Bypassing the TPM Requirement for Windows 11 Installation: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Bypassing the TPM Requirement for Windows 11 Installation: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Bypassing the TPM Requirement for Windows 11 Installation: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Bypassing the TPM Requirement for Windows 11 Installation: A Comprehensive Guide
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Bypassing the TPM Requirement for Windows 11 Installation: A Comprehensive Guide
- 3.1 Understanding the TPM Requirement
- 3.2 Methods for Installing Windows 11 Without a TPM
- 3.3 The Implications of Bypassing the TPM Requirement
- 3.4 Alternatives to Bypassing the TPM Requirement
- 3.5 Frequently Asked Questions
- 3.6 Tips for Installing Windows 11 with a TPM
- 3.7 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Bypassing the TPM Requirement for Windows 11 Installation: A Comprehensive Guide

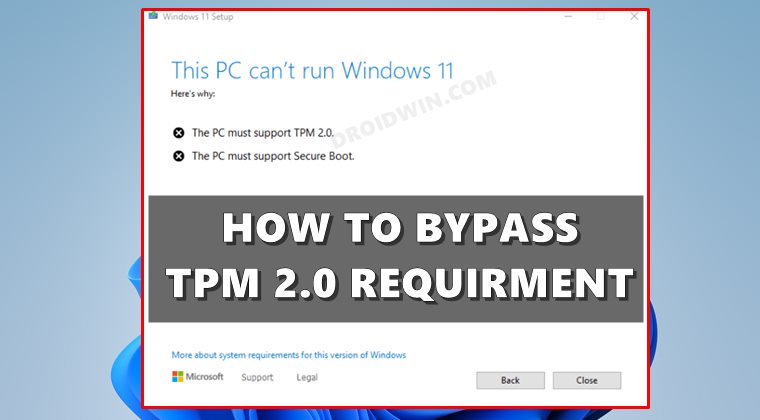
Microsoft’s Windows 11 operating system introduced a new security requirement: the Trusted Platform Module (TPM) 2.0. This technology, embedded in modern hardware, enhances system security by providing a dedicated hardware component for cryptographic operations. While the TPM requirement is intended to bolster security, it has presented a hurdle for users with older systems that lack this feature. This article delves into the intricacies of bypassing the TPM requirement for Windows 11 installation, providing a comprehensive understanding of the implications and alternative approaches.
Understanding the TPM Requirement
The TPM requirement in Windows 11 is a deliberate design choice by Microsoft to strengthen system security. The TPM chip acts as a secure enclave, safeguarding cryptographic keys and other sensitive data, making it more difficult for malicious actors to compromise the system. This security enhancement is particularly crucial in today’s threat landscape, where sophisticated cyberattacks are becoming increasingly prevalent.
However, the widespread adoption of the TPM 2.0 standard has not kept pace with the rapid evolution of hardware. Consequently, many users with older PCs find themselves unable to upgrade to Windows 11 due to the lack of a compatible TPM chip. This has sparked a debate about the necessity of the TPM requirement and its potential to limit access to the latest operating system for a significant portion of users.
Methods for Installing Windows 11 Without a TPM
While Microsoft encourages users to comply with the TPM requirement for optimal security, several methods exist for bypassing this limitation and installing Windows 11 on systems without a TPM 2.0 chip. These methods involve manipulating system settings or utilizing specific tools, but it’s essential to understand the potential risks and implications associated with each approach.
1. Disabling the TPM Check:
This method involves modifying system settings to disable the TPM check during the Windows 11 installation process. It’s a straightforward technique, but it should be considered a temporary workaround as it compromises the security features that the TPM provides. Disabling the TPM check can leave the system vulnerable to attacks, and Microsoft strongly discourages this approach.
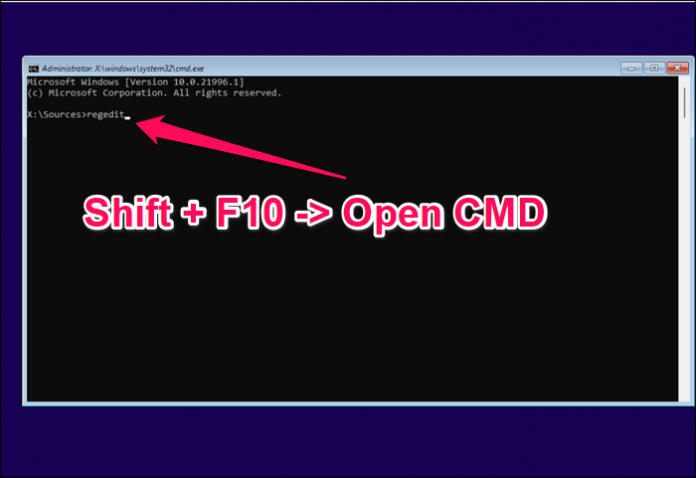
2. Using a Registry Hack:
This method involves modifying specific registry keys to bypass the TPM check. This approach is more complex than disabling the TPM check but can provide a more permanent solution. However, modifying the registry is a sensitive operation that requires caution and technical expertise. Incorrect modifications can lead to system instability or data loss.
