick Resumes: If you need to quickly resume your work, sleep mode might be a better option than hibernation mode.
- Check System Compatibility: Verify that your computer or device supports hibernation mode before attempting to enable it.
Conclusion
Hibernate mode is a valuable power-saving feature in Windows 11, offering users a way to conserve battery life, preserve data, and enjoy a faster startup experience than a cold boot. By understanding the benefits and considerations of hibernation mode, users can make informed decisions about how to best utilize this feature to enhance their computing experience.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Enabling Hibernate Mode in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!