3. Employing Third-Party Tools:
Several third-party tools are available that can bypass the TPM requirement during Windows 11 installation. These tools typically work by modifying system files or injecting drivers to circumvent the TPM check. However, it’s crucial to exercise caution when using third-party tools, as they may come with security risks or compatibility issues.
4. Upgrading from Windows 10:
If you have a Windows 10 system that meets the minimum requirements for Windows 11, you can attempt to upgrade without a TPM. Microsoft’s upgrade process may overlook the TPM requirement in some cases, allowing you to install Windows 11 even without a compatible TPM chip. However, this approach is not guaranteed to succeed and may lead to unexpected issues.
The Implications of Bypassing the TPM Requirement
While bypassing the TPM requirement for Windows 11 installation might seem like a quick solution, it’s crucial to weigh the potential implications carefully.
- Security Risks: The TPM chip plays a crucial role in securing your system. Disabling or bypassing the TPM check significantly reduces the security of your system, making it more susceptible to malware, data breaches, and other threats.
- Compatibility Issues: Bypassing the TPM requirement may lead to compatibility issues with certain applications or features of Windows 11. Some applications may require a TPM for proper functionality.
- Software Updates: Microsoft may discontinue support for systems that bypass the TPM requirement, preventing you from receiving critical security updates and software patches.
- System Stability: Modifying system settings or using third-party tools to bypass the TPM requirement can potentially lead to system instability, crashes, or data loss.
Alternatives to Bypassing the TPM Requirement
Instead of compromising security by bypassing the TPM requirement, consider exploring alternative solutions:
- Upgrade Your Hardware: If your system lacks a TPM 2.0 chip, consider upgrading to a newer PC that meets the Windows 11 requirements. This is the most secure and reliable approach, ensuring full compatibility and security features.
- Use a Virtual Machine: Install Windows 11 in a virtual machine environment, such as VirtualBox or VMware. Virtual machines provide a sandboxed environment, isolating the operating system from your host system and mitigating potential security risks.
- Dual Boot: Install Windows 11 alongside your existing operating system, such as Windows 10. This allows you to access both operating systems without compromising the security of your primary system.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Is it safe to install Windows 11 without a TPM?
A: Installing Windows 11 without a TPM is not recommended. It compromises system security, leaving your system vulnerable to various threats. While it may seem convenient, the potential risks outweigh the benefits.
Q: Can I disable the TPM check permanently?
A: Disabling the TPM check permanently is not advisable. It weakens system security and could lead to compatibility issues. Microsoft may also discontinue support for systems that bypass the TPM requirement.
Q: What are the benefits of using a TPM?
A: The TPM provides several security benefits, including:
- Secure Boot: Prevents malicious software from loading before the operating system starts.
- Hardware Encryption: Encrypts sensitive data stored on the hard drive, protecting it from unauthorized access.
- Key Storage: Stores cryptographic keys securely, preventing unauthorized access and tampering.
Q: Can I upgrade to Windows 11 without a TPM if I have a Windows 10 system?
A: While Microsoft’s upgrade process may overlook the TPM requirement in some cases, it’s not guaranteed. It’s best to ensure your system meets the minimum requirements, including a compatible TPM chip, for a smooth and secure upgrade.
Tips for Installing Windows 11 with a TPM
If your system has a TPM 2.0 chip, follow these tips for a secure and successful Windows 11 installation:
- Enable the TPM in BIOS: Access your system’s BIOS settings and enable the TPM 2.0 chip.
- Check TPM Status: Use the Windows 11 PC Health Check app to verify that your TPM is enabled and recognized by the system.
- Back Up Your Data: Before installing Windows 11, back up all your important data to prevent accidental loss.
- Download the Latest Windows 11 ISO: Ensure you’re using the latest version of the Windows 11 ISO for a smooth and stable installation.
- Follow Installation Instructions Carefully: Carefully read and follow the on-screen instructions during the Windows 11 installation process.
Conclusion
While bypassing the TPM requirement for Windows 11 installation might seem appealing, it’s crucial to understand the potential security risks and implications associated with this approach. The TPM chip plays a critical role in safeguarding your system, and disabling or bypassing it significantly weakens its security posture. For a secure and stable Windows 11 experience, consider upgrading your hardware, using a virtual machine, or dual booting Windows 11 alongside your existing operating system. If your system has a compatible TPM, ensure it’s enabled in BIOS and follow the recommended installation procedures for a secure and reliable upgrade.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Bypassing the TPM Requirement for Windows 11 Installation: A Comprehensive Guide. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